Show the B.Tech. AKTU Quantum Book Short Question Notes on Analog and Digital Communication. For effective communication systems, investigate the concepts of signal transmission, modulation, coding, and decoding.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Analog and Digital Communication: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Amplitude Modulation (Short Question)
Q1. Define communication process.
Ans. Information is transferred from one point to another through a series of processes in this process.
Q2. What are the fundamental limitations in communication system ?
Ans. The fundamental limitations in communication system are:
- 1. Noise limitation: Baseband transmissions that are not modulated are primarily impacted by channel noise due to their low frequency.
- 2. Bandwidth limitation: Baseband transmissions cannot be multiplexed due to the minimal bandwidth available.
- 3. Equipment limitation: The original form of the baseband signal is not received at the destination due to the high transient noise of the active equipment in the communication system.
Q3. What is modulation ?
OR
Define modulation and explain the need of modulation.
Ans. A. Modulation: Modulation is the process through which a signal’s carrier property is changed in line with the current value of the baseband or modulating signal.
B. Need:
- 1. To reduce height of antenna.
- 2. Transmit data across a great distance without any interruptions.
- 3. Reduce bandwidth.
Q4. Define demodulation process.
Ans. After passage via the channel, the receiver reconstructs the original message signal from a deteriorated version of the sent signal. Demodulation, a method, is used to achieve this reconstruction.
Q5. What do you mean by amplitude modulation ?
Ans. Amplitude Modulation (AM) is a type of modulation in which the frequency of the carrier is maintained constant while the amplitude of the carrier is made proportional to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating voltage.
Q6. Giving the drawback of DSB-SC, explain the need of SSB-SC.
Ans. A. Drawbacks of DSB-SC : Complex detection.
B. Need of SSB-SC:
- 1. Better management of the frequency spectrum.
- 2. Low power consumption.
Q7. What is the envelope of AM wave ?
Ans. When the carrier and message signal are modulated, the envelope of an AM wave is the waveform that is seen as time vs. amplitude.
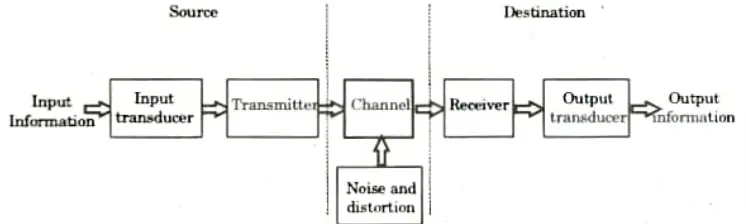
Q8. Draw the basic block diagram of analog communication system.
Ans.


Q9. Give the formula of power relation in AM wave.
Ans.
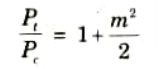
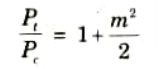
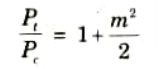
where, Pd = Total power
Pc = Carrier power
m = Modulation index
Q10. Write the limitations of amplitude modulation.
Ans. 1. It is wasteful of power.
2. It is wasteful of bandwidth.
Q11. Define modulation index for AM wave in AM system.
Ans. The ratio of the carrier wave’s change in amplitude to its own amplitude is known as the modulation index. It is denoted by ‘𝜇’.
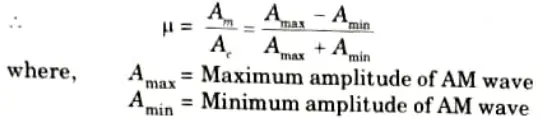
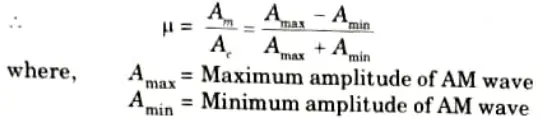
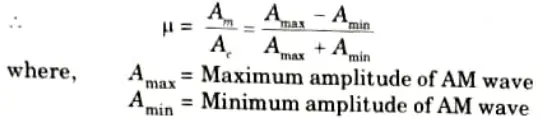
Q12. Define baseband frequency range.
Ans. Baseband frequency range is the term used to describe the spectral range that the original signal occupied.
Q13. What is heterodyning ?
Ans. Mixing or heterodyning is the process of multiplying a signal with an extra sinusoidal signal.
Q14. What is the purpose of multiplexing?
Ans. Multiplexing is used to make better use of the transmission capacity that is available so that various data sources can use the same channel.
Q15. Compare baseband and passband signal.
Ans.
| S. No. | Baseband signal | Passband signal |
| 1. | Baseband signal refers to the message signal produced by the information source. | Passband signal refers to the message signal following modulation. |
| 2. | Baseband transmission is the act of transmitting a baseband signal directly, that is, without modulation. | Passband transmission is the term used to describe the transmission of a modulated signal via a channel. |
| 3. | At short distances and low frequencies, baseband transmission is ideal. | At high frequencies, long-distance passband communication is frequently used. |
Q16. Name the two types of multiplexing techniques.
Ans. Two types of multiplexing techniques are:
- i. Frequency division multiplexing.
- ii. Time division multiplexing.
Q17. Write the advantage of SSB-SC over DSB-SC.
Ans. The main benefit of SSB-SC modulation is that it requires half as little bandwidth as DSB-SC modulation.
Q18. Write the advantages of superheterodyne receiver.
Ans.
- 1. It weakens signals coming from extremely high frequency sources, where regular components would not function.
- 2. It enables a large number of components to run at a set frequency, allowing for optimisation or more bland design.
- 3. It can be utilised to increase arithmetic selectivity and signal isolation.
Unit-II: Angle Modulation (Short Question)
Q1. What is angle modulation and give its types ?
Ans. A. Angle modulation: It involves maintaining a fixed carrier amplitude while altering the overall phase angle of a carrier wave in accordance with the current value of the modulating signal.
B. Types:
- 1. Phase modulation
- 2. Frequency modulation.
Q2. Define phase modulation.
Ans. In this type of angle modulation, the phase angle 𝞧(t) is varied linearly with a modulating signal f(t) about an unmodulated phase angle 𝟂ct.
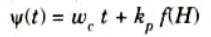
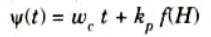
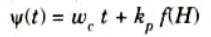
Q3. Explain frequency modulation.
Ans. In this type of angle modulation, the instantaneous frequency 𝟂i is varied linearly with a modulating signal f(t) about an unmodulated frequency 𝟂c.
Q4. What is percent modulation for an FM?
Ans. In FM, the percentage of modulation is defined as the actual frequency deviation divided by the maximum permitted frequency deviation.
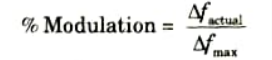
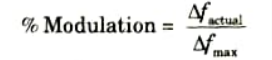
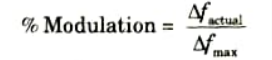
Q5. What is frequency deviation and explain the Carson’s rule ?
OR
What is Carson’s rule ?
Ans. A. Frequency derivation: The instantaneous frequency of FM signal varies with time. The maximum change in instantaneous frequency from the average i.e., 𝟂c is called frequency deviation.
B. Carron’s rule: Carson’s rule provides an empirical calculation for a single tone wideband FM’s bandwidth. According to this rule, the FM bandwidth is given by
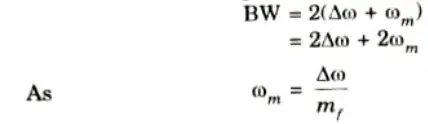
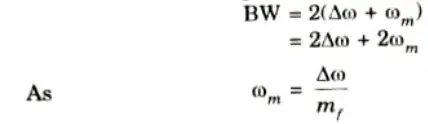
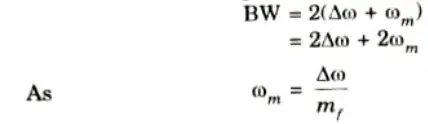
where, mf = FM modulation index
Q7. Define noise.
Ans. Noise is the general term for unwanted signals that tend to interfere with signal processing and transmission in communication systems and over which we have little control.
Q8. What is thermal agitation noise?
Ans. Thermal agitation, white noise, or Jonnson noise are all terms for the random noise produced by a resistance or resistive component. It is brought on by the molecules inside the component itself moving quickly and randomly.
Q9. Discuss signal to noise ratio.
Ans. The ratio of signal power to noise power at a given place is how it is defined. Therefore,
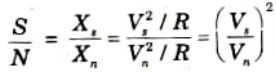
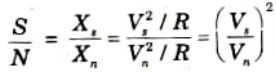
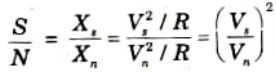
S = Signal power
N = Noise power
Q10. Define modulation index.
Ans. The ratio of the frequency deviation 𝞓f to the modulation frequency fm is called modulation index.
Q11. A single tone modulating signal cos(15𝝅 x 103t) frequency modulates a carrier of 10 MHz and produces a frequency deviation of 75 kHz. If another modulating signal produces a modulation index of 100 while maintaining the same deviation, find frequency of modulating signal.
Ans.
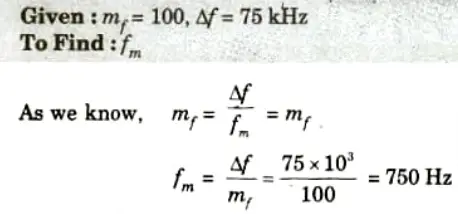
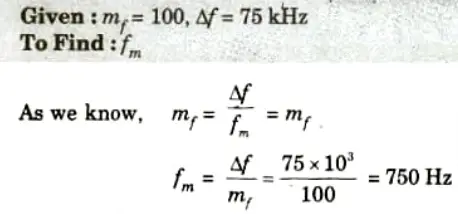
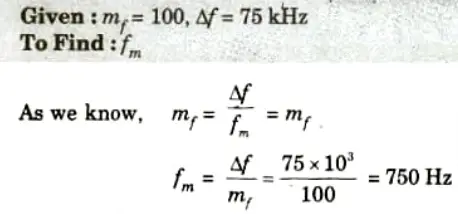
Q12. Write some features of angle modulation.
Ans. i. The ability to trade signal strength for transmission bandwidth is a property of angle modulation.
ii. In angle modulation, the transmission bandwidth can be adjusted by adjusting 𝞓f.
iii. For angle modulation, the SNRis roughly proportional to the square of the transmission of bandwidth BT.
Q13. Define frequency discriminator.
Ans. When a frequency detector uses frequency dependent circuits, or circuits whose output voltage relies on input frequency, to transform a frequency modulating signal into a corresponding amplitude modulated (AM) signal. Frequency discriminators are the name given to such circuits.
Unit-III: Pulse Modulation (Short Question)
Q1. What is pulse modulation ?
Ans. The carrier in pulse modulation is made up of a pulse train, some of whose properties are adjusted in response to the immediate value of the modulating signal.
Q2. Name the two methods of getting the pulse amplitude modulated waveform.
Ans. 1. Natural sampling theorem
2. Flat top sampling.
Q3. What is sampling theorem ?
Ans. The following sentences apply to the transmitter and receiver of a pulse modulation system, respectively, and state the sampling theorem for precisely bandlimited signals of finite energy and n two equivalent portions as follows:
- i. The values of the signal at instants of time separated by 1/2W seconds are used to fully characterize a bandlimited signal with finite energy and no frequency component higher than W hertz.
- ii. Using knowledge of its samples obtained at a rate of 2W samples per second, a bandlimited signal with finite energy and no frequency components over W hertz may be fully reconstructed.
Q4. Define Nyquist rate and Nyquist interval.
OR
What do you mean by Nyquist rate ?
Ans. The Nyquist rate, or sampling rate, is 2W samples per second for a W hertz signal bandwidth, while the Nyquist interval, or reciprocal, is 1/2W (measured in seconds).
Q5. What is aliasing ?
Ans. A high-frequency component of the signal’s spectrum that appears to take on the identity of a lower frequency component of the spectrum of its sampled form is known as aliasing.
Q6. Give the corrective measures to combat the effects of aliasing in practice.
Ans. These are :
- i. A low-pass anti-aliasing filter is employed before sampling to alternate the high-frequency signal components that are not necessary for the signal to carry its information.
- ii. The sample rate for the filtered signal is slightly higher than the Nyquist rate.
Q7. Define pulse position modulation (PPM).
Ans. In PPM, the message signal determines how a pulse is positioned in relation to its unmodulated time of occurrence.
Q8. What is encoding?
Ans. The discrete set of sample values is converted to a more suitable signal type using encoding.
Q9. Compare digital modulation and pulse modulation.
Ans.
| S. No. | Digital modulation | Pulse modulation |
| 1. | In this modulation, a signal is modulated by changing one or more carrier wave parameters in relation to two or more discrete, finite states of the signal. | A signal’s amplitude is represented by this modulation, in which pulses are altered in some way, such as width or amplitude. |
Q10. What are the applications of sampling theorem ?
Ans. A continuous temporal signal can be replaced by a discrete series of integers according to the sampling theorem, which is crucial for signal analysis, processing, and transmission.
Q11. Why is line coding required in communication system ?
Ans. Line coding required in communication system because:
- I. lt assists in error recovery and allows for the extraction and processing of clock information.
- ii. A limited transmission bandwidth exists.
- iii. Its spectral density is advantageous.
Q12. What is quantizer ?
Ans. A function called a quantizer has a discrete and typically finite set of output values. It converts the message signal’s sampled amplitude values into a discrete amplitude value.
Unit-IV: Digital Modulation Technique (Short Question)
Q1. Define amplitude shift keying (ASK).
Ans. 1. Depending on the carrier frequency, the input data determines whether the output amplitude should be zero or a range of positive and negative values.
2. It uses fluctuations in a signal’s amplitude to express binary data.
3. When ASK is modulated, the binary signal outputs the carrier signal for HIGH input and zero for LOW input.
Q2. Define frequency shift keying (PSK).
Ans. 1. Depending on the input data used, the output signal’s frequency will either be high or low.
2. In this, the carrier signal’s frequency changes in accordance with the discrete digital modifications.
3. A FSK modulated wave has a high frequency output for binary HIGH inputs and a low frequency output for binary LOW inputs.
Q3. What is phase shift keying (PSK) ?
Ans. Depending on the input, the output signal’s phase is altered.
Q4. Give the generation of ASK.
Ans. The incoming binary data and sinusoidal carrier can be applied to the two inputs of a balanced modulator or product modulator to create an ASK signal. The ASK waveform will be the final output.
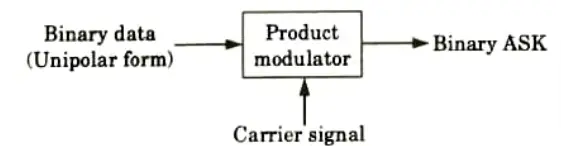


Q5. Briefly explain DPSK.
Ans. The non-coherent PSK can be thought of as differential phase shift keying. By combining two fundamental transmitter processes, it does away with the requirement for a coherent reference signal at the receiver:
- a. Differential encoding of the input binary wave
- b. Phase shift keying
Hence, it is named as differential phase-shift keying.
Q6. Draw the block diagram of coherent detection of binary ASK.
Ans.
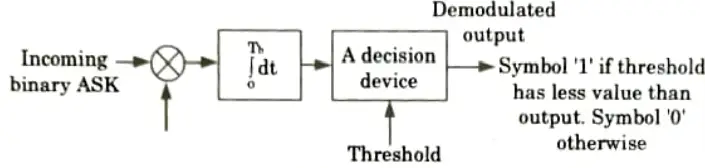


Q7. Draw the block diagram of non-coherent detection of binary ASK.
Ans.
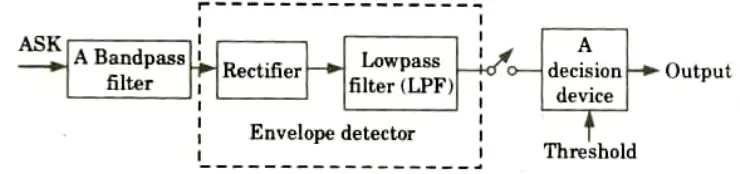


Q8. Which passband modulation can’t be detected using non coherent technique ? What is the reason for this ?
Ans. Non-coherent techniques cannot identify PSK modulation because PSK modulation changes the phase of the modulation in accordance with the phase of the baseband signal. The same frequency should be utilized at both the transmitter and receiver ends when doing noncoherent detection.
Q9. Briefly explain the generation of PSK.
Ans. 1. To generate a binary PSK wave, the input binary sequence is represented in polar form with symbols 1 and 0 represented by constant amplitude levels of
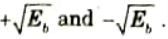
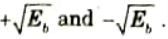
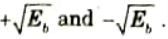
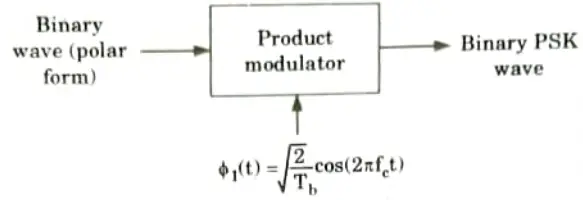


2. The binary wave and sinusoidal carrier wave 𝝓1(0) are applied to product modulator.
3. The carrier and the timing pulses needed to produce the binary wave are typically taken from a shared master clock. It is possible to output the desired PSK wave.
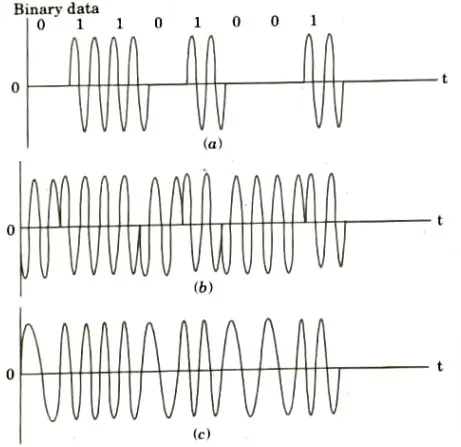
Q10. Draw the various waveforms for amplitude, frequency and phase shift keying.
Ans. Waveforms of ASK, PSK and FSK:


Q11. Compare digital modulation and pulse modulation.
Ans.
| S. No. | Digital modulation | Pulse modulation |
| 1. | In this modulation, a signal is modulated by changing one or more carrier wave parameters in relation to two or more discrete, finite states of the signal. | A signal’s amplitude is represented by this modulation, in which pulses are altered in some way, such as width or amplitude. |
Unit-V: Time Division Multiplexing (Short Question)
Q1. What is time division multiplexing ?
Ans. Time division multiplexing (TDM) allows a number of independent message sources to jointly use a single communication channel without interfering with one another.
Q2. What do you mean by information ?
Ans. The minimum amount of binary digits necessary to encode a message can be thought of as the information in the message.
Q3. Define entropy of a source.
Ans. Entropy is the measure of average information per message interval.
Q4. Explain the advantages of TDM.
Ans. 1. TDM circuitry is not very complex.
2. Problem of cross-talk is not severe.
3. Only one carrier in the medium at any time.
Q5. Explain the difference between TDM & FDM.
Ans.
| S. No. | TDM | FDM |
| i. | It divides the channel by giving each channel a certain amount of time. | In order to allow more users, the channel is divided into a number of smaller frequency bands. |
| ii. | Much better flexibility compared to FDM. | Less flexibility. |
| iii. | Less latency. | It proves much better latency compared to TDM. |
Q6. An analog signal is bandlimited to 4 kHz. It is sampled at the Nyquist rate and the samples are quantized into 4 levels. The quantization levels are independent messages having probability P1 = P2 1/8 and P3 = P4 = 3/8. Find the information rate of the source.
Ans.



Q7. What is information rate ?
Ans. If the same source of the message generates messages at the rate r message per second, then the information rate is defined as :
R= rH = average number of bits of information / second
Q8. Give a comment on channel capacity.
Ans.It is described as a channel’s innate capacity to transmit information.
Q9. Give the functions of commutator.
Ans. In most cases, electrical switching circuitry is used to implement commutators. Mainly two functions are done by commutator:
- a. To take a narrow sample of each of the N input messages at a rate fs that is slightly higher than 2W, where W is the cutoff frequency of the anti-aliasing filter.
- b. To sequentially interleave these N samples inside the sampling interval Ts.
Q10. A Gaussian channel has 1 MHz bandwidth. Calculate channel capacity if the signal power to noise spectral density ratio is 105 Hz.
Ans.
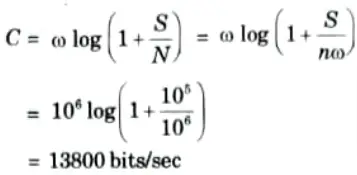
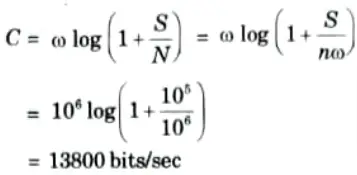
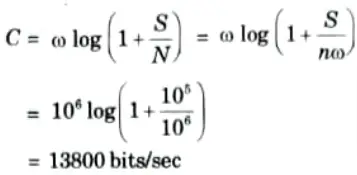
Q11. What is Kraft Inequality ?
Ans. The Kraft-MeMillan inequality states that we can construct a uniquely decodable code with word-lengths l0, l1,……………..lk-1 if and only if these length satisfy the given condition
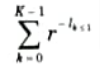
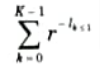
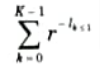
where r is the radix of the alphabet of encoded symbols.
2. Prefix codes are a specific example of uniquely decodable codes, and the kraft inequality holds true for them.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Analog and Digital Communication Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Analog and Digital Communication Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |

1 thought on “Analog and Digital Communication KEE-058 Aktu Btech Short Question Pdf”