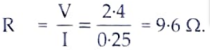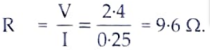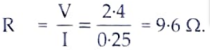Improve your CBSE 10th Class Science learning experience with comprehensive notes, solved papers, and key questions. This useful educational content will help you excel in your academics.
Time allowed:3 Hours Maximum Marks:80
SECTION – A
1. Write two advantages associated with water harvesting at the community level.** [1]
2. Should the resistance of a voltmeter be low or high ? Give reason. [1]
Ans. The resistance of a voltmeter should be high, because voltmeter is connected parallel to the component of a circuit and it also takes negligible current from the circuit in order to measure the potential difference accurately.
SECTION – B
3. Draw electron dot structure of carbon dioxide and write the nature of bonding between carbon and oxygen in its molecule. [2]
Ans.

Covalent bond (double bond) is present in between C and O.
OR
List two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us, giving reason for each.
Ans. Two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds are :
- (i) Catenation: It is the ability of carbon to form bonds with other atoms of carbon.
- (ii) Tetravalency: With the valency of four, carbon is capable of bonding with 4 other atoms. This forms huge number of compounds.
4. Given reasons : [2]
(a) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
Ans. Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction because obtaining a metal from its metal oxide is much easier than from metal carbonates and sulphides.
(b) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal; still it is widely used in making cooking utensils.
Ans. Aluminium is highly reactive metal still We have, it is widely used in making cooking utensils because it reacts with O2 present in air to from aluminium oxide that forms a protective layer and protects the metal from corrosion.
5. The power of a lens in +5 diopters. What is the nature and focal length of this lens ? At what distance from this lens should an object be placed so as to get its inverted image of the same size ? [2]
Ans. Given, P = +5D
We have,



Focal length, f = 20 cm (or + 20 cm).
Since, focal length of the lens is positive.
Therefore, the nature of lens is convex.
Same size and inverted image is formed when
Magnification, m = -1
Also, m = v/u
v = – u
From the lens formula,
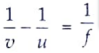
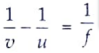
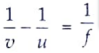
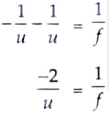
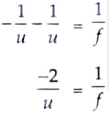
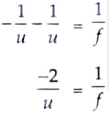
u = -2f
u = -2 x 20 [∵ f = 20 cm]
= -40 cm.
SECTION – C
6. List the two types of transport system in human beings and write the functions of any one of these. [3]
Ans. Lymphatic system and blood circulatory system are the two types of transport system in human beings.
Functions of blood circulatory system :
- (i) It carries nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body.
- (ii) It removes CO2 from the body cells.
- (iii) It carries digested food from the small intestine to other parts of the body.
- (iv) It carries hormones from endocrine glands to different organs of the body.
7. Distinguish between pollination and fertilisation. Mention the site and the product of fertilisation in a flower. [3]
Ans. (i) The transfer of pollen grains from anther of a stamen to the stigma of a carpel is called pollination whereas fertilisation is the process when the male gamete present in pollen grain joins the female gamete present in ovule.
(ii) Pollination is an external mechanism whereas fertilisation is an internal mechanism which takes place inside the flower.
Site of fertilisation in flower is ovary.
Product of fertilisation in flower is zygote.
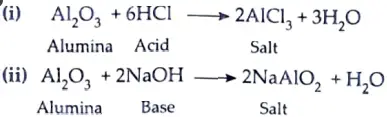
8. What are amphoteric oxides ? Give an example. Write balanced chemical equations to justify your answer. [3]
Ans. Those oxides which behave both as acidic and basic oxides are called amphoteric oxides.
Example: Al2O3 (Alumina)


9. What is a homologous series of carbon compounds ? Give an example and list its three characteristics. [3]
Ans. A homologous series is a group of organic compounds having similar structures and similar chemical properties in which the successive compounds differ by CH2 group.
Example: Alkanes with general formula CnH2n+2
Characteristics :
- (i) All the members of a homologous series can be represented by the same general formula and they have same functional group.
- (ii) Any two adjacent homologues differ by 1 carbon atom and 2 hydrogen atoms in their molecular formulae.
- (iii) The difference in the molecular masses of any two adjacent homologues is 14 u.
10. List three environmental consequences of using fossil fuels. Suggest three steps to minimise the pollution caused by various energy sources. ** [3]
11. What is transpiration ? List its two functions. [3]
Ans. The evaporation of water from the aerial parts of a plant is called transpiration.
Functions of transpiration:
- (i) It helps in the upward movement of water and minerals from root to the aerial parts through the stem and in the absorption.
- (ii) It helps in cooling the plant surface. It helps in the movement of dissolved minerals from root to leaves.
OR
(a) What is translocation ? Why is it essential for plants ?
Ans. The transport of food from leaves to other parts of the plant is called translocation. Translocation is essential for plants because without it food prepared by the leaves cannot reach other parts of the plant for their growth and development.
(b) Where do the substances in plants reach as a result of translocation ?
Ans. The substances in plants reach to other tissues in plants from the leaves, fruits, seeds and other growing organs as a result of translocation.
12. What is carpel ? Write the function of its various parts. [3]
Ans. The flask-shaped organ in the centre of a flower is called carpel. It is also called as female reproductive organ of the plant.
It is made up of three parts :
- (i) Stigma is the top part of carpel and is sticky. So, it receives the pollen from the anther of stamen.
- (ii) Style connects stigma to ovary and acts as the passage for the growth of pollen tube.
- (iii) Ovary contains female gametes of the plant and helps in reproduction, it is the site of fertilization.
13. A student holding a mirror in his hand, directed the reflecting surface of the mirror towards the Sun. He then directed the reflected light on to a sheet of paper held close to the mirror. [3]
(a) What should he do to burn the paper ?
Ans. He should place the sheet of paper at the focus of the mirror to burn the paper.
(b) Which type of mirror does he have ?
Ans. He has a concave mirror.
(c) Will he be able to determine the approximate value of focal length of this mirror from this activity ? Give reason and draw ray diagram to justify your answer in this case.
Ans. Yes, the sheet of paper will start burning at the focus of the mirror which will give approximate value of focal length, i.e., the distance between mirror and the focal point where the sheet of paper starts burning.
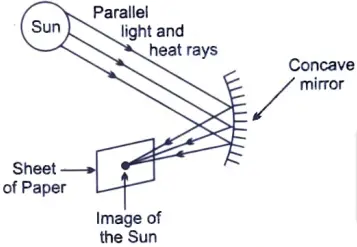


A concave mirror forms a real image of the sun.
OR
A 10 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 12 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 18 cm. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
Ans. Given: Height of object, h1 = + 10 cm.
Focal length, f = + 12 cm.
Object distance, u = – 18 cm.
From the lens fomula,
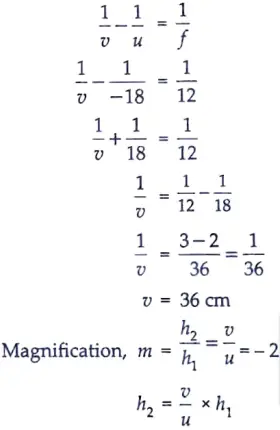
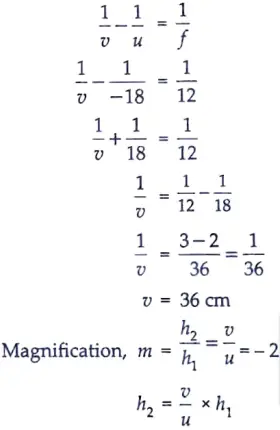
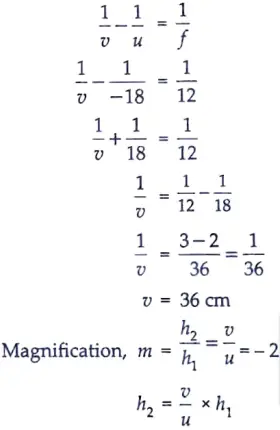
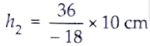
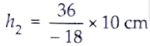
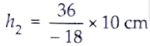
= – 20 cm
The position of image formed is at distance of 36 cm from convex lens.
Since the value of magnification is more than 1 (it is 2), the image formed is larger than object.
The minus sign of magnification shows that image is formed below the principal axis. Hence, the image formed is real and inverted.
14. Which compounds are called (i) alkanes, (ii) alkenes and (iii) alkynes ? C4H10 belongs to which of these ? Draw two structural isomers of this compound. [3]
Ans. (i) The hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms are connected by only single covalent bonds are called alkanes.
(ii) The hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms are connected by double bond are called alkene.
(iii) The hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms are connected by triple bond are called alkynes.
C4H10 belongs to alkane.
Structural Isomers of C4H10:
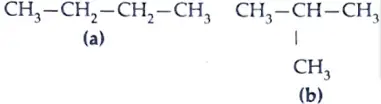
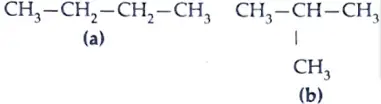
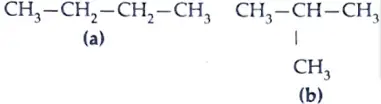
15. Write the essential function performed by ozone at the higher levels of the Earth’s atmosphere ? How is it produced ? Name the synthetic chemicals mainly responsible for the drop of amount of ozone in the atmosphere. How can the use of these chemicals be reduced? [3]
Ans. Ozone layer absorbs most of the harmful ultraviolet radiations from the sun to the earth. It is formed high up in the atmosphere by the action of ultraviolet radiation on oxygen gas. Chlorofluorocarbons are the synthetic chemicals responsible for the drop of amount of ozone in the atmosphere.
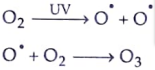


The use of these chemicals can be reduced by:
- (i) Replacement of chlorofluorocarbons with hydrochlorofluorocarbons because it breaks down more quickly.
- (ii) Safe disposal of old appliances such as refrigerators and freezers.
- (iii) Finding substitute chemicals that are ozone friendly.
SECTION – D
16. (a) What are dominant and recessive traits ?
Ans. The trait which can express its effect over contrasting trait is called dominant trait whereas the trait which cannot express its effect over contrasting trait or which gets suppressed by the contrasting trait is called recessive trait. The inherited trait which is not expressed will be a recessive trait.
(b) “Is it possible that a trait is inherited but may not be expressed in the next generation ?” Give a suitable example to justify this statement. [5]
Ans. Yes; in Mendel’s experiment, when pure tall pea plants were crossed with pure dwarf pea plants, only tall pea plants were obtained in F1 generation. On selfing the pea plants of F1 generation both tall and dwarf pea plants were obtained in F2 generation. Reappearance of the dwarf pea plants in F2 generation proves that the dwarf trait was inherited but not expressed in F1 generation. The recessive trait does not express itself in the presence of the dominant trait. So, it is possible that one trait may be inherited but may not be expressed in an organism.



17. (a) Why is the use of iodised salt advisable? Name the disease caused due to deficiency of iodine in our diet and state its one symptom.
Ans. Iodised salt is advisable because iodine is necessary for the formation of thyroxine hormone by thyroid gland. Goitre is the disease caused due to its deficiency.
Symptom: The neck of the person appears to be swollen due to the enlargement of thyroid gland.
(b) How do nerve impulses travel in the body? Explain.
Ans. Two neurons are not joined to one another completely. There is a small gap between a pair of neuron. This gap is called synapse. The nerve impulse are carried out to this gap by the help of neuro transmitter (chemical substance). The conduction of nerve impulse through the synapse takes place in the form of electrical nerve impulse. When a stimulus acts on the receptor, an electrical impulse is produced with the help of chemical reaction. This electrical impulse passes through the synapse and then to the other neuron. Thus, in this way nerve impulses travel in the body.
OR
What is hydrotropism ? Design an experiment to demonstrate this phenomenon. [5]
Ans. The movement of root of plants towards water is called hydrotropism.
Take two glass troughs A and B fill each one of them two-thirds with soil. In trough A plant a tiny seedling figure (a). In trough B plant a similar seedling and also place a small ‘clay pot inside the soil figure (b). Water the soil in trough A daily and uniformly. Do not water the soil in trough B but put some water in the clay pot buried in the soil. Leave both the troughs for a few days.
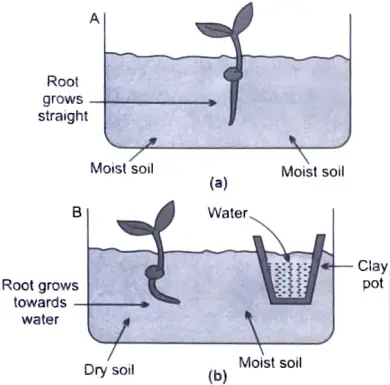


Now, dig up the seedlings carefully from both the trough without damaging their roots. We will find that the root of seedling in trough A is straight. On the other hand, the root of seedling in trough B is found to be bent to the right side (towards the clay pot containing water) figure (b)This can be explained as follows.
In trough A, the root of seedling gets water from both sides (because the soil is watered uniformly) in trough B, the roots gets water oozing out from the clay pot which is kept on the right side. So, the root of seedling in trough B grows and bends towards the source of water to the right side. The experiment shows that the root of a plant grows towards water. In other words, the root of a plant is positively hydrotropic.
18. (a) What are homologous structures ? Give an example.**
(b) “The sex of a new born child is a matter of chance and none of the parents may be considered responsible for it.” Justify this statement with the help of a flow chart showing sex-determination in human beings. [5]
Ans. The sex of a newborn depends on what happens at the time of fertilization.
- (i) If a sperm carrying X chromosome fertilizes the ovum carrying X chromosome, then the girl child will be born and the child will have XX combination of sex chromosomes.
- (ii) If a sperm carrying Y chromosome fertilizes the ovum carrying X chromosome, then the child born will be a boy and the child will have XY combination of sex chromosome.
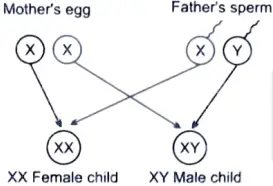


The above presentation clearly shows that it is matter of chance whether the newborn will be boy or girl and none of the parents may be considered responsible for it.
19. When do we consider a person to be myopic or hypermetropic ? List two causes of hypermetropia. Explain using ray diagrams how the defect associated with hypermetropic eye can be corrected. [5]
Ans. Myopia is the defect in vision in which a person cannot see the distant objects clearly whereas in hypermetropia is the defect in which a person cannot see nearby objects clearly.
Hypermetropia is caused due to:
- (i) Decrease in converging power of eye lens.
- (ii) Too short eye ball.
In a hypermetropic eye, the image of near by object lying at normal near point N (at 25 cm) is formed behind the retina.
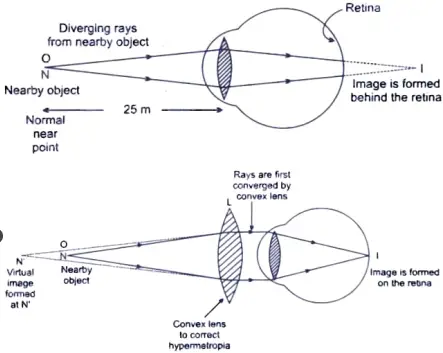


Hypermetropia and its correction by using convex lens.
Hypermetropic eye can be corrected using convex lenses. When a convex lens of suitable power is placed in front of hypermetropic eye, then the diverging rays of light from the object are converged first by the convex lens used. This form a virtual image of the object at another near point N.
Now, the rays can be easily focused by the eye lens to form an image on retina.
20. (a) What is scattering of light ? Explain how the colour of the scattered light depends on the size of the scattering particles. [5]
Ans. Scattering of light is the phenomenon in which a part of the incident light is dispersed in different directions.
Dependence of colour and scattered light on the size of particles :
- (i) When the particles like dust and water droplets present in the atmosphere are large in size, the scattered light appears white.
- (ii) When the particles are extremely minute in size, they will scatter blue light present in the white sunlight.
(b) Explain the reddish appearance of the Sun at sunrise or sunset. Why does it not appear red at noon ?**
21. Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines produced around a current carrying straight conductor passing perpendicularly through a horizontal cardboard. State and apply right hand thumb rule to mark the direction of the field lines. How will the strength of the magnetic field change when the point where magnetic field is to be determined is moved away from the straight conductor ? Give reason to justify your answer. [5]
Ans. Maxwell’s Right Hand Thumb rule states that if current carrying wire is imagined to be held in the right hand so that thumb points in the direction of current, then the direction in which fingers encircle the wire will give the direction of magnetic field lines around the wire. If we hold the current carrying straight wire so that thumbs.
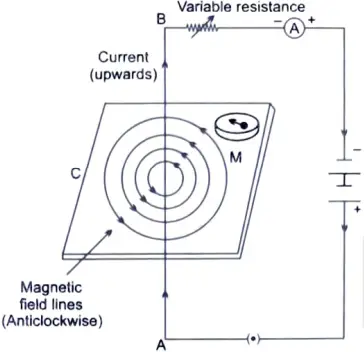


Magnetic field pattern due to a straight current-carrying wire
in upward direction points the direction of current, the direction of magnetic field lines will be anticlockwise. The strength of magnetic field is inversely proportional to the distance of the point of observation from the wire. So, as we move away from the wire the strength of magnetic field decreases.
SECTION – E
22. A teacher provided acetic acid, water, lemon juice, aqueous solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate and sodium hydroxide to students in the school laboratory to determine the pH values of these substances using pH papers. One of the students reported the pH values of the given substances as 3, 12, 4, 8 and 14 respectively. Which one of these values is not correct ? Write its correct value stating the reason. [2]
Ans. The value of pH for water is not correct. The correct value of pH of water is 7 because it has almost equal concentration of H+ and OH– due to which it is neutral.
OR
What would a student report nearly after 30 minutes of placing duly cleaned strips of aluminium, copper, iron and zinc in freshly prepared iron sulphate solution taken in four beakers ?
Ans. Aluminium displaces the iron from iron sulphate and the colour of two solution changes from green to colourless.
No change takes place when copper strip is dipped in iron sulphate solution.
No change will be observed when iron strips are dipped in iron sulphate solution.
The colour of the solution changes from green to colourless when zinc is added to iron sulphate solution.
23. What is observed when a pinch of sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to 2 mL of acetic acid taken in a test tube ? Write chemical equation for the reaction involved in this case. [2]
Ans. CO2 gas is evolved with brisk effervescence when sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to acetic acid.
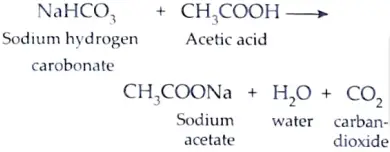


24. List in proper sequence four steps of obtaining germinating dicot seeds. [2]
Ans.
- (i) The root is formed when radicle of seed grows.
- (ii) The root grows downward into the soil and absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
- (iii) The shoot is formed from the upward growth of plumule.
- (iv) The green leaves are developed when shoot comes above the ground.
OR
After examining a prepared slide under the high power of a compound microscope, a student concludes that the given slide shows the various stages of binary fission in a unicellular organism. Write two observations on the basis of which such a conclusion may be drawn.
Ans. (i) The nucleus of mature cell seems elongated and a grove is formed in cell which divides the nucleus.
(ii) A single parent divides to form two daughter cells. Constriction appears due to the division of the cytoplasm.
25. List four precautions which a student should observe while preparing a temporary mount of a leaf peel to show stomata in his school laboratory. [2]
Ans.
- (i) Freshly plucked leaf should be taken for epidermal peel.
- (ii) Hold the slide by its edges.
- (iii) Peel should be cut to a proper size.
- (iv) The peel should be allowed to dry.
26. Draw the path of a ray of light when it enters one of the faces of a glass slab at an angle of nearly 45°, Label on it (i) angle of refraction, (ii) angle of emergence and (iii) lateral displacement. [2]
Ans.
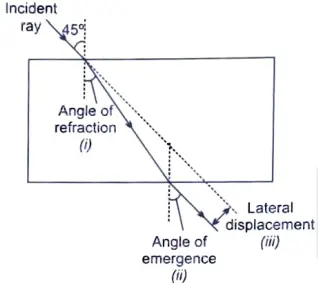


OR
A student traces the path of a ray of light through a glass prism as shown in the diagram, but leaves it incomplete and unlabelled. Redraw and complete the diagram. Also label on it ∠i, ∠e, ∠r, and ∠D.
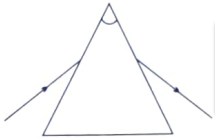


Ans.
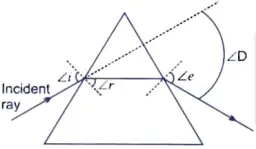


27. The current flowing through a resistor connected in a circuit and the potential difference developed across its ends are as shown in the diagram by milliammeter and voltmeter readings respectively : [2]
(a) What are the least counts of these meters ?
Ans. 10 mA and 0.1 V
(b) What is the resistance of the resistor ?
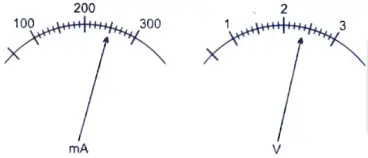


Ans. V = 2.4 volt, I = 250 mA = 0.25A
From Ohm’s law.