With these key, recurring questions from Quantum Notes, you can improve your preparation for the Aktu Btech Power System-I exam. Improve your comprehension to perform better in exams! Unit-3 Elements of Management and Network Techniques
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Quantity Estimation and Construction Management: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Q1. What are the six main functions of management in undertaking a construction project ? Discuss.
Ans. Following are the six main functions of management in construction project:
- 1. Planning:
- i. Planning is the initial managerial task. The task involves developing a thorough plan to accomplish a certain organisational goal.
- ii. When you plan, you define the tasks that must be completed in order to attain the desired goals, specify how they should be carried out, and specify when and by whom they must be completed.
- iii. Planning is centred on achieving goals, thus understanding the mission and vision of the organization is necessary.
- 2. Organizing:
- i. Organization is the next task in the management cycle after planning. It involves putting together the physical, financial, and other resources that are already available and employing them to accomplish the organizational purpose.
- ii. It involves a specific pattern of power and responsibility distribution among group members, ensuring that the task is completed quickly, precisely, and economically to meet organizational goals.
- 3. Staffing:
- i. The process of staffing involves linking people with employment.
- ii. Management is in a position to determine the company’s workforce requirements at various levels of the organisation after organising all of the operations that need to be completed.
- iii. Management is responsible for taking the appropriate actions for personnel recruitment, selection, training, and placement.
- iv. Staffing is a constant process because both new hires and existing employees may depart the company.
- 4. Directing:
- i. Management is fundamentally the art of working with people to complete tasks. As a result, management is accountable for not only organizing and planning the business’s activities, but also leading its employees in achieving the company’s overall objective.
- ii. It is the most crucial management duty carried out by managers and supervisors at all organizational levels.
- iii. Any decision that is made must be put into practise, and in order to put a decision into practise, guidance is needed.
- 5. Co-ordinating:
- i. The coordination process entails aligning individual efforts with the objectives of the organisation.
- ii. Coordination is crucial to achieving harmony between individual efforts and the achievement of corporate goals.
- iii. Inefficient coordination between a business enterprise’s various tasks (such as production, sale, administration, etc.) might cause the enterprise to fail.
- 6. Controlling:
- i. Control involves ensuring that everything happens in accordance with the adopted plans, the instructions given, and the established principles.
- ii. It must identify flaws and mistakes in order to fix them and stop them from happening again.
- iii. It uses both human and non-human resources to function. Periodic checks and examinations are necessary to make sure that instructions are not misunderstood, laws are not broken, and objectives have not unintentionally changed or become obscured.
- iv. The control function follows the three basic steps:
- a. Establishing standards,
- b. Appraising performance, and
- c. Taking corrective actions.
Q2. In what respect does the functional organization differ from the line and staff organization ?
Ans.
| S. No. | Line and Staff Organization | Functional Organization |
| 1. | There are experts known as staff to advise and assist the line officials. | Functional managers are specialists in their respective areas |
| 2. | Line authority and staff people with advisory authority. | Functional or diagonal lines of authority are present. Wherever a function is done, the functional manager has authority over it. |
| 3. | Less discipline. | More discipline. |
| 4. | It is based upon planned specialization. | Based on high degree of specialization. |
| 5. | Unity of command observed to a great extent. | Since each subordinate receives instructions from both his line boss and the functional bosses, unity of command is not upheld. |
| 6. | Suitable for medium scale operations. | It is appropriate for large-scale activities where mastery of a particular field is essential. |
| 7. | Little costlier. | Very costly. |
Q3. Explain the different classification of scheduling in detail.
Ans. Following are the various types of scheduling:
- 1. Material Scheduling:
- i. It offers sophisticated scheduling capabilities for a variety of goods and products, including purchased raw materials, shops, spare parts, and consumables.
- ii. The scheduling of raw materials is carried out on the basis of daily production schedules for materials with short lead and cycle times, master production schedules for materials with longer lead times, and replenishment schedules for imported materials with lengthy lead/cycle times.
- 2. Labour Scheduling:
- i. Employee labour schedules are made, updated, and reviewed using it. An employee’s compensation is allocated to Oracle Grants Accounting, Oracle Projects, or Oracle General Ledger according to the terms of a labour schedule.
- ii. For each employee assignment, several labour schedules can be made.
- iii. Charge instructions for general ledger, projects, or grant accounting are included in each schedule’s schedule lines.
- iv. Each payroll is allocated in accordance with the schedule lines in force during the payroll distribution period. A worker is permitted an infinite number of schedule lines.
- 3. Equipment Scheduling:
- i. A wide range of equipment is required for a civil engineering project, so it is crucial for the engineer or contractor to understand what kind, how many, and when (precise dates) of each piece of equipment would be required.
- ii. In order to avoid work delays caused by equipment shortages, he can arrange them in a timely manner through recruiting, purchase, or other ways.
- 4. Financial Scheduling:
- i. It highlights the audited financial situation of the audited entity and is included in an audited annual report.
- ii. Another use of the phrase is the planning of key financial events’ quantities, not necessarily by date, in terms of anticipated receipts, payments, costs, etc.
Q4. Discuss the various types of civil engineering construction and their unique features.
Ans. Following are the various types of civil engineering construction:
- 1. Agricultural: Mostly used for affordable structures and other agricultural improvements. Barns, shelters for tools and animals, customized fencing, silos and elevators for storing goods, and water and supply drains such wells, tanks, and ditches are a few examples.
- 2. Residential: Houses, apartments, townhouses, and other smaller, low-rise dwelling and small office kinds fall within the category of residential building.
- 3. Commercial: Construction for private trade, commerce, and services is meant by this. Examples include office buildings, “big box stores,” malls, theaters, casinos, resorts, golf courses, and more substantial residential buildings like high-rise hotels.
- 4. Institutional: The requirements of the government and other public organizations fall under this area. Schools, police and fire stations, libraries, museums, dorms, research buildings, hospitals, transportation hubs, some military installations, and governmental structures are a few examples.
- 5. Industrial: Buildings and other manmade objects used for product production and storage, such as steel mills, oil refineries, platforms, manufacturing facilities, pipelines, and seaports.
- 6. Heavy Civil: The building of infrastructure for transportation, including highways, bridges, trains, tunnels, airports, and fortified military sites. Although the majority of other water-related infrastructure is categorized as environmental, dams are also included.
- 7. Environmental: Once a subset of heavy civil construction, environmental construction today deals only with initiatives that enhance the environment. Examples include sanitary and storm sewers, solid waste management, water and wastewater treatment facilities, and air pollution control.
Q5. What is resource allocation ? How is it achieved through network techniques ?
Ans. Resources Allocation:
- i. Resource allocation simply refers to determining the amount of resources that are needed for each project activity. The Histogram is created for this resource usage profile either based on the earliest start of each activity or the latest start of each activity.
- ii. Fitting activities into patterns of resource availability within allotted time frames is the main goal of the resource allocation process, which is accomplished in the following methods, namely.
1. Resource Smoothing: In this method, resource smoothing is used to modify some of the activity start periods based on their availability float to provide more or less consistent demand without changing the overall project duration.
Example:
- i. The project duration (6 days) is maintained, so the critical activity (10-40) will start earliest and finish in 6 days.
- ii. But the path (10 – 20 – 40) has 3 days float and path (10 – 30 – 40) has 2 days float.
- iii. The float period may be distributed among the activities lying on the path or the float may be distributed over one activity on the path.
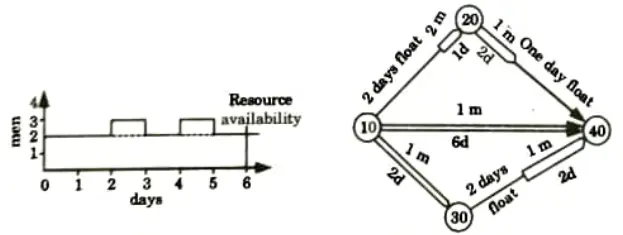


- iv. Various trials and errors are taken and finally the resource smoothing is obtained and is presented in the form of histogram and the corresponding network showing start time of each activity.
2. Resource Levelling:
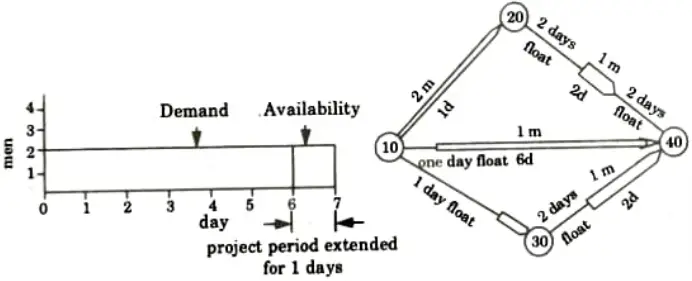
This method reschedules the activity start timings in such a way that the peak demand does not exceed the resource limit. If taking into account floats does not yield the desired results, resource levelling may be used to extend the project’s duration to a minimum extent.
Example:
- i. If the resource availability is quite limited. It cannot meet period by period variation.
- ii. Critical activity (10-40) is given one day float in the start time making project period of 7 days instead of 6 days.
- iii. Float of 4 days in the path of (10-20-40) has been totally used in the activity of (20 40) only such that the activity starts 2 days late and finishes 2 days earlier
- iv. 3 days float of the path (10- 30 – 40) has been distributed such that activity (10-30) starts 1 day late and activity (30-40) starts 2 days late.
- v. Consequently a uniform demand of 2 men each day agrees exactly with the availability of 2 men.


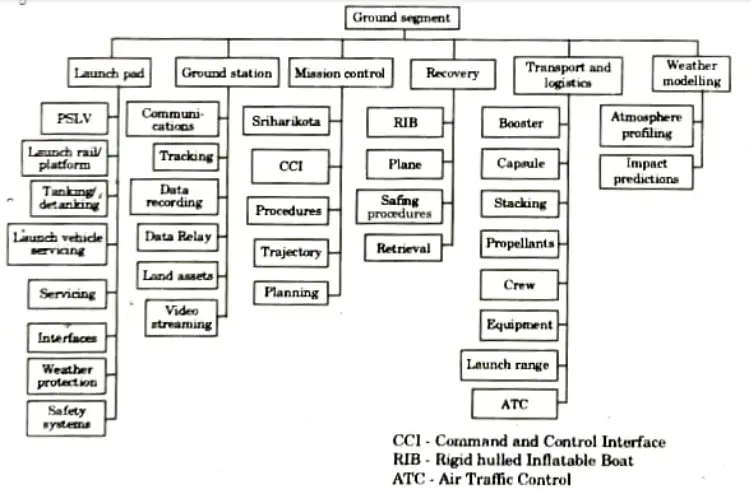
Q6. Explain work breakdown structure, prepare the work breakdown structure for the launching of a communication satellite. Assume the activities suitably.
Ans. A. Work Breakdown Structure:
- 1. The schedule or work breakdown structure is a visual depiction of the complete programme.
- 2. It is a preliminary diagram showing how all of the supporting goals interact and work together to enable the achievement of the main goal.
- 3. Complex projects with hundreds of events and activities require a breakdown structure like this more than other types of initiatives.
- 4. The top-down method to planning is used in work breakdown structures. Such a strategy guarantees that the entire project is thoroughly planned.
- 5. The task breakdown schedule helps the planner view the big picture of the project and supports objective identification.
- 6. The selection of project end items marks the highest level of the programme when the construction of the task breakdown structure begins.
- 7. The principal end products are then broken down into their sub-component portions (systems, subsystems, and components), and the component parts are then further broken down into their more specific units.
- 8. The work breakdown structure is further subdivided at progressively lower levels until the end item subdivisions are finally manageable for planning and controlling purposes.
- 9. Major work packages are then created from the end item subdivisions that exist at this level of the work breakdown structure (i.e., engineering. manufacturing, testing etc.).
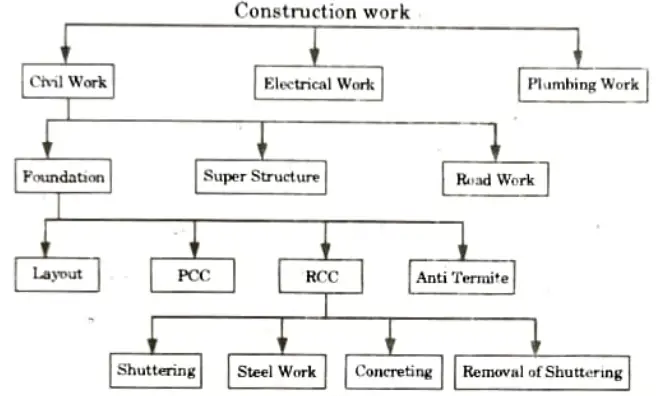


B. Breakdown Structure for the Launching of a Communication Satellite:





Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Quantity Estimation and Construction Management Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Quantity Estimation and Construction Management Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |