Table Of Contents
Enhance your B.Tech path with quantum notes from Aktu, which include critical and commonly repeated questions in advanced welding. Dive into this material for a thorough understanding and exam achievement. Unit-2 Welding Processes
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Advance Welding: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
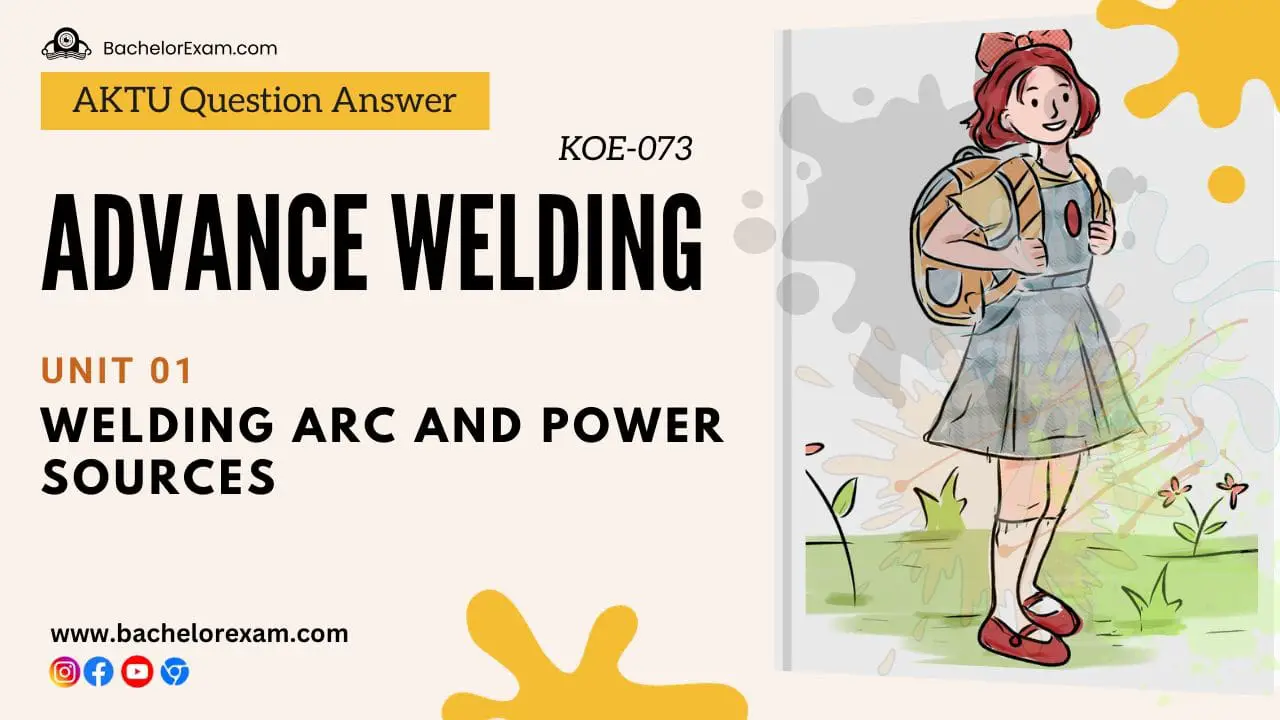
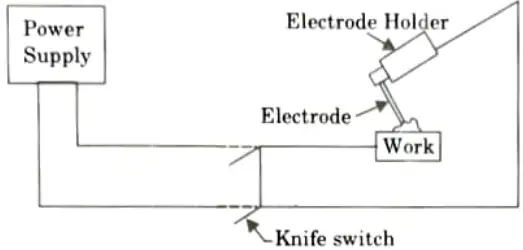
Q1. What is a manual metal are welding or shielded metal are welding?
Ans.
- 1. In the welding method known as arc welding, coalescence is created by heating the joint with an electric arc.
- 2. Depending on the thickness of the parent plate, the majority of electric arc welding is performed without pressure and with or without the use of filler metal.
- 3. When an electric current flows between two electrodes that are very slightly apart from one another, an electric arc is created.
- 4. When welding, the metal to be welded is placed between two electrodes, one of which is a welding rod or wire (workpiece).
- 5. An arc is linked to the supply with one end attached to the positive terminal and the other to the negative terminal.
- 6. Arc is started by momentarily touching the electrode on the plate and then withdrawing it to about 3 to 4 mm from the plate.


- 7. A current flows when the electrode makes contact with the plates. As the electrode is removed from the plate, the current continues to flow across the initially very small gap in the form of a spark. This causes the air gap to become ionised or made conducting, which allows the current to flow across the gap.
- 8. Approximately 2/3rd of the heat is generated on positive pole and 1/3rd on the negative pole.
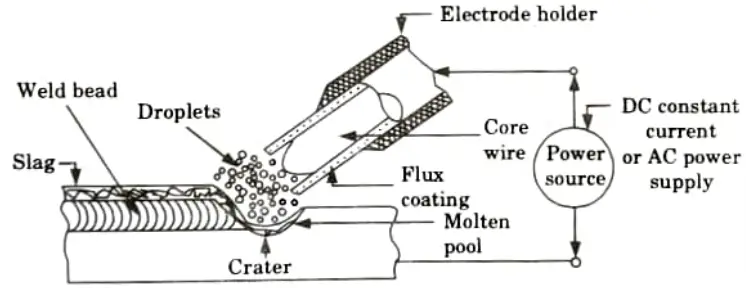
Q2. Using neat sketch, explain TIG welding process. State its applications. What are the variants of TIG welding ?
Ans. A. TIG Welding:
- 1. Coalescence is created during the arc welding process by heating the joint with an electric arc created by striking a tungsten electrode against the joint.
- 2. In order to protect the molten weld pool from atmospheric contamination, a shielding gas is utilized (such as argon, helium, nitrogen, etc.).


B. Principle of Operation of TIG Welding:
- 1. The supplies of water, inert gas, and welding current are turned on.
- 2. Either a high frequency unit or a scrap piece of tungsten metal are used to strike the arc.
- 3. In this arc, the initial strike is made on a piece of scrap metal, and the arc is then shattered by lengthening it.
- 4. The tungsten electrode is warmed up by repeating this technique twice or three times.
- 5. The arc is then created between the electrodes and the previously cleaned welding job.
- 6. By using this technique, work contamination, electrode tip cracking, and tungsten loss are avoided.
- 7. TIG welding is also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW).
- 8. Both the AC and DC power source can be used for GTAW.
- 9. Electrodes employed varies in diameter from 0.5 to 6.5 mm carrying current from 5 A to 6.5 A.
- 10. Among widely used arc welding methods, GTAW produces the highest quality welds and can be employed in any location.
C. Applications of TIG Welding:
- 1. Atomic energy, aerospace, chemical, and instrument industries all use precision welding.
- 2. Welding of materials such as copper, nickel, magnesium, aluminium, and their alloys.
- 3. The construction of rocket motor chambers in launch vehicles.
- 4.Welding of can-sealing joints, transistor casings, and expansion bellows.
D. Advantages of TIG Welding:
- 1. As no flux is used when welding refrigerator and air conditioner parts, there is no risk of flux entrapment.
- 2. The operator may exert superior control over the welding process due to clear view of the arc and the task.
- 3. For the high-quality welding of thin materials, this is ideally suited.
- 4. It is a particularly effective method for joining stainless steel and non-ferrous metals.
E. Disadvantages of TIG Welding:
- 1. The cost of the equipment is higher than for flux-shielded metal arc welding.
- 2. MIG welding is quicker than TIG welding for the same purposes.
F. Variants of TIG Welding:
- 1. Two such variations that use adequate activating flux to enhance certain aspects of standard TIG welding are flux bound tungsten inert gas (PB-TIG) welding and activated tungsten inert gas (A-TIG) welding.
- 2. As a coating of activating flux must be applied to the components being joined, these procedures are also known as flux assisted TIG welding.
Q4. Explain the process of needle are micro plasma welding.
Ans.
- 1. To fuse metal in a joint area and create a molten weld pool, a micro plasma welding (MPAW) arc is generated between the electrode and the work piece in an inert atmosphere.
- 2. What sets MPAW apart from other welding techniques is the placement of the electrode inside the torch’s body and the separation of the plasma-forming gas from the shielding gas envelope. The electrode is not exposed to the environment throughout the other procedures.
- 3. To start the main welding arc, a device known as the pilot arc is struck between the electrode and nozzle. After the main are starts, the pilot arc can either be turned off or left on continuously.
- 4. The current range of micro plasma are varies from 0.1A – 15A. Even at welding current at 0.1A the length can be varied possibly up to 10 mm without affecting stability of the arc.
- 5. The needle like stiff arc minimizes wander and distortion.
- 6. Both manual and fully automated micro plasma arc welding torches are offered.
- 7. Fully mechanized MPAW can only be used in the flat and horizontal positions, but manual MPAW can be used in all situations.
- 8. Typically, a DC current source is employed for micro plasma arc welding. The typical range of micro plasma arc welding current is 0.01 amp to 15 amp.
- 9. A power source provides the ability to pulse. The pulsed arc has the capacity to create welds of the highest and most accurate grade.
Q5. Explain the procedure of electron beam welding process. What are the difficulties encountered during EBW ? Support with neat sketch.
Ans. A. Procedure of Electron Beam Welding:
- 1. Electron beam welding is a type of welding in which the heat generated by a concentrated beam, primarily made up of high-velocity electrons, striking the joint being welded causes coalescence.
- 2. Intense local heating results from the conversion of the electrons’ kinetic energy into heat upon interaction with the work.
- 3. An electron cannon that typically consists of a tungsten cathode, a grid or forming electrode, and an anode produces the electron beam in a high vacuum environment.
- 4. A tungsten filament heated to around 2200 °C emits a stream of electrons.
- 5. The potential difference between the cathode and the anode collects the electrons, accelerates them to high speeds, and shapes them into a beam.
- 6. By passing through the magnetic field of a lens or an electromagnetic focusing coil, the beam is collimated and focussed.
- 7. Beams have a power density of around 10 kW/mm2 and are concentrated to a diameter of 0.25 to 1 mm, which is adequate to melt and vaporise any metal.
- 8. Because the operation is done in a vacuum, the beam source can be placed up to roughly 1 m away from the task.
- 9. This method produces a relatively small heat impacted zone with deep penetration.
- 10. With a width of fusion area equal to roughly one-tenth of the penetration, aluminium can be fused up to a depth of approximately 40 mm and stainless steel up to 30 mm.
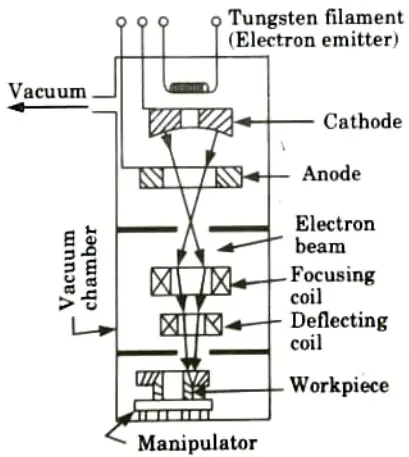


B. Difficulties Encountered During EBW:
- 1. Atmospheric scattering and energy absorption of the beam are minimal in EBW or vacuum welding systems.
- 2. Moreover, vacuum prevents the lowering of electron velocity, but the size of the vacuum chamber that is necessary imposes significant limits on the size of the workpiece, which might hinder the beam’s passage and absorb some of its power.
- 3. Moreover, if the welding is done in a vacuum chamber, a lot of time is wasted pumping down the work chamber for each new workpiece.
- 4. As a result of these issues, various electron beam machines have been created that allow the workpiece to remain outside the vacuum chamber while it is being welded.
Q6. Explain type of underwater welding and their working mechanisms.
Ans. Types of underwater welding are as follows :
i. Wet Welding:
- 1. The work to be welded is linked to one side of an electric circuit, and a metal electrode is attached to the other side, in this welding process.
- 2. The circuit’s two components are brought together and then gently separated.
- 3. The electric current leaps the gap, creating a persistent spark that burns the bare metal and creates a pool of weld.
- 4. Metal droplets are propelled into the weld pool at the same time that the electrode tip melts.
- 5. The flux covering the electrode melts during this process, creating a shielding gas that is employed to protect the transfer metal and stabilize the column.
- 6. The arc burns in a cavity formed inside the flux covering which is designed to burn slower than the metal barrel of the electrode.


ii. Dry Welding:
- 1. This is done in a chamber that is tightly enclosed around the structure that needs to be welded.
- 2. A gas, typically helium (He), that contains 0.5 bar of oxygen at the atmospheric pressure is pumped into the chamber.
- 3. The habitat is attached to the pipeline with a seal and is filled with a breathing gas mixture of oxygen and helium that is at or slightly over the ambient pressure required for welding.
- 4. This technique creates weld joints of excellent quality that adhere to X-ray and code criteria.
- 5. This process uses the gas tungsten arc welding method.
- 6. The habitat’s subfloor is exposed to the water.
- 7. As a result, welding is carried out dry but under the hydrostatic pressure of the surrounding sea water.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Advance Welding Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Advance Welding Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |