Table Of Contents
Aktu’s Quantum Notes can help you succeed in B.Tech. Explore the world of Computer Graphics with these helpful notes that answer frequently asked questions. Exam success has never been easier! Unit-1 Introduction and Line Generation
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Computer Graphics: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Q1. What is computer graphics ? Explain important applications of computer graphics.
Ans.
- 1. The art of painting images on computer screens with the aid of programming is known as computer graphics.
- 2. It entails calculation, data production, and manipulation.
- 3. A rendering tool for the creation and modification of images is computer graphics.
Applications of computer graphics:
- 1. Graphical User Interface (GU): Computer graphics tools are used to make GUI.
- 2. Computer arts: Computer graphics are used in designing object shapes and specifying object such as cartoon drawing, logo design.
- 3. Education and training: Computer generated models of physical financial and economic systems are used as educational aids. Learning with visual aids is fast, easy to understand and cost effective.
- 4. Entertainment: Graphics and image processing techniques can be used to transform an object into another object.
- 5. Visualization: Visualization is used to convert large data value into patterns, charts, graphs, etc., with the help of computer graphics.
- 6. Presentation graphics: With the help of computer graphics large volumes of business data can be presented easily, making it attractive and useful.
Q2. Discuss the various types of computer graphics.
Ans. Various types of computer graphics are:
- 1. Passive (off-line) computer graphics: The most typical instance of passive computer graphics is a static website where the user has no control over what is displayed on the screen. Development occurs in this independently and in off-line mode.
- 2. Interactive computer graphics: Interactive computer graphics allow the user to interact with the system however they see fit. Interactive computer graphics are used in videogames, dynamic websites, movie special effects, and cartoons.
Computer graphics can be broadly divided into the following classes:
- 1. Business graphics, or the broader category of presentation graphics, refers to visuals intended to show quantitative information to inform and persuade the audience, such as bar charts (also known as histograms), pie charts, pictograms (i.e., scaled symbols), x-y charts, etc.
- 2. Scientific graphics such system or programme flowcharts, x-y plots, curve fitting, contour plots, etc.
- 3. Scaled drawings, such as those of machineries, bridges, and buildings that are architectural representations.
- 4. Cartoons and other works of art, including commercials.
- 5. Graphical User Interfaces (GUls), the graphics that nowadays show on nearly all computer screens and are made to make it easier for the user to use the software without having to consult manuals or read a lot of text on the screen.
Q3. Explain the working of Cathode Ray Tube (CRT).
Ans.
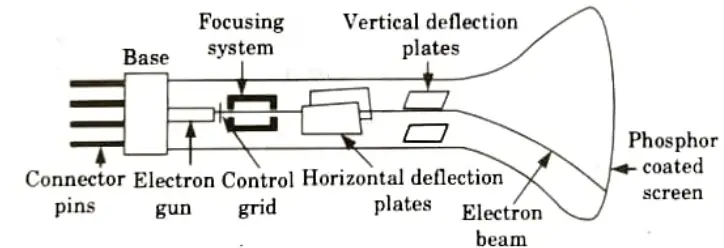


Working of CRT:
- 1. As illustrated in Fig., a CRT is an evacuated glass tube with a variety of components.
- 2. To produce the desired image on the phosphor-coated screen, an electron cannon emits a beam of electrons (cathode rays) that travels through focusing and deflection devices.
- 3. A spot of high-frequency light produced by high-speed electrons striking a phosphor-coated screen is controlled by a video controller.
- 4. A heated metal cathode and a control grid make up the CRT’s electron gun.
- 5. The filament, which is a coil of wire, is heated by a current flowing through it.
- 6. The electrons move as electron beams that pass via horizontal and vertical deflection plates after being cooked off the heated cathode surface.
- 7. A strong positive voltage accelerates the negatively charged electrons in the direction of the phosphor coating.
- 8. Either an accelerating anode or a positively charged metal layer on the inside of the CRT can produce the accelerating voltage.
- 9. When fast electrons from the electron beam clash with the phosphor coating and the phosphor absorbs their kinetic energy, spots of light are created.
- 10. The leftover beam energy is used to shift electrons in the phosphor atom into higher energy levels after some of it is transformed into heat energy by friction.
- 11. These excited electrons return to their stable ground state after a brief period of time and release their additional energy as a tiny quantum of light energy.
- 12. The energy difference between the excited quantum state and the ground state is inversely correlated with the colour of the light these electrons release.
- 13. Several phosphor types (based on colour and persistence) can be coated on the CRT screen.
- 14. The phosphor’s light output soon declines. Refresh CRT displays are used when we need to fast direct the electron beam back over the same places in order to repeatedly redraw the image to keep it on the screen.
Q4. What do you understand by shadow mask CRT ? Give its advantages and disadvantages.
Ans.
- 1. In the majority of colour tubes, a shadow mask is a metal screen that three electron beams traverse back and forth.
- 2. Thousands of small holes are dotted across this mask.
- 3. A group of red, green, and blue phosphor dots are located in front of each hole on the faceplate.
- 4. One point of light is produced by each cluster, and the three beams that travel through each hole regulate its colour and intensity.
- 5. Because the two other phosphor colours are hidden by the shadow mask, the blue beam, for instance, will only hit blue phosphors.
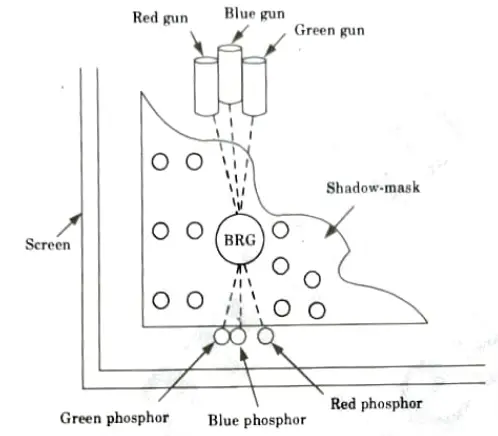


Advantages of shadow-mask method (of CRT):
- 1. The entire screen is updated continuously.
- 2. It enables the display of even solids.
- 3. It makes use of affordable CRT hardware.
- 4. The technology uses brilliant light-emitting displays.
Disadvantages of shadow-mask method:
- 1. It needs a memory array with a size comparable to our screen.
- 2. It carries out discrete pixel spatial sampling.
- 3. The e-beam approaches the CRT face at various angles. Convergence is therefore challenging.
- 4. It also produces erroneous X-ray radiation.
- 5. It requires good dot-pitch and shadow-mask frequency matching.
Q5. Explain frame buffer and video basics. Write a note on video controller.
Ans. Frame buffer:
- 1. In raster displays, the frame buffer is a particular section of memory reserved for graphics.
- 2. It stores the collection of intensities for each screen point.
- 3. The frame buffer is used to retrieve the stored intensity values, which are then displayed on the screen one row (or scanline) at a time.
- 4. A pixel or pel is the term for each screen point (shortened forms of picture element).
- 5. The row and column numbers of each pixel on the screen can be used to identify it. So, we can specify the pixel position on the screen by providing the row and column numbers.
Video basics:
- 1. Video, or any moving image in general, is made up of a series of snapshots known as frames.
- 2. The appearance of movement is simulated by recording baek frames, which are then played back quickly one after the other.
- 3. By eliminating some frames and integrating clips sequences of frames into one long timeline, video can be altered.
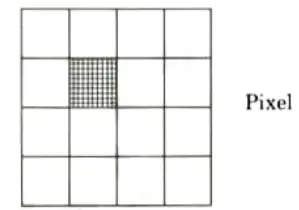
Pixel:
- 1. Pixel is the smallest part of the screen.
- 2. Each pixel has its own intensity, name or address by which we can control it.


Aspect ratio:
- 1. An aspect ratio is an attribute that describes the relationship between the width and height of an image.
- 2. Aspect ratio is expressed by the symbolic notation i.e., x : y.
Resolution:
- 1. The amount of pixels on the horizontal and vertical axes is referred to as resolution.
- 2. The resolution and screen size of the monitor affect how sharp the image is on the display.
Video controller:
- 1. A video controller is a crucial piece of hardware that enables computers to produce graphic data for any type of video display device, including a monitor or projector.
- 2. They are additionally referred to as motherboard-integrated graphics or video adapters.
- 3. They produce television video signals in computer systems as an integrated circuit in a video signal generator.
- 4. In addition to offering rapid image rendering, they also provide features like TV output and multiple monitor connectivity.
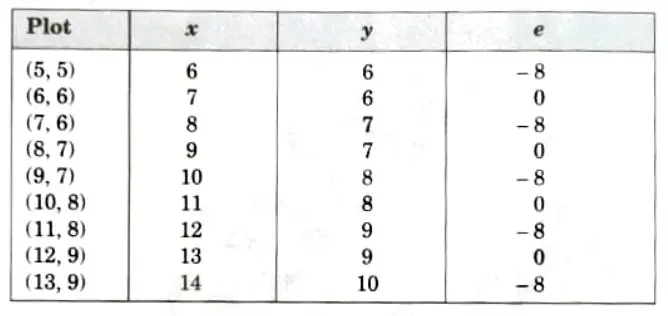
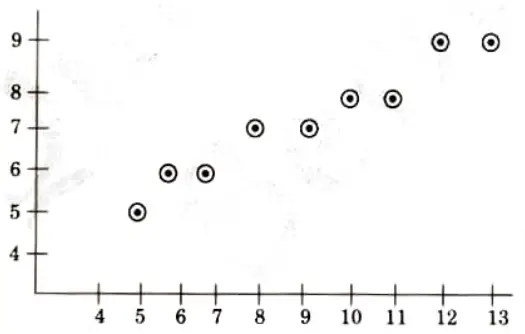
Q6. Consider the line from (5, 5) to (13,9). Use the Bresenham algorithm to rasterize the line.
Ans. Given:
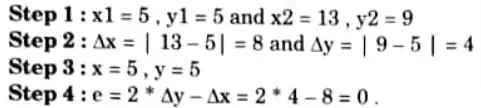
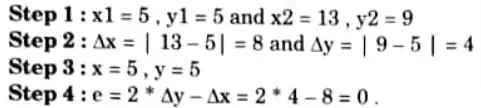
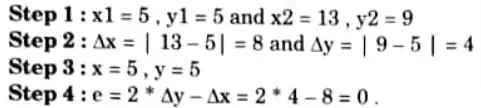
Tabulating the result of each iteration:







Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Computer Graphics Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Computer Graphics Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |
