Learn more about Advance Welding Short Question Notes for B.Tech. from AKTU. Explore the most innovative welding methods, supplies, and tools for precision welding applications across a range of industries.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Advance Welding: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Welding Arc and Power Sources (Short Question)
Q1. Define welding. Make comparison with other joining process.
Ans. Welding:
The term “welding” refers to the localized coalescence of metal, which is accomplished by heating the metal to the proper temperature, applying pressure, and maybe using filler metal as well.
Comparison:
| S. No. | Welding | Soldering | Brazing |
| 1. | Comparing the strength of the joint to brazing and soldering, it is the strongest. | In comparison to brazing and welding, soldered junctions are the weakest. | While weaker than welded joints, brazed joints are stronger than soldered joints. |
| 2. | The composition of filler metal is normally same as that of base metal. | Essentially filler metals are alloys of ead and tin. | The filler metals are alloys of copper. |
Q2. Give the two main advantages of welding.
Ans. Two main advantage of welding are as follows:
- 1. Welding results in good material savings and a decrease in labor-intensive production.
- 2. The efficiency of a welding joint is up to 100%, and it is as strong as base metal.
Q3. What are the limitations of welding ?
Ans. Limitations of welding as follows :
- 1. To facilitate welding, certain fixtures and jigs are needed.
- 2. The heat from welding affects the workpiece’s metallurgy.
Q4. Write down three applications of welding.
Ans. Applications of welding are as follows:
- 1. Automobile industries,
- 2. Railroad industries, and
- 3. Aircraft industries.
Q5. What is physics of arc welding ?
Ans. It deals with intricate physical phenomena like heat, electricity, magnetism, light, etc. that are related to welding.
Q6. What are the different power sources used for various arc welding processes ?
Ans. Different power sources used for various arc welding processes are as follows :
- 1. C type,
- 2. DC type, and
- 3. ACIDIC type.
Q7. Write down three V-I characteristics used in arc welding.
Ans. Three V-I characteristics used in are welding are as follows:
- 1. Dropping arc voltage or constant current,
- 2. Constant arc voltage, and
- 3. Rising arc voltage
Q8. What is welding are and arc initiation ?
Ans. Welding Arc: The term refers to a continuous electrical discharge through an ionized gas.
Arc Initiation: Arcs can be started by ionizing the space between the electrode and the job or by creating a conducting channel between them.
Q9. What is arc efficiency?
Ans. The ratio of heat created at the anode to overall heat development is known as arc efficiency.
Q10. What is metal transfer ?
Ans. When an electric arc forms between the workpiece and the consumable electrode, the electrode begins to melt and hovers towards the work before finally falling upon it. The technique is referred to as metal transfer.
Q11. Write down the types of metal transfer?
Ans. Types of metal transfer are as follows:
1. Dip transfer, 2. Spray transfer,
3. Jet transfer, and 4. Globular transfer.
Q12. Compare vacuum brazing with welding.
Ans.
| S. No. | Vacuum Brazing | Welding |
| 1. | Vacuum brazing does not require post-heat treatment. | Frequently, post-heat treatment is necessary. |
| 2. | As only filler material can make joints, it is essentially necessary to employ filler material. | The filler material may or may not be used. |
| 3. | Distortion is low. | Distortion is high. |
Q13. What are the effects of gases in welding ?
Ans. Effect of gases in welding are as follows:
- 1. Gases absorbed in the weld metal result in the formation of porosity.
- 2. Reduce the tensile strength of weld.
- 3. Lower the corrosion resistance of weld metal.
- 4. Decrease ductility and impact resistance.
Q14. Write short note on arc blow in welding process.
Ans. 1. Arc blow is the unintentional deflection or straying of a welding arc from its planned course.
2. Magnetic disturbances that throw off the symmetry of the self-induced magnetic field surrounding the electrode, arc, and workpiece are what cause an arc blow.
Unit-II: Welding Processes (Short Question)
Q1. What is manual metal arc welding ?
Ans. In the manual metal arc welding technique, coalescence is created by heating the metal with an electrical arc.
Q2. Define TIG welding.
Ans. When using tungsten inert gas (TIG), coalescence is created on the job by heating it with an electric arc created between the tungsten and the task.
Q3. Define MIG welding.
Ans. In the metal inert gas (MIG) welding technique, the joint is heated by an electric arc formed between a continuously fed metal electrode and the joint, which results in coalescence.
Q4. Write down applications of MIG welding.
Ans. Applications of MIG welding are as follows:
- 1. For welding tool steel and dies.
- 2. For the manufacture of refrigerator parts.
Q5. Define plasma arc welding.
Ans. It is a type of arc welding in which the heat generated by a confined arc formed between a tungsten electrode and a water-cooled nozzle causes coalescence.
Q6. Give two advantages and two disadvantages of plasma are welding.
Ans. Advantages of Plasma Arc Welding:
- 1. Arc stability and consistent penetration.
- 2. Saved on rewelding the joint’s root and simplified fixtures.
Disadvantages of Plasma Arc Welding:
- 1. Special protection equipment is required for infrared and ultraviolet radiation.
- 2. A lot of inert gas is consumed.
Q7. Define submerged arc welding.
Ans. In the process of submerged arc welding, an electric arc is created up between a bare metal electrode and the workpiece to heat the material, causing coalescence.
Q8. What is electroslag welding ?
Ans. The filler metal and the surface of the item to be welded are melted during the process of electroslag welding, which is a type of are welding.
Q9. Explain electrogas welding process.
Ans. A method of gas metal arc welding called electrogas welding confines the molten weld metal for a vertical position welding piece by using an external gas source and moulding shoes.
Q10. Name the types of resistance welding.
Ans. Types of resistance welding are as follows:
- 1. Spot welding,
- 2. Seam welding,
- 3. Projection welding,
- 4. Percussion welding, and
- 5. Flashbutt welding.
Q11. What is friction welding ?
Ans. Friction welding is a type of solid state welding in which heat produced by mechanically generated sliding motion between the rubbing surfaces is used to stimulate coalescence. Under pressure, the components are held together.
Q12. What is deformation resistance welding ?
Ans. Resistance heating is used in this method to bring the temperature of the materials being welded up to the proper forging range, and shear deformation is then used to enhance the contacting surface area of the materials being welded.
Q13. How radial friction welding is used to join collars to shafts and tubes?
Ans. Steps to join collars to shafts and tubes:
- 1. Axial alignments are used to hold the two parts together.
- 2. One component rotates while the other, which is stationary, advances to exert pressure on the revolving component.
- 3. Until the resulting high temperature transforms the components’ metal into plastic for welding, pressure and rotation are kept constant.
- 4. Allow the joint soften for weld.
Q14. What are the advantages of constricting plasma in PAW ?
Ans. The advantages of constricting plasma in PAW are as follows:
- 1. It increases the stability of the arc.
- 2. It enhances the arc’s form.
- 3. It has better qualities for heat transfer.
Q15. List different type of brazing techniques available. Explain any one in detail.
Ans. Brazing Techniques:
- 1. Furnace brazing
- 2. Dip brazing
- 3. Induction brazing, and
- 4. Torch brazing etc.
Torch Brazing:
- 1. It is the most used technique; heat is generated using a standard gas welding torch by acetylene and oxygen gas combustion.
- 2. Oxy-hydrogen torches are also used to braze non-ferrous metals, such as aluminium.
Q16. Give two examples of adhesives and mention its general characteristics.
Ans. A. Examples of Adhesives: Glue and cement.
B. Characteristics:
- 1. High strength to weight ratio.
- 2. Superior vibration and fatigue.
Unit-III: Heat Flow Welding and Welding Metallurgy (Short Question)
Q1. Define heat affected zone (HAZ).
Ans. Heat-affected zone refers to the area of the parent metal that has experienced metallurgical change as a result of thermal cycle (HAZ).
Q2. Write down the different regions of HAZ.
Ans. Different regions of HAZ are as follows:
- 1. Grain growth region,
- 2. Grain refined region, and
- 3. Transition region.
Q3. Give the formula of cooling rate in welding.
Ans. Cooling rate when t < 0.75 mm,



Q4. What is weld metal solidifications ?
Ans. The change of a liquid phase to a solid often takes place by a process of nucleation and growth, and this is how metals are typically thought to solidify.
Q5. What are the effects of thermal cycle in the weld metal ?
Ans. Some alloys, especially hardenable alloy steels, have properties that are significantly impacted by the temperature cycle in the weld metal and heat affected zone, and for such materials, controlling the thermal cycle may be necessary for successful welding.
Q6. Define residual stress in welding ?
Ans. The stress that persists in a welded structure even in the absence of an external load is known as residual stress. They are self-balancing inside the structure itself as a result.
Q7. What are the factors responsible for residual stresses in welding ?
Ans. Factors responsible for residual stresses in welding are as follows:
- 1. The weld heat source differentially heats the plates.
- 2. Plastic deformation that is not uniform.
- 3. The rate of cooling after the welding operation.
Q8. Define dilution.
Ans. The weld bead could display a composition that falls in between that of the filler metal and the base metal when the base metal and filler metal have different compositions. Dilution is the term for this outcome.
Q9. Explain weld affected zone.
Ans. The weld metal hardens from a molten condition, creating a weld impacted zone. This is a mixture of parent metal and electrode (or filler metal), with the ratio varying according on the type of joint, welding process, plate thickness, etc.
Unit-IV: Repair and Maintenance Welding (Short Question)
Q1. What do you mean by cladding and surfacing ?
Ans. Cladding: The act of covering one material with another is known as cladding. Cladding is the joining of different metals in metallurgy.
Surfacing: In order to achieve the necessary qualities or dimensions, filler metal is deposited on a metal surface using arc or gas welding.
Q2. Give the classifications of surfacing.
Ans. Classifications of surfacing are as follows:
- 1. Hardfacing,
- 2. Cladding,
- 3. Built up, and
- 4. Buttering.
Q3. What do you mean by hardfacing ?
Ans. In hardfacing, metal is applied to one surface to make it harder and more resistant to abrasion, convolution impact, erosion, and other wear-and-tear processes.
Q4. What is metallizing process ?
Ans. The method of “metallizing” involves putting molten metal in the form of a fine spray to the surface of a base metal such that it adheres to the base metal and produces a metal covering.
Q5. Define reclamation welding.
Ans. The simplest type of reclamation is welding, which involves employing a suitable electrode to weld together metallic components that have been cracked or broken.
Q6. What is weldability ? How carbon content affects the weldability?
Ans. Weldability is the ability of a material to be welded easily, the ease with which the materials may be welded. The metal’s ability to weld decreases as its carbon concentration rises.
Q7. Write down the factors affecting the weldability.
Ans. The factors which affect the weldability are follows:
- 1. Metallurgical compatibility,
- 2. Mechanical properties, and
- 3. Serviceability.
Q8. Define effect of sulphur on weld.
Ans. Sulfur gives the parent metal on the weld free-machining properties.
Q9. What are the effects of manganese in parent metal on weld ?
Ans. Strength and hardness are both influenced by manganese. If manganese is present in steel in high concentrations along with high carbon content, it also reduces steel’s ductility and weldability.
Q10. Write down the welding methods of plain carbon steel.
Ans. Welding methods of plain carbon steel are as follows:
- 1. Oxy acetylene welding.
- 2. Flux shielded metal arc welding,
- 3. Submerged arc welding,
- 4. Gas metal arc welding, and
- 5. Gas tungsten arc welding.
Q11. Mention welding processes used for welding of cast iron ?
Ans. Welding processes used for welding of cast iron are as follows:
- 1. Metal arc welding
- 2. Oxy acetylene welding,
- 3. Brazing, and
- 4. Thermite welding.
Q12. Enlist the welding methods used for aluminium.
Ans. Welding methods used for aluminium are as follows:
- 1. Oxy-gas welding,
- 2. TIG or MIG welding,
- 3. Resistance welding,
- 4. Brazing,
- 5. Atomic hydrogen welding, and
- 6. Solid state welding.
Q13. What are the applications of hardfacing?
Ans. Construction tools like bulldozer blades, scraper blades, textile industry equipment, and engine valve facing all require hardfacing.
Unit-V: Weld Design and Welding Codes (Short Question)
Q1. What do you understand by welded joint ?
Ans. The combining of two or more metals with or without the use of pressure, with or without filler material, and with the application of heat results in a weld joint, which is a permanent joint.
Q2. What types of welded joints used in welding?
Ans. The main types of welded joints are as follows:
- 1. Butt joint,
- 2. Lap joint,
- 3. T-joint,
- 4. Corner joint, and
- 5. Edge joint.
Q3. What do you mean by weld joint design?
Ans. The design of the weld joint is a crucial phase in the welding process because good joint design helps to prevent distortion and other welding flaws.
Q4. Describe various welding symbols.
Ans. Various welding symbols are as follows :
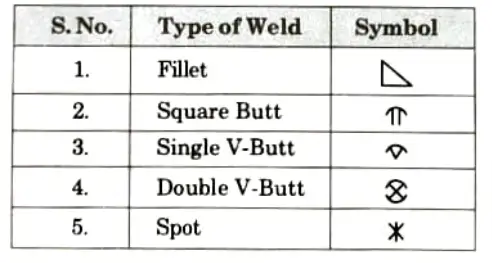


Q5. What is the objective of weld inspection ?
Ans. Weld inspection’s goal is to determine whether the welding performed to unite the two pieces soundly was successful.
Q6. Why the welded joint is in tension ?
Ans. While still in a liquid state, weld filler metal experiences both solidification shrinkage and cooling contraction. The parent metal, which is cooler and heavier in mass, prevents the weld material from contracting, causing the weld to be in tension.
Q7. What is the weld testing ?
Ans. In order to check the quantitative measurement of specific weldment properties, such as their mechanical properties, weld testing entails performing physical activities on the weldments.
Q8. What are types of weld testing methods ?
Ans. There are two types of weld testing methods:
- 1. Destructive testing, and
- 2. Non destructive testing.
Q9. What is weld distortion and its prevention ?
Ans. Weld Distortion: When anything gets bent out of form or takes on an irregular shape, it is said to be distorted.
Prevention:
- 1. Instead of single-sided welding, use double-sided welding.
- 2. Make use of small gap sizes.
- 3. Utilize fixtures, jigs, clamps, or strong backs.
- 4. Use of sub assemblies is number four.
Q10. What are the types of weld distortion ?
Ans. Types of weld distortion are as follows:
- 1. Longitudinal shrinkage,
- 2. Transverse shrinkage, and
- 3. Angular shrinkage.
Q11. What are the factors responsible for weld distortion?
Ans. Factors responsible for weld distortion are as follows:
- 1. Non uniform stresses because of expansion and contraction.
- 2. Thermal stresses produced in welds.
Q12. List down the factors affecting the distortion.
Ans. Factors affecting the distortion are as follows:
- 1. Parent material properties,
- 2. Amount of restraint,
- 3. Joint design,
- 4. Part fitup, and
- 5. Welding procedure
Q13. Enlist destructive methods to measure the stresses in weld structure.
Ans. Destructive methods to measure the stresses in weld structure are as follows:
- 1. Strain gauge method,
- 2. Brittle coat method, and
- 3. Photostress technique.
Q14. What are the main factors affecting the welding design ?
Ans. Factor affecting the welding design are as follows:
- 1. Material going to be welded.
- 2. Nature of the process.
- 3. Dimensions of workpiece.
- 4. Length of weldment etc.
Q15. Name any four weld defects.
Ans. Four weld defects are as follows:
1. Cracks, 2. Inclusions,
3. Crater, and 4. Distortion.
Q15. What are the factors that cause slag inclusion?
Ans. Factors that cause slag inclusion are as follows:
- 1. Too high or too low arc current.
- 2. Too small included angle of the joint.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Advance Welding Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Advance Welding Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |

5 thoughts on “Btech Aktu Advance Welding KME-055 Short Question, Notes, Quantum Pdf”