Discover B.Tech AKTU Quantum Book Short Question Notes on Wireless and Mobile Communication. Investigate signal transmission fundamentals, networking, and cutting-edge wireless technologies for seamless connectivity.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Wireless and Mobile Communication: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 4th Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Wireless Communication Fundamentals (Short Question)
Q1. What is handoff ?
Ans. When a mobile phone travels into a different cell while a call is in process, the MSC instantly changes the call to a new channel assigned to the new base station. Handoff refers to the procedure of exchanging channels between two cells.
Q2. How call termination can be avoided during handoff ?
Ans. To avoid such occurrences, each cell must set aside a specified number of channels for handoff. When designating channels for handoff, keep in mind that they are not idle for whatever reason. They must be used to their full potential.
Q3. Write the advantage of handoff.
Ans. Advantage of handoff :
- 1. There is a shift in frequency or timing during the user’s mobility, therefore there are almost no dead zones.
- 2. It provides more stable networking continuity with a lower likelihood of call termination than hard handoff.
Q4. Differentiate hard and soft handoff.
Ans.
| S. No. | Soft Handoff | Hard Handoff |
| 1. | A mobile station communicates with two base stations at the same time. | A mobile station communicates with only one base station. |
| 2. | Soft handoff is used in CDMA. | Hard handoff is used in FDMA and TDMA. |
Q5. What is the basic work of base station in mobile communication ?
Ans. The transcoder rate adapter unit (TRAU) in the base station performs coding and decoding as well as rate adaptation when the data rate varies.
Q6. What is mean by frequency reuse ?
Ans. The process of identifying and allocating channel groups for all of a system’s cellular base stations is known as frequency reuse or frequency planning.
Q7. What is channel assignment ? What are the types ?
Ans. Channel assignment refers to the process of allocating channels or spectrum bands to radio interfaces for communication.
Types of channel assignment :
- i. Fixed
- ii. Dynamic
Q8. What is the main objective of using channel assignment strategies ?
Ans. The major objective of adopting channel assignment techniques is to optimise frequency reuse scheme utilisation and interference mitigation so that overall channel capacity can be raised.
Q9. List the various techniques possible to improve coverage and capacity in cellular systems.
Ans. Techniques to improve coverage and capacity in cellular systems are as follows:
- 1. Cell splitting.
- 2. Cell sectoring.
- 3. Microcell zone concept.
- 4. Increasing number of repeaters.
Q10. What is fading ?
Ans. Fading is the term used to describe the phenomena of the received signal power changing over time due to changes in the transmission medium or path.
Q11. Define Brewster angle.
Ans. 1. The Brewster angle is the angle at which no reflection occurs in the medium of origin.
2. It occurs when the incident angle θB is such that the reflection coefficient Г|| (Parallel reflection coefficient) is equal to zero. It is given by
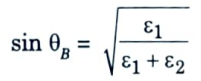
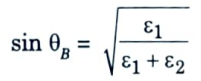
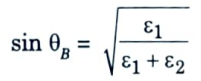
where θB is the Brewster angle.
Q12. Find the number of duplex channels, if 20 MHz of total spectrum is allocated for a duplex wireless cellular system and each simplex channel has 25 kHz RF bandwidth.
Ans. Given: Total bandwidth = 20 MHz, Channel bandwidth = 2 x 25 = 50 kHz/duplex channel.
To Find: Number of duplex channel.
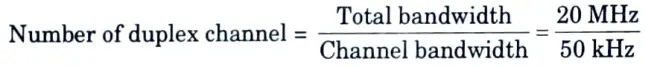
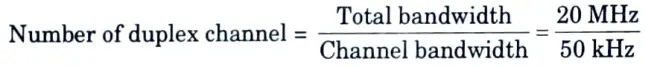
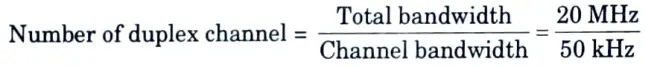
= 400
Q13. If I = 3 and J = 0, what is the cluster size in cellular system ?
Ans. Given: I = 3, J = 0
To Find: N
N = I2 + IJ + J2 = 32 + 0 + 0 = 9
Q14. What do you mean by channel modelling ?
Ans. There are two techniques to modelling a channel: physical and statistical. The physical approach considers reflection, multipath, attenuation, and so on, whereas the statistical approach considers input-output elements and transaction probability.
Q15. How scattering is different from reflection with respect to surface ?
Ans. 1. Reflection happens when an electromagnetic wave impinges on an object with unusually large proportions in comparison to the wavelength, such as the earth’s surface, a building, or walls.
2. Scattering occurs when the medium contains items smaller or comparable to the wavelength (tiny objects, rough surface, and other channel imperfections). In practise, plants, traffic signs and lampposts cause dispersal.
Q16. Define AWGN channel.
Ans. An AWGN channel is one that adds white Gaussian noise to the signal it receives.
Q17. What are the types of channel models ?
Ans. Channel models are primarily divided into two main categories:
- i Outdoor channel model (e.g., Longley-Rice model, Okumura-Hata model, Nakagami model, and Rician model)
- ii. Indoor channel model (e.g., Rayleigh model)
Q18. What do you understand by Okumura-Hata model ?
Ans. The Okumura-Hata model is an empirical model for path loss calculation in urban or semi-urban areas.
Q19. What are the main reasons for path losses ?
Ans. 1. Path losses caused by the natural expansion of the radio wave front in free space.
2. Path losses are caused by reflection, diffraction and scattering.
Q20. What is slow fading channel, fast fading channel and frequency selective channel ?
Ans. Slow fading channel: If the baseband signal bandwidth is significantly bigger than the Doppler spread BD, the effects of Doppler spread at the receiver are insignificant. This is a channel that fades slowly.
Fast fading channel: If the baseband signal bandwidth is less than the Doppler spread BD, the Doppler spread effect causes frequency dispersion. This is a channel that fades quickly.
Frequency selective channel: If the channel has a constant-gain and linear phase response over a bandwidth narrower than the bandwidth of the sent signal, frequency selective fading occurs on the received signal.
Unit-II: Spread Spectrum and Diversity (Short Question)
Q1. What is vocoder ?
Ans. Vocoders are a type of speech coding system that analyses the voice signal at the transmitter, transmits parameters obtained from the analysis, and then uses those parameters to synthesise the voice at the receiver.
Q2. List some advantages and disadvantages of vocoders.
Ans. A. Advantages of vocoders :
- 1. Low bit rate.
- 2. Can be time domain and frequency domain.
B. Disadvantages of vocoders :
- 1. Much more complex.
- 2. Less robust.
- 3. Relatively low synthetic speech quality.
Q3. Give the types of vocoders.
Ans. Vocoders are divided into following four types:
- 1. Channel vocoder.
- 2. Formant vocoder.
- 3. Cepstrum vocoder.
- 4. Voice-excited vocoder.
Q4. Give the classification of spread spectrum systems.
Ans. The following are the spread spectrum techniques :
- 1. Direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS).
- 2. Frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS).
- 3. Time hopping spread spectrum (THSS).
- 4. Hybrid methods.
- 5. Chirped spread spectrum (CSS).
Q5. State some applications of spread spectrum modulation.
Ans.
- 1. It is used to reduce crosstalk interference.
- 2. Better voice quality data integrity and less static noise.
- 3. Inherent security.
- 4. Co-existence.
Q6. What do you mean by DSSS system ?
Ans. In a DSSS system, the user signal is amplified by a high bandwidth PN code sequence. The resulting coded signal is sent through radio channel. DS is in charge of sharing the bandwidth.
Q7. Define processing gain (PG).
Ans. The processing gain is given by
PG = BS/Bm
where BS = Bandwidth of the SSM or PN signal
Bm = Bandwidth of the message signal.
Q8. What do you understand by FHSS system ?
Ans. The transmitter in FHSS systems changes the carrier frequency according to a specific hopping pattern, which means that the frequency is constant in each time chip but varies from chip to chip.
Q9. What are the ways to reduce intersymbol interference (ISI) ?
Ans. The following are some measures to mitigate ISI:
- 1. By using equalizers.
- 2. By using OFDM modulation.
- 3. By using a filter satisfying the Nyquist zero ISI criterion.
- 4. By controlling the transmission rate.
Q10. Define diversity.
Ans. Another strategy used to compensate for fading channel impairments is diversity, which is often achieved by having two or more receiving antennas. Diversity enhances the quality of a wireless communication link without changing the common air interface or boosting transmitted power or bandwidth.
Unit-III: Equalization and Multiple Access (Short Question)
Q1. What is equalization ?
Ans. Equalization is a technique for compensating for intersymbol interference (ISI) caused by multipath in time-division multiplexed channels.
Q2. How equalization, channel coding and diversity are different in link performance improvement ?
Ans. Equalization compensates for ISI, diversity compensates for fading, and channel coding enhances mobile communication connection performance by including redundant data bits in the sent message.
Q3. Why we are using equalization in wireless communication ?
Ans. Intersymbol interference (ISI) is a major barrier in wireless communication that has a significant impact on data quality. The purpose of equalization approaches is to recreate the actual signal using a filter or other methods and remove the effect of ISI so that data transmission reliability is maintained.
Q4. Explain FDMA.
Ans. Individual channels are assigned to specific users using frequency division multiple access (FDMA). A particular frequency band or channel is allotted to each user. Users who want services have these channels assigned on demand.
Q5. Explain TDMA.
Ans. Time division multiple access (TDMA) systems divide the radio spectrum into time slots, with each slot allowing only one user to send or receive. Each user has a time slot that repeats cyclically. TDMA systems use a buffer and burst mechanism to transport data.
Q6. What is CDMA ?
Ans. The narrowband message signal is multiplied by a high bandwidth signal termed the spreading signal in code division multiple access (CDMA) systems. The spreading signal is a pseudo-noise code sequence with a chip rate orders of magnitude higher than the message data rate.
Q7. What do you mean by packet radio access ?
Ans. Many customers attempt to access a single channel in an uncoordinated manner using packet radio (PR) access mechanisms. Data bursts are used for transmission.
Q8. What do you understand by CSMA ?
Ans. In CSMA, carrier sensing is used to identify whether the channel is busy before transmission. There are two versions of CSMA :
- 1. CSMA with collision detection (CSMA/CD).
- 2. CSMA with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA).
Q9. What is the principle of RAKE receiver?
Ans. By providing a separate correlation receiver for each of the multipath signals, a RAKE receiver collects the time-shifted versions of the original signal. A RAKE receiver is essentially a diversity receiver optimised for CDMA.
Q10. Write a short note on OFDMA.
Ans. Orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) is a multicarrier modulated hybrid multiple access or multiplexing system that divides the available spectrum into several carriers, each of which is modulated by a low-rate data stream.
Q11. What do you mean by SDMA?
Ans. The radiated energy for each user in space is controlled by space division multiple access (SDMA). SDMA uses spot beam antennas to serve multiple consumers. The various areas served by the antenna beam may be served by the same or separate frequencies.
Q12. Explain FHMA.
Ans. Frequency hopping multiple access (FHMA) is a digital multiple access system in which the carrier frequencies of individual users are altered in a pseudo random fashion inside a wideband channel.
Q13. Consider a GSM system, which is a TDMA/FDD system that uses 20 MHz for forward link which is broken into radio channel of 200 kHz and if no guard band is assumed, find the number of simultaneous users that can be accommodated in GSM.
Ans.
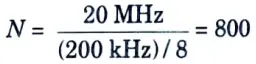
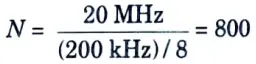
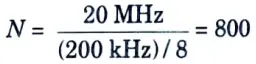
Thus, GSM can accommodate 800 simultaneous users.
Unit-IV: Cellular Networks (Short Question)
Q1. What is GSM ?
Ans. The Global System for Mobile (GSM) is a second generation cellular system standard that was created to address the fragmentation issues of Europe’s first cellular systems.
Q2. What are the services offered by GSM ?
Ans. User services may be divided into three categories:
- i. Telephone services.
- ii. Bearer services or data services.
- iii. Supplementary ISDN services.
Q3. What are the signaling features in GSM ?
Ans. 1. All GSM signaling is based on the OSI model used for computer systems.
2. The MSC uses ITU’s signaling system number 7 (SS7) for its signaling.
3. The air interface and A-bis signaling is based on ISDN link access protocol.
Q4. Mention two services aspects in IS-95.
Ans. 1. Provides extensive path diversity.
2. Improved performance in difficult propagation environment.
Q5. Write range of frequency for forward and reverse link operation for IS-95.
Ans. 1. The range of frequency for forward link is from 869 to 894 MHz.
2. The range of frequency for reverse link is from 824 to 849 MHz.
Q6. What are the categories of GPRS devices ?
Ans. Categories of GPRS devices are:
Class A: This kind of phones can connect to both GPRS and GSM services at the same time.
Class B: Mobile phones of this type can connect to both GPRS and GSM services, although they can only use one at a time.
Class C: Mobile phones in this class can connect to either GPRS or GSM services, but the user must manually switch between the two.
Q7. How many types of LTE channels ?
Ans. There are three types of LTE channels.
- i. Physical channel
- ii. Logical channel
- iii. LTE transport channel.
Q8. What do you understand by EDGE technology ?
Ans. Enhanced data for GSM evolution (EDGE) is a GSM mobile cellular phone system upgrade. It allows data to be transmitted via a GSM TDMA system at speeds of up to 384 kbps. It is classified as a 2.5G system.
Q9. Compare the different second generation mobile communication systems, particularly in terms of multiple access technology, modulation technique, and channel bandwidth.
Ans.
| S. No. | Parameter | GSM | IS-136 | PDC |
| 1. | Multiple access | TDMA/FDMA/FDD | TDMA/FDMA/FDD | TDMA/FDMA/FDD |
| 2. | Channel bandwidth | 200 KHz | 30 KHz | 25 KHz |
Q10. What are the key features of IMT-2000 ?
Ans. IMT-2000 has the following features:
- 1. Flexibility.
- 2. Affordability.
- 3. Compatibility with existing systems.
- 4. Modular design.
Unit-V: Wireless Networks (Short Question)
Q1. Explain MANET.
Ans. In the absence of fixed infrastructure, mobile adhoc networks (MANET) are collections of mobile nodes that dynamically construct short-lived networks. Each mobile node has a wireless transmitter as well as a receiver with a suitable antenna.
Q2. What is adhoc routing protocol ?
Ans. An adhoc routing protocol is a standard that governs how mobile nodes in a mobile adhoc network decide which way to route messages between computing devices.
Q3. What is demerit of adhoc network ?
Ans. Demerits of adhoc network are:
- 1. Limited wireless transmission range.
- 2. Broadcast nature of the wireless medium.
- 3. Packet losses due to transmission errors and mobility.
- 4. Battery constraints.
Q4. What are the three main wireless technologies ?
Ans. Bluetooth, Wifi, and Li-Fi.
Q5. What is the reason behind the name bluetooth ?
Ans.
- 1. The wireless communication field needs some unification in the mid-1990s. Many corporations were developing standards that were incompatible with one another.
- 2. Several people see this widening schism as a barrier to mainstream wireless adoption. That’s when Intel engineers stepped in as a cross-corporate mediator, bringing together multiple firms to create an industry-wide standard for low-power, short-range radio connection.
- 3. The Intel engineers studied Frans G. Bengtsson’s book The Longships, which chronicled the journeys of Danish soldiers during the reign of King Harald “Bluetooth” Gormsson. King Harald “Bluetooth” became famous for bringing opposing parties together in order to unite Scandinavia.
- 4. Thus, Intel engineers adopted the term “Bluetooth” from monarch Harald Bluetooth, the second monarch of Denmark in the 10th century, who unified Scandinavia just as they were attempting to combine the PC and cellular sectors with a short-range wireless link.
Q6. What is bluetooth ?
Ans. Bluetooth is an open wireless technology for transmitting data over short distances between fixed and mobile devices, resulting in highly secure personal area networks (PANs).
Q7. What are the different modes of a bluetooth device in the connection state ?
Ans. A bluetooth device in the connection state can be in any of the four mode:
- 1. Active mode
- 2. Sniff mode
- 3. Hold mode
- 4. Park mode.
Q8. Give two examples for Wi-Fi technology.
Ans. 1. Internet access.
2. Wi-Fi sensor networks.
Q9. What is WiMax ?
Ans. WiMAX is a new broadband wireless data communications technology or mobile internet based on the IEEE 802.16 standard that delivers high-speed data communications (70 Mbps) over a wide region.
Q10. What is mobile data network ?
Ans. By mobile data networks, we mean services, technologies, and standards linked to data services over wide area coverage, or areas larger than a local area or campus.
Q11. How IMT-2000 is useful for node to node communication ?
Ans. IMT-2000 is beneficial for node-to-node communication since it provides universal usage via a single global frequency band.
Q12. What are the advantages of 4G system ?
Ans.
- 1. Affordable communication services.
- 2. High speed, high capacity and low cost per bit.
- 3. Better spectral efficiency.
- 4. Seamless network of multiple protocol and air interfaces.
Q13. What are the components of Next Generation Networks ?
Ans.
- 1. Packet based networks
- 2. Access gateways
- 3. Trunking gateways
- 4. Soft switch/MGC
- 5. Application server (AS)
Q14. List the services provided by NGN.
Ans. The services provided by NGN are as follows:
- 1. Specialized resource services.
- 2. Processing and storage services.
- 3. Middleware services.
- 4. Content provision services.
- 5. Management services.
- 6. Interworking services.
Q15. Calculate the spectral efficiency if the bandwidth is 684 kbps and transmission data rate is 1.152 Mbps.
Ans. Given: Bandwidth, BW = 684 kbps, Transmission rate, RT = 1.152 Mbps
To Find: Spectral efficiency.
We have,
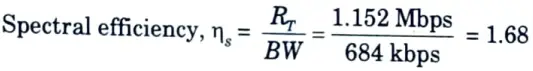
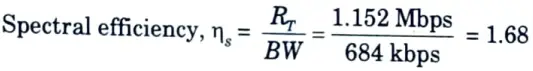
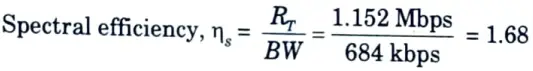



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Wireless and Mobile Communication Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Wireless and Mobile Communication Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |
