With Quantum Notes, improve your readiness for Strength of Materials. See the important questions that appear regularly in Aktu Btech exams. Obtain the advantage you require for success. Unit-5 Curved Beam and Unsymmetrical Bending
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Strength of Material: * Aktu Quantum * B.tech-Syllabus * Circulars * B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Q1. Why position of neutral axis from centroid for curved beams in Winkler Bach theory is given as
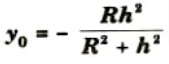
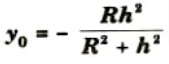
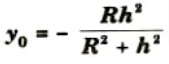
Ans. A. Neutral Axis: A layer inside the beam known as the neutral axis experiences neither compressive nor tensile stress. There will be no stress at the neutral axis.
B. Position of Neutral Axis:
- 1. As we know that the stress acting on the beam is
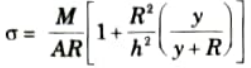
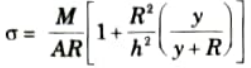
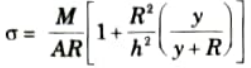
- 2. At neutral axis stress will become zero, so 𝝈 = 0



- 3. This equation shows that y is negative means the position of neutral axis is below the centroidal axis.
C. Value of h2 and Position of Neutral Axis for Rectangular Cross Section:
- 1. Let us consider a curved beam of rectangular cross-section (B x D). R is the distance between centre of curvature and centroid of rectangular cross-section.
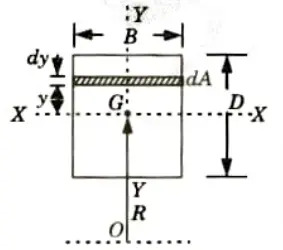


- 2. Consider a strip of depth dy and width B having elemental area as dA.
- 3. Area of rectangular cross-section, A = BD
- 4. Area of elemental strip, dA = Bdy
- 5. Putting the values of A and dA in equation given below,
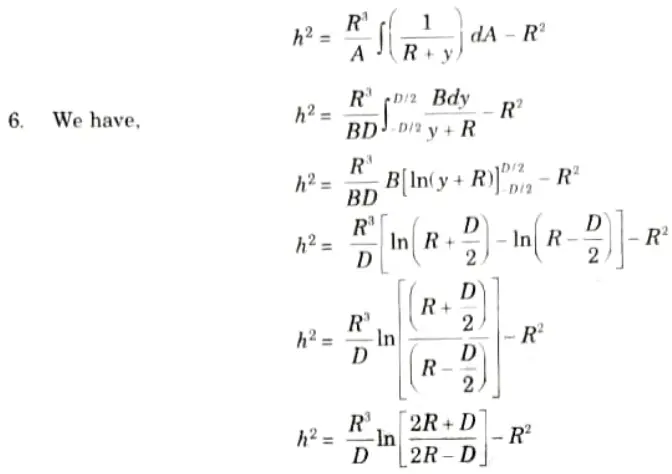
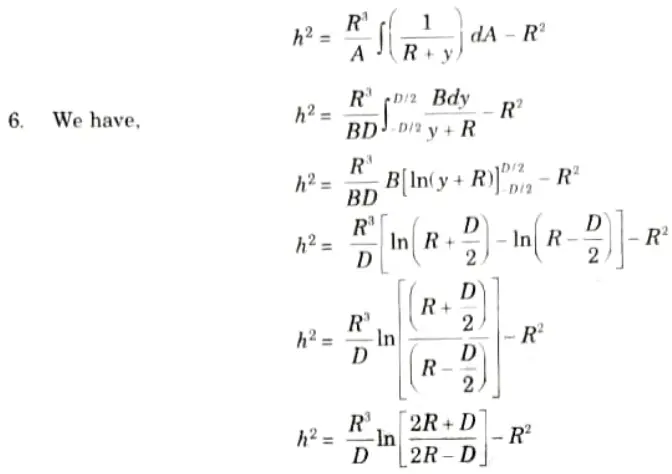
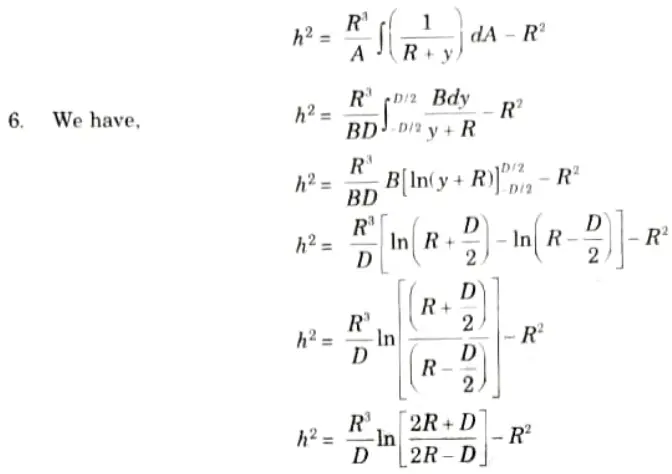
- 7. Position of neutral axis:
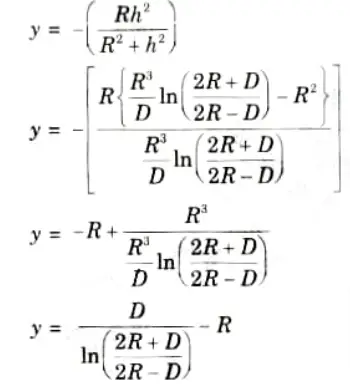


Q2. The bending moment acting on the curved beam with a rectangular cross section is M 8 kN-m. Calculate the bending stress at point B.
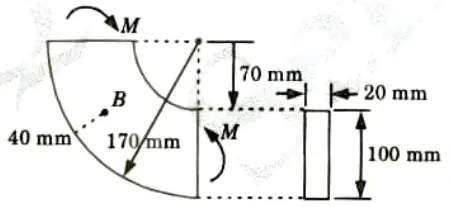


Ans. Given: M=8 kN-m, b =20 mm, d= 100 mm, Position of point B=40 mm from bottom
To Find: Stress at point B
1. Mean radius of curvature,
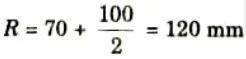
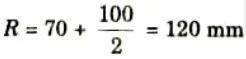
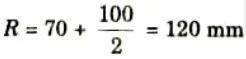
2. The value of h2 can be obtained as,
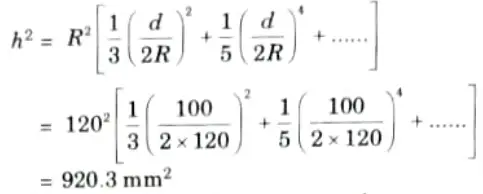
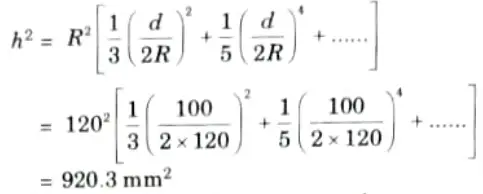
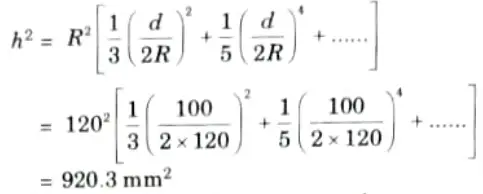
3. Position of neutral axis from centroidal axis is given by,
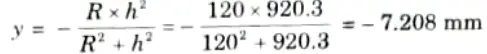
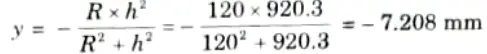
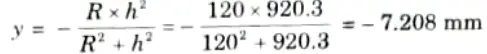
4. Stress at point B is calculated by using given equation,
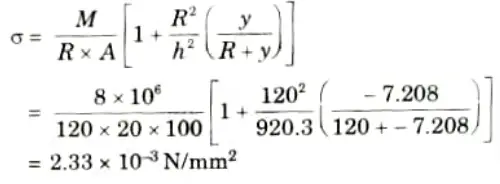
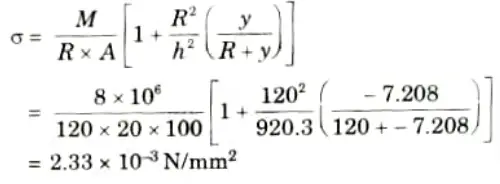
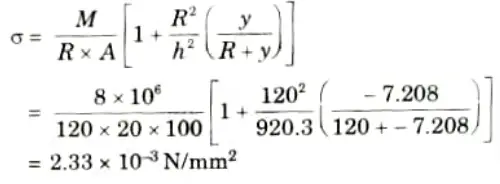
Q3. Why is the knowledge of shear center of a beam being important ?
Ans.
- 1. The shear center is the point of intersection of the bending axis and the plane of the transverse section.
- 2. Shear centre of a section can be defined as a point about which the applied force is balanced by the set of shear forces obtained by summing the shear stresses over the section
- 3.. As shear centre tells about the point about which the beam will not twist, so it becomes important to know about the shear centre.
Q4. Define shear centre. Find the shear centre of the section shown in Fig.
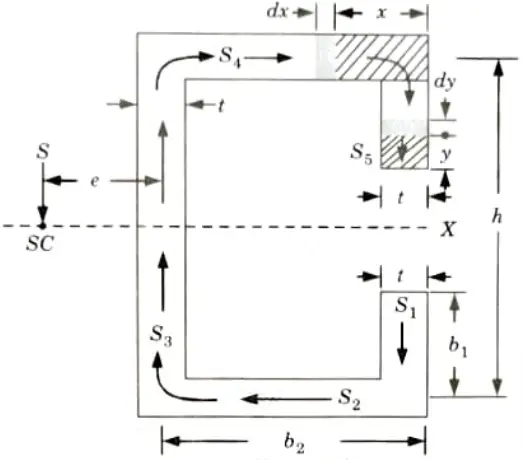


Ans. A. Shear Centre:
- 1. A section’s shear centre is defined as a point about which the applied force is balanced by the set of shear forces derived by adding the shear stresses over the section. The shear centre is also known as the twist centre.
- 2. The shear centre coincides with the centroid in the case of a beam with two axes of symmetry.
- 3. In sections with one axis of symmetry, the shear centre does not coincide with the centroid but instead resides on the axis of symmetry.
- 4. When the load passes through the shear center, the cross-section will only bend and not twist.
The loads acting on the beam must lie in a plane that contains the resultant shear force on each cross-section of the beam as computed from the shearing stresses produced in the beam when it is loaded so that it does not twist at its ends.
Fig.
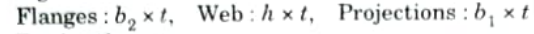
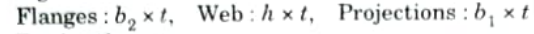
B. Derivation :



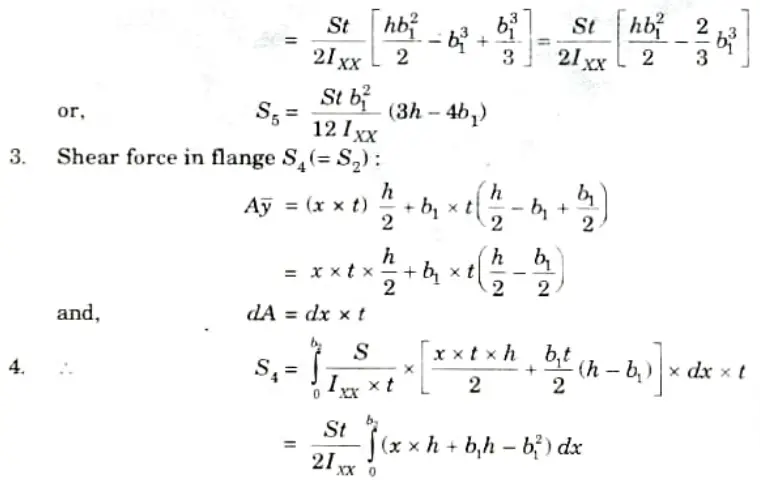
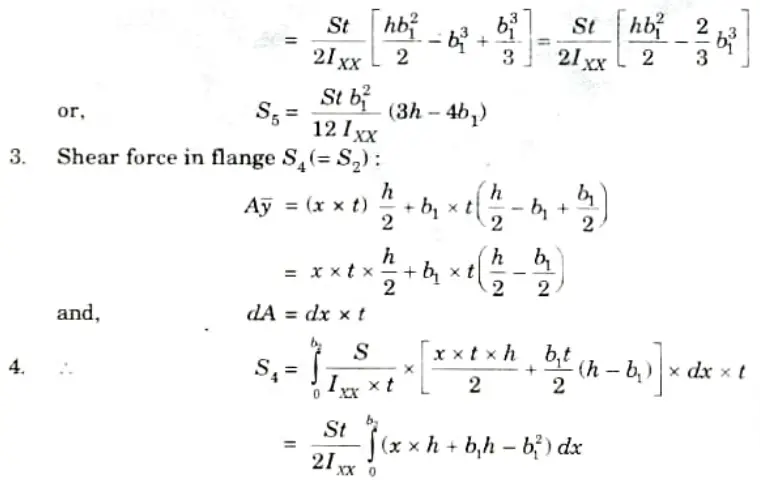
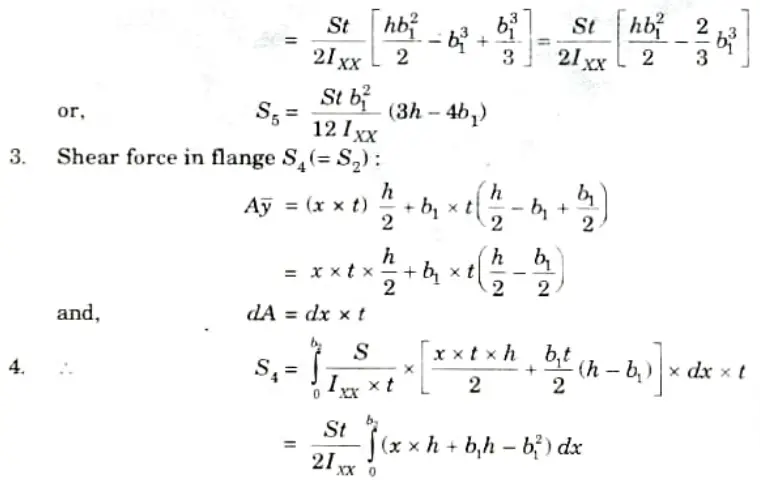
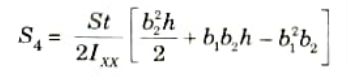
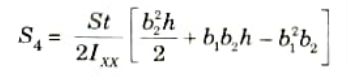
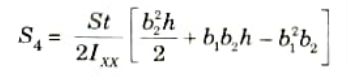
5. Taking moments about the centre of the web, we get
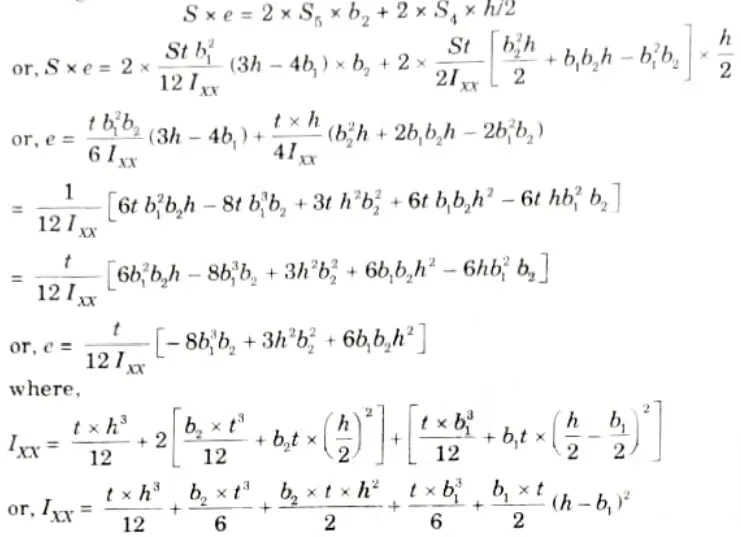
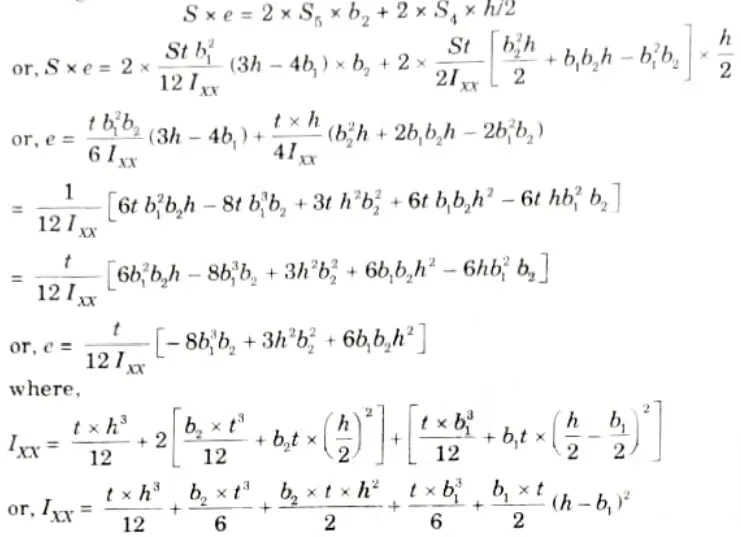
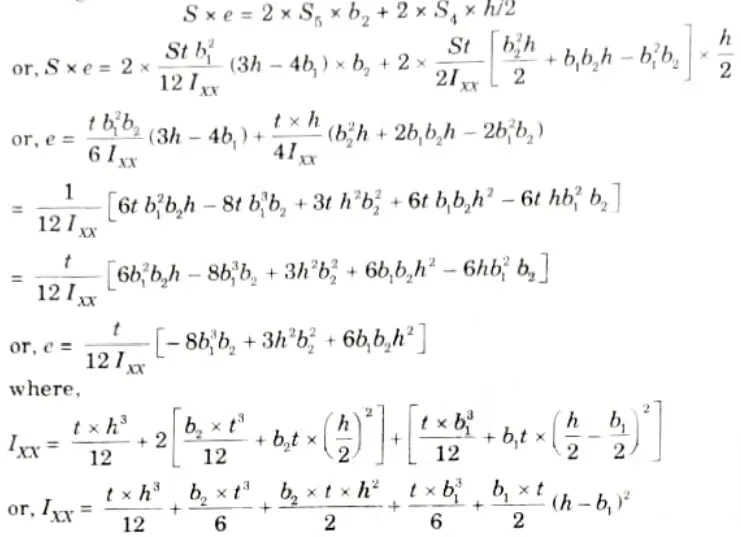
Q5. Define product of inertia and principal moment of inertia.
Ans. A. Product of Inertia:
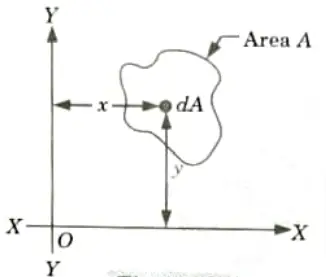
- 1. Consider a plane area or section (area A) as shown in the Fig.
- 2. Further consider an elemental area dA at a distance x and y from the Y-Y axis, and X-X axis respectively.
- 3. The 𝜮xydA is defined as the product of inertia of the cross-section. Mathematically,
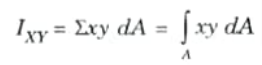
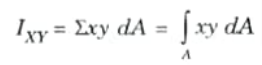
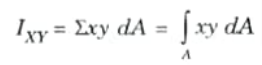
B. Principal Moment of Inertia:
- 1. If the two axes about which the product of inertia is found, are such that the product of inertia becomes zero, the two axes are then called the principal axes.
- 2. The moment of inertia about a principal axis is called the principal moment of inertia.





- 4 The values of lUU and IVV are given by:
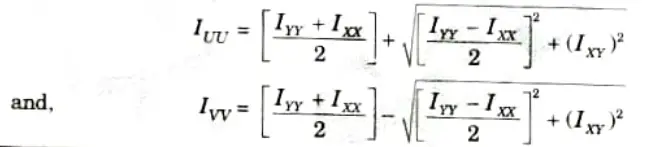
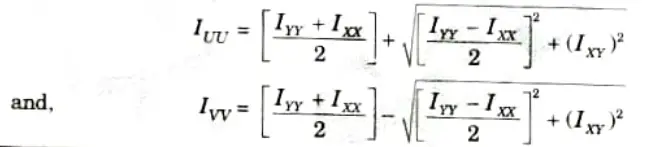
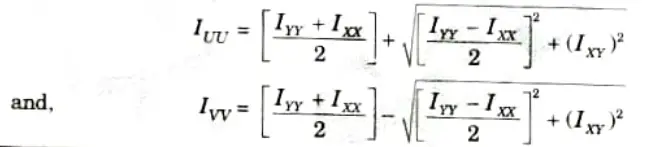
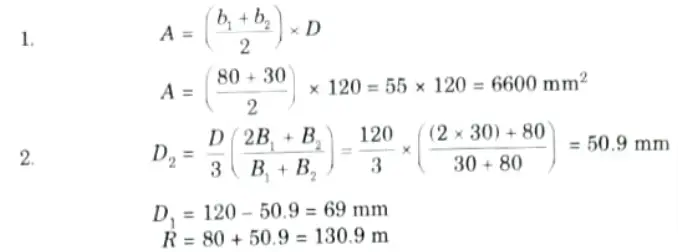
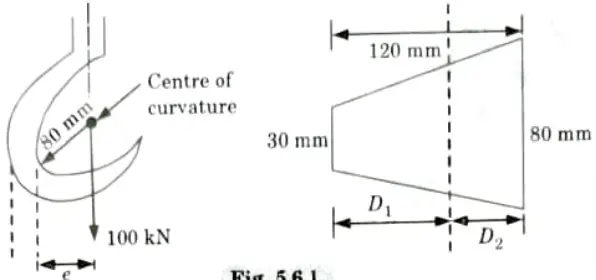
Q6. A crane hook is of trapezoidal c/s having inner side 80 mm, outer side 300 mm and depth 120 mm. The radius of curvature of inner side is 80 mm. If a load of 100 kN is applied to the hook passing through the centre of curvature, determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses at the critical cross section.
Ans. Given: B2 = 80 mm, B1 = 300 mm, D = 120 mm, W 100 kN
To Find: Maximum tensile stress and compressive stress.
Note: Hook problem can’t be solve with outer side = 300 mm, so we are solving it by using outer side = 30 mm.







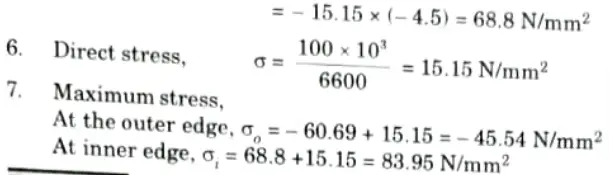
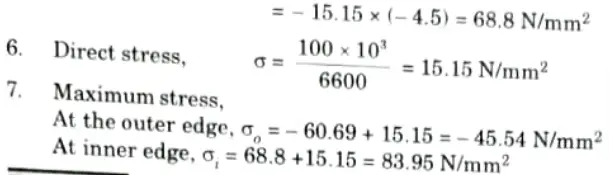
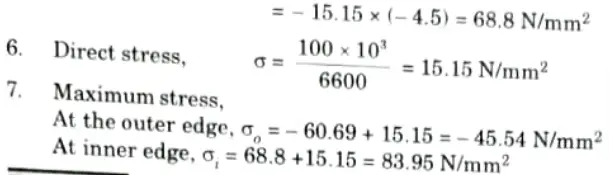



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Strength of Material Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Strength of Material Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |