The Electromagnetic Field Theory Btech course at AKTU includes fundamental ideas, Maxwell’s equations, wave propagation, transmission lines, and electromagnetic radiation. It gives students a solid foundation in electrical and electronics engineering.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Electromagnetic Field Theory: *Unit-01 *Unit-02 *Unit-03 *Unit-04 *Unit-05 *Short-Q/Ans *Question-Paper with solution 21-22
Unit – 1 (Co-ordinate System)
Q1. Define the terms scalar and vector.
Ans. A. Scalar: When a quantity is referred to as scalar, it means that it only has magnitude and no direction.
Example: Mass, density etc.
B. Vector: A quantity that possesses both magnitude and direction in space is referred to be a vector.
Example: Force, velocity etc.
Q2. Define unit vector.
Ans.
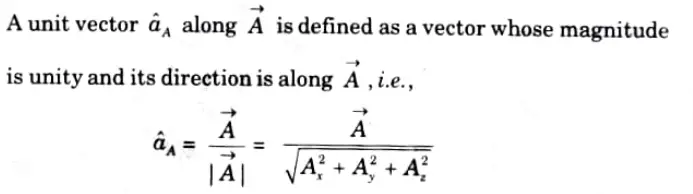
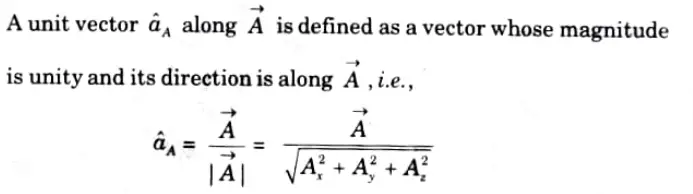
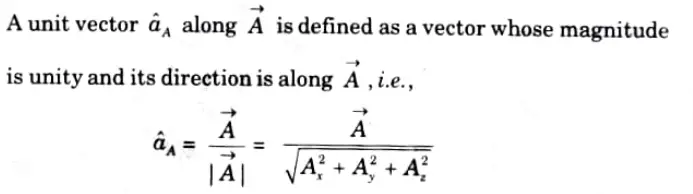
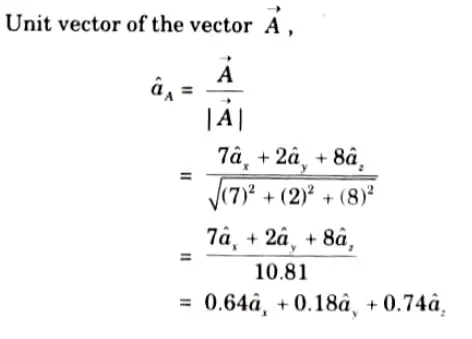
Q3. Find the unit vector of the vector ![]()
![]()
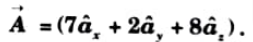
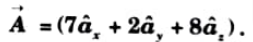
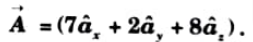
Ans.


Q4. Find the value of (3âx +6ây) × (2âx +3ây +5âz) where x denotes cross product.
Ans.



Q5. Transform the point P(5, 3, 6) in cylindrical coordinate system.
Ans. Given: Point P(5, 3, 6)
To Transform: In cylindrical coordinate.
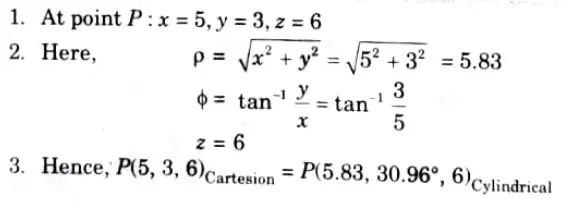
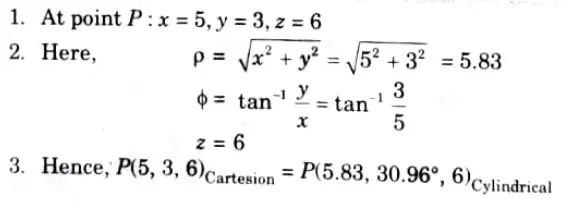
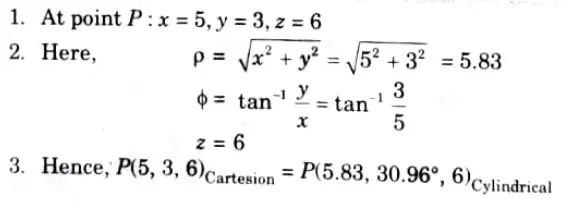
Q6. Convert the point (-2,6, 3) into spherical coordinate system.
Ans. 1. At point P(-2, 6, 3):x = -2, y = 6 and z = 3
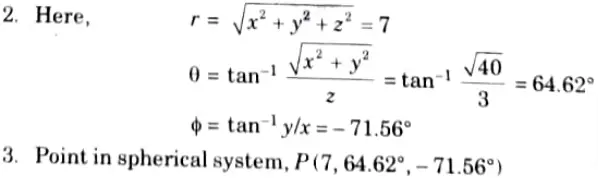
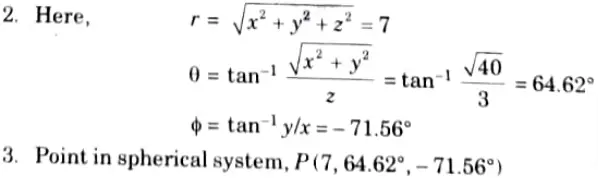
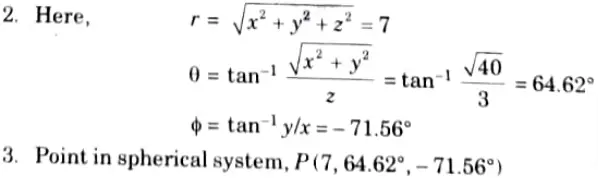
Q7. Find the gradient of the scalar field f(x, y, z) = a2 + y + z at a point P(2, 0, 1).
Ans.
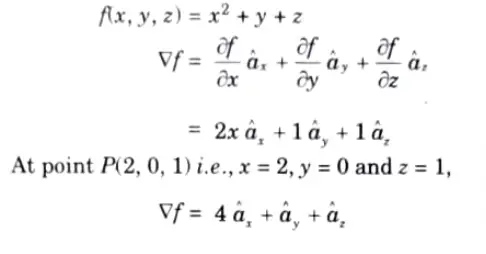
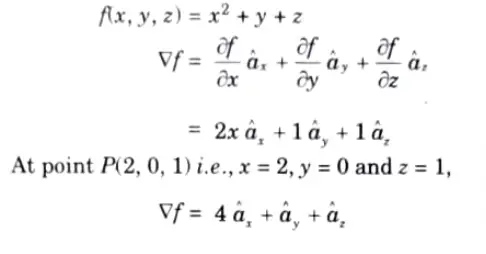
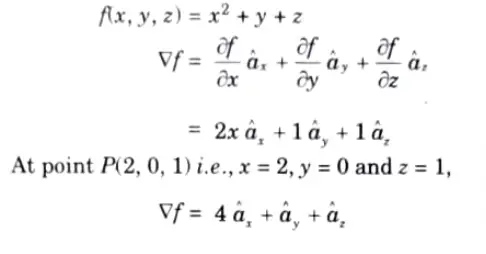
Q8. Prove that curl
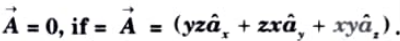
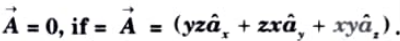
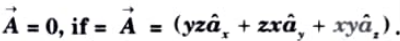
Ans.



Q9. Define divergence theorem for a vector.
Ans. The divergence theorem states that the volume integral of the



Q10. State Stoke’s theorem.
Ans. Stoke’s theorem states that the circulation of vector field ->A (Vector A) around a closed path L is equal to the surface integral of the curl of ->A over the open surface S bounded by L, provided A and ▽ x A are continuous on S.
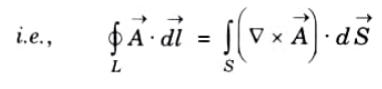
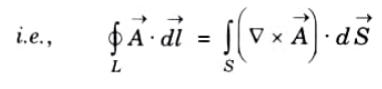
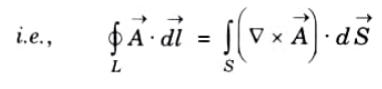
Q11. Explain the physical significance of divergence and curl.
Ans. A. Physical significance of divergence: “Divergence of a vector function ->F (Vector F) at each point gives the rate per unit volume at which the physical entity is issuing from that point”.
B. Physical significance of curl: A vector field’s curl has physical significance since it gives the greatest value of the field’s circulation per unit area and shows the direction along which it happens.
Unit – 2 (Electrostatic) Important Short Questions
Q1. State Coulomb’s law.
Ans. Coulomb’s law states that force (F) between the two point charges Q1 and Q2 is:
1. Directly proportional to the product Q1Q2 of the charges.
2. Inversely proportional to the square of the distance R between them along the line joining them i.e.,
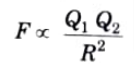
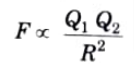
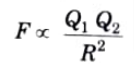
Q2. Explain electric field intensity.
Ans. The electric field intensity ->E (Vector E) is defined as the force per unit charge when placed in an electric field.
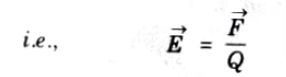
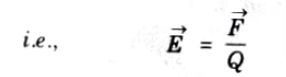
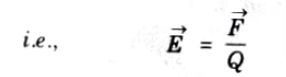
Q3. State point form of Ohm’s law and Gauss’s law.
Ans. A. Ohm’s law : The current I flowing through t is directly proportional to the potential difference V across the terminals of a resistor R.
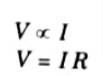
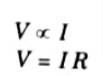
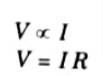
B. Gauss’s law : Gauss’s law states that the total electric flux (Ψ) through any closed surface is equal to the total charge enclosed by that surface.
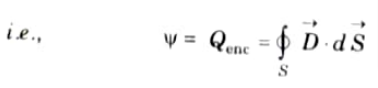
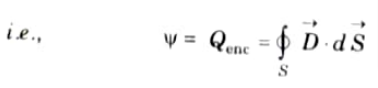
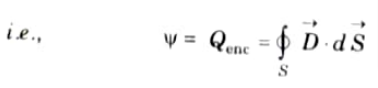
Q4. Explain relaxation time constant.
Ans. The relaxation time constant (τ) is defined as the time required by the charge density to decay to 36.8 % of its initial value.



Q5. Prove that ->E = – grad V, where E is electric field intensity and V is electric potential.
Ans.
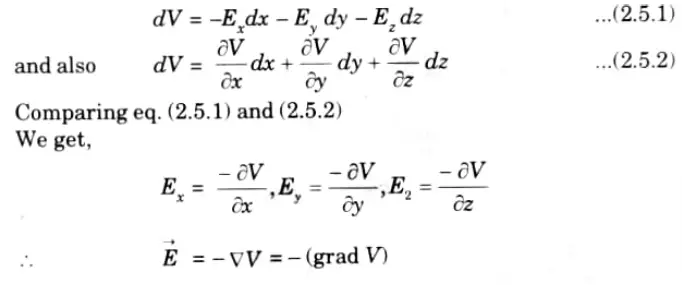
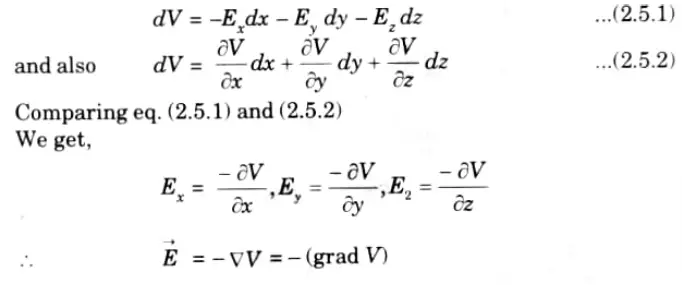
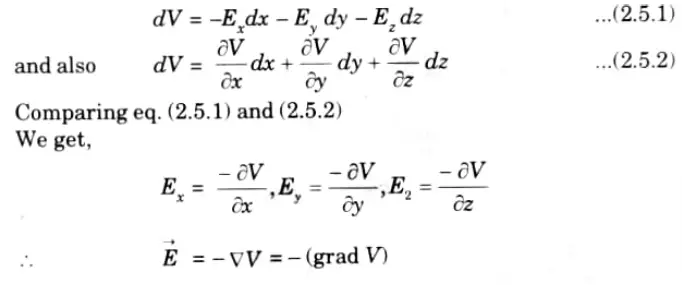
Q6. Explain the significance of continuity equation in a good conductor.
Ans. The rate at which the charge within a small volume element is decreasing must be equal to the current diverging from that element.
Q7. Narrate the concept of electric dipole moment.
Ans. 1. It is the result of the size of the charges and their distance from one another. The dipole moment controls how powerful an electric dipole must be to generate an electric field.
2. Mathematically, the electric dipole moment is given by.
P = q x 2a
Q8. Write the Poisson’s and Laplace equation.
Ans. The equations of Poisson and Laplace are utilised to address the boundary value issues.
For a homogeneous medium,
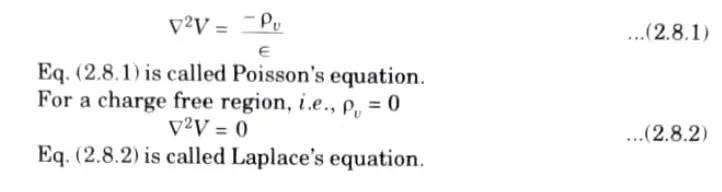
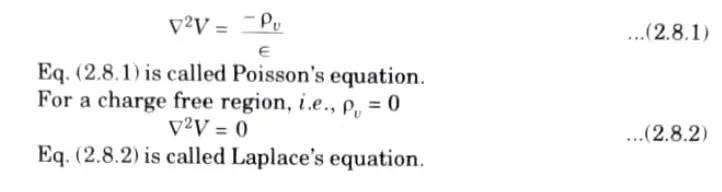
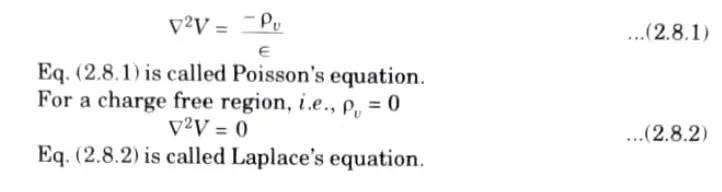
Q9. Find electric field density for infinite line charge using Gauss’s law.
Ans. According to Gauss’s law
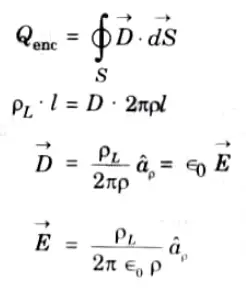
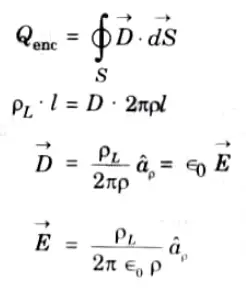
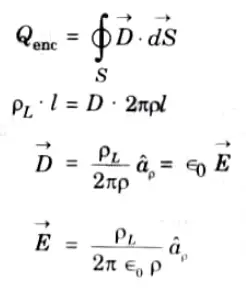
Q10. What is continuity equation ?
Ans. According to the continuity equation, which is derived from the rule of conservation of charge, there can never be an accumulation of charge.
Continuity equation is given by
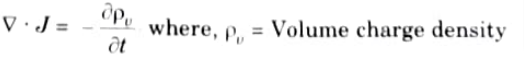
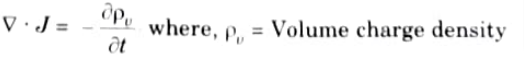
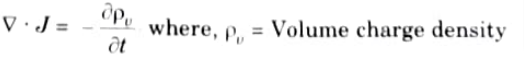
Q11. Why work done on a charge is zero when it is moved in close path ?
Ans. This is the case because a closed path has a single starting and ending point. Therefore, the top and lower limits of integration are the same, and the work is zero. Such an integral over a closed path is denoted as,
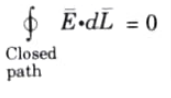
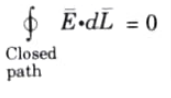
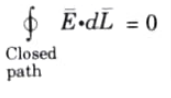
Q12. Prove line integral of static electric field in a close path is zero.
Ans. 1. As we know that the potential difference between point A and B is independent of path taken. Hence,



2. The eq. (2.13.1) shows that the line integral of
3. It also implies that no net work is done in moving a charge along a closed path in an electrostatic field.



4. Applying Stoke’s theorem to eq. (2.13.1)
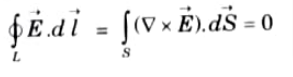
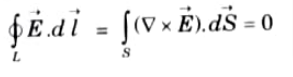
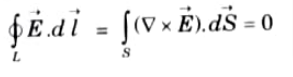
Unit – 3 (Magnetostatics)
Q1. Explain Biot-Savart’s Law.
Ans. According to Biot-law, Savart’s dH is produced at a differential magnetic field intensity point P by the differential current element Idl and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance R between P and the element. It is also proportional to the product of Idl and the sine of the angle (a) between the element and the line connecting P to the element. Mathematically,
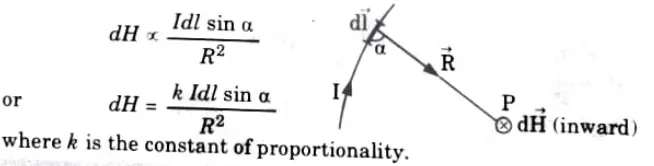


Q2. Name the two major laws governing magnetostatic field.
Ans. Two major laws are:
1. Biot-Savart’s law.
2. Ampere’s circuit law.
Q3. Explain Ampere’s circuital law for magnetostatics.
Ans. Ampere’s circuit law states that the line integral of magnetic field intensity around any closed path is exactly equal to the net current enclosed by that path. Mathematically,
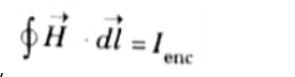
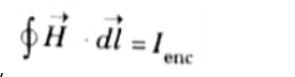
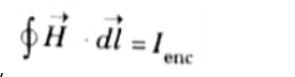
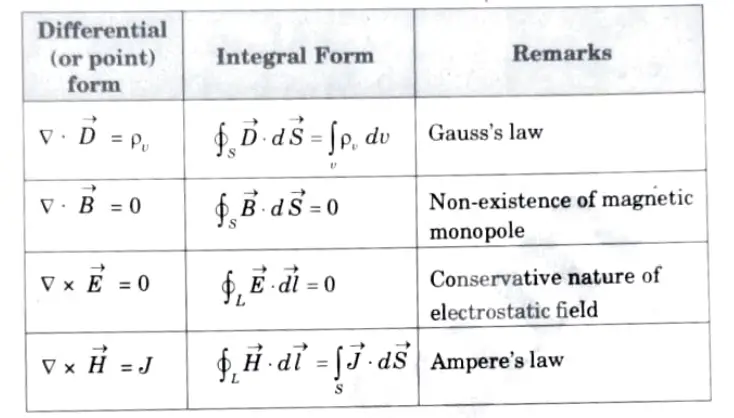
Q4. Give Maxwell’s equations in differential and integral form.
Ans.


Q5. What are the various characteristics of vector magnetic potential (->A) Vector A ?
Ans. 1. It exists even when (->J Vector J ) is present.
2. is used to find near and far fields of antennas.
Q6. What are the characteristics of scalar magnetic potential(Vm)?
Ans. 1. The negative gradient of Vm gives
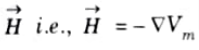
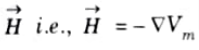
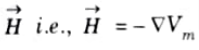
2. It exists where ->J Vector J = 0
Q7. The vector magnetic potential (->A) Vector A due to a direct current in a conductor in free space is given by
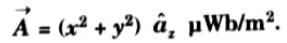
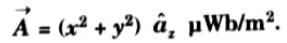
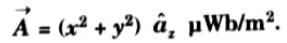
Determine the magmetic flux density
Ans.
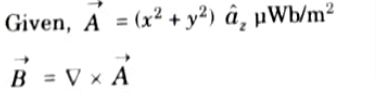
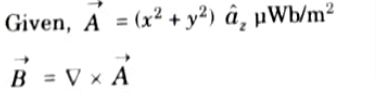
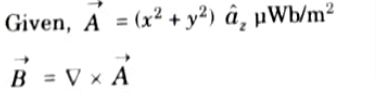
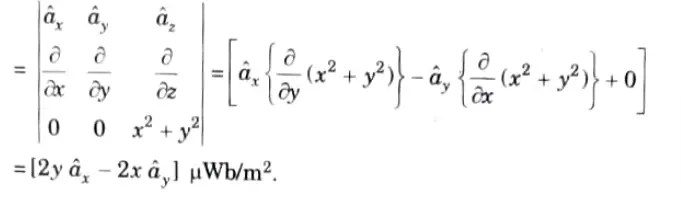
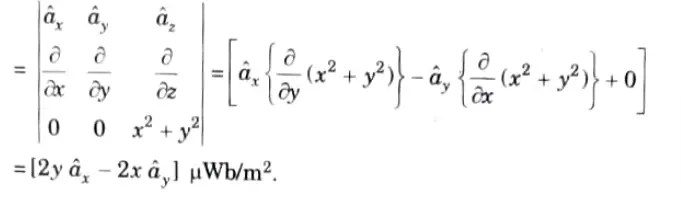
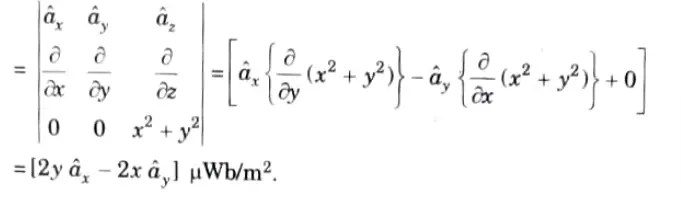
Q8. Explain the concept of magnetic flux density.
Ans. The flux per unit Area (A), measured in a plane perpendicular to the flux is defined as the flux density. It is measured in Tesla (T) and denoted by B.
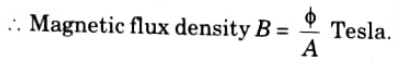
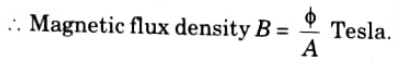
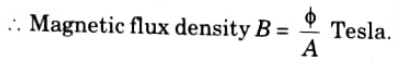
Q9. Write the unit of magnetic flux density.
Ans. The unit of magnetic flux density is Wb/m2.
Q10. An isotropic material has magnetic susceptibility of 4 and Calculate magnetization
Ans.
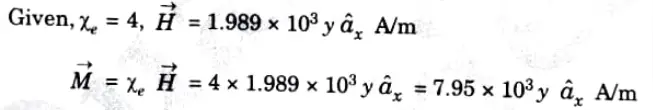
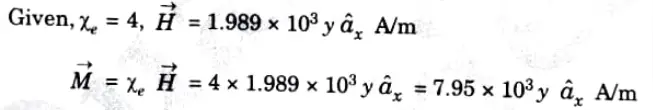
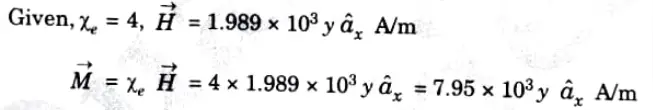
Unit – 4 (Magnetic Forces)
Q1. Enlist the ways in which force due to magnetic fields can be experienced.
Ans. 1. Due to a moving charged particle in (->B) Vector B field.
2. on a component of a current in a magnetic field outside.
3. Between two current elements.
Q2. What is Lorentz force equation ?
Ans. For a moving charge Q in presence of both electric and magnetic field, total force on the charge is given by
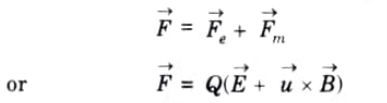
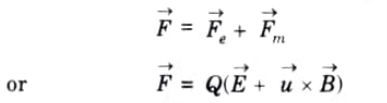
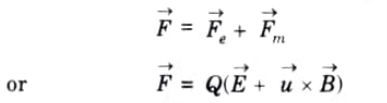
This is known as Lorentz force equation.
Q3. What is magnetic torque ?
Ans. The magnetic torque (->T) Vector T on the loop is the vector product of the force (->F) Vector F and the moment arm
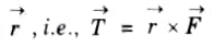
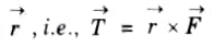
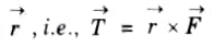
Q4. Write difference between magnetic and electric dipole.
Ans.
| S. No. | Electric dipole | Magnetic dipole |
| 1. | It is used to gauge how well positive and negative charges are separated in a system. | It is the torque that a substance subjected to a magnetic field experiences. |
| 2. | The electric field that spins the dipole is diminished by materials comprised of electric dipoles. | The magnetic field that spins a dipole is amplified by materials consisting of magnetic dipoles. |
Q5. Define magnetic dipole moment ?
Ans. It is the product of current and area of the loop. The direction of magnetic dipole moment is perpendicular to the loop and is given by
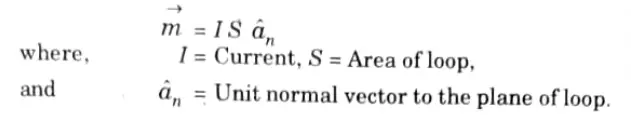
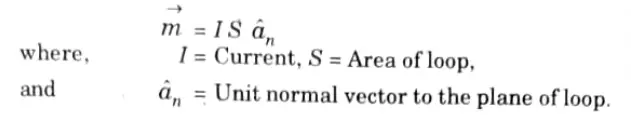
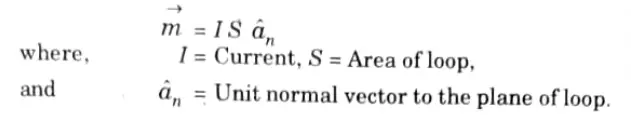
Q6. What is magnetization ?
Ans. It is defined as the magnetic dipole moment per unit volume and is measured in amperes per meter. ‘The total magnetization is given by
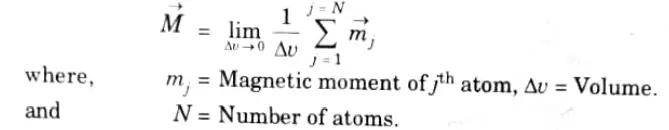
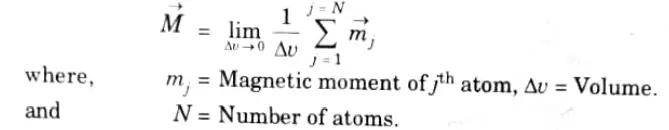
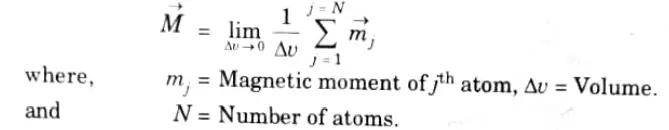
Q7. Derive the expression for inductance per unit length of coaxial conductors.
Ans. The inductance per unit length is given by,
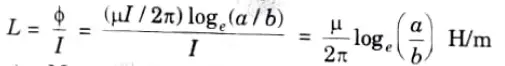
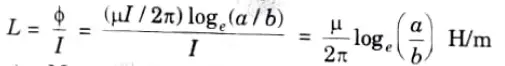
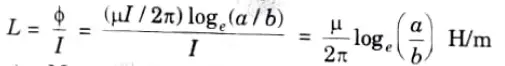
where, 𝟇 = Magnetic flux
a = Outer diameter of the conductor
b Inner diameter of the conductor.
Q8. List any four analogies between electric and magnetic circuits.
Ans.



Q9. Explain the term Inductance’.
Ans. An inductor, also known as inductance, is a passive part that stores magnetic energy in the form of a field.
Q10. Write the expression of energy stored in magnetic field.
Ans. Energy stored in magnetic field,
W = (1/2) LI2
Unit – 5 (Waves and Applications)
Q1. Explain Faraday’s law.
Ans. Faraday discovered that the induced emf. Vemf (in volts) in any closed circuit is equal to the time rate of change of the magnetic flux linkage by the circuit. This is called Faraday’s law, and it can be expressed as
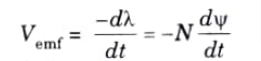
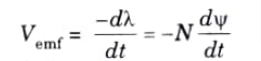
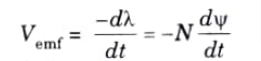
where, λ = Νψ is the flux linkage, N is the number of turns in the circuit and ψ is the flux through each turn.
Q2. Define the term depth of penetration.
Ans. The depth at which a wave attenuates to 1/e of its original amplitude is known as the depth of penetration. Skin depth is another name for penetration depth. It is a gauge of how deeply an EM wave may go through a medium. Skin depth is given by,
δ=1/α = where, α = Attenuation constant
Q3. Explain behaviour of a conductor at high frequency.
Ans. The conductor’s skin depth decreases significantly at high frequencies.
Q4. Explain Poynting vector.
Ans. The vector product of electric field intensity (->E) Vector E and magnetic field intensity (->H) Vector H at any point is a measure of rate of energy flow per unit area at that point. The quantity VECTOR(E * H) is known as the Poynting vector and is denoted by P.
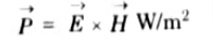
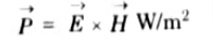
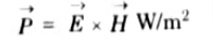
Q5. State Poynting’s theorem.
Ans. According to Poynting’s theorem, the net power leaving a given volume is equal to the rate at which the energy stored within is vanishing over time less any Ohmic losses. Mathematically,



Q6. Explain reflection and transmission coefficients.
Ans. A. Reflection coefficient: It is the ratio of the magnitude of reflected electric field to incident electric field.
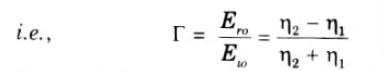
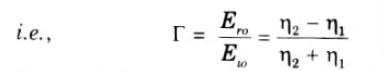
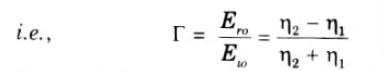
B. Transmission coefficient: It is the ratio of the magnitude of transmitted electric field to incident electric field.
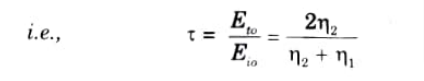
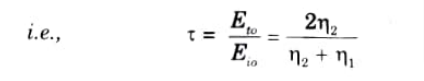
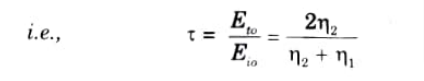
Q7. Explain the significance of loss tangent.
Ans. tan 𝞱 or 𝞱 may be used to determine how lossy a medium is. A medium is said to be a good dielectric (lossless or perfect) if tan 𝞱 is very small (𝞼 << 𝟂𝟄) or a good conductor if tan 0 is very large (𝞼 >> 𝟂𝟄).
Q8. Write an equation of EM wave
Ans. The wave equation is of the form
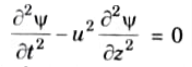
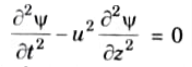
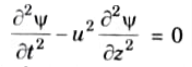
with the solution, 𝟁 = A sin (𝟂t – 𝞫z)
Q9. Explain parameters of a transmission line.
Ans. 1. The four parameters of an electric transmission line are resistance, inductance, capacitance, and shunt conductance.
2. These factors affect the electrical design and functionality of a line.
3. The line resistance and inductance form the series impedance of the line.
4. The capacitance and conductance form the shunt admittance of the line.
Q10. Give application of Smith chart.
Ans. 1. Computations for admittance on any transmission line, with any load.
2. computations of impedance for any transmission line and load.
Q11. Explain the physical significance of Poynting vector.
Ans. Any closed surface’s net power flowing out can be calculated by integrating the Poynting vector over that surface.
Q12. Write an equation for an EM wave propagating in a conductor.
Ans. The wave equations in a conductor,
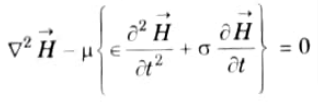
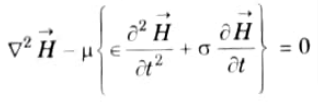
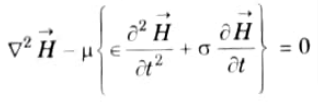
Q13. Explain the reflection of a plane wave in a normal incidence.
Ans. If load impedance (ZL)is not equal to characteristic impedance (Z0) then mismatch occurs. In this case the part of the wave gets absorbed by the load while the rest part is reflected back to the source. Thus, due to mismatch in impedance the reflection occurs.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Electromagnetic Field Theory Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Important Unit-1 | Unit-1 |
| Important Unit-2 | Unit-2 |
| Important Unit-3 | Unit-3 |
| Important Unit-4 | Unit-4 |
| Important Unit-5 | Unit-5 |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Electromagnetic Field Theory Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |
Important Links-Btech (AKTU)
