Analyse the B.Tech AKTU Quantum Book Short Question Notes on Power System Protection. Investigate protective relays and fault detection to provide stable and reliable power distribution systems.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Power System Protection: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 4th Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Protection Scheme (Short Question)
Q1. Define switchgear.
Ans. Switchgear is the apparatus used in an electrical power system for controlling, regulating, and switching the electrical circuit ON or OFF. Switchgear devices include switches, fuses, circuit breakers, isolators, relays, current and potential transformers, indicating instruments, lightning arresters, and control panels.
Q2. Discuss what you understand by stability of a protective relay.
Ans. Stability is the quality of protective relays that allows the system to remain inoperative and stable under specific conditions such as transitory, etc.
Q3. What do you understand by primary and backup protection ?
OR
Explain the terms primary and backup protection.
Ans. 1. Primary protection: It is used to protect any equipment by separating it from the system, or it is the protection that each zone provides to its elements. It serves as the first line of defense.
2. Backup protection: It is the one that kicks in when primary protection fails. It works after a time delay to allow the primary relay to operate.
Q4. Explain what you understand by pickup value of actuating quantity.
Ans. It is the value of actuating quantity at which the relay is on the verge of operation. These quantities can be current, voltage, frequency etc.
Q5. What are the desirable qualities of protective relaying ?
Ans.
- 1. Reliability
- 2. Speed and time
- 3. Sensitivity
- 4. Stability
- 5. Adequateness.
Q6. Explain the need of protective system.
Ans. 1. It is needed for the protection of short circuit condition arising in a power system.
2. To minimize damage to the system components involved in the failure.
Q7. Give the uses of summation transformer.
Ans. 1. Summation transformer is used for converting the three-phase quantities into a single phase quantity.
2. Summation transformer is used during unbalanced or faulty conditions in the system, in order to ensure the relay operates normally.
Q8. Write the different types of protection scheme.
Ans.
- 1. Overcurrent protection
- 2. Distance protection
- 3. Carrier-current protection
- 4. Differential protection
Q9. What is auto re-closing ?
Ans. About 90% of transmission line problems are transient in nature. It vanishes if the line circuit breakers are briefly tripped to isolate the line. By re-closing the circuit breakers, the line is re-energized. Auto re-closing refers to the automatic re-closing of circuit breakers.
Q10. Write the different types of potential transformer.
Ans. 1. Electromagnetic
2. Capacitor type
3. Opto electric type.
Q11. What is protection zone ?
Ans. 1. A protective zone covers one or at the most two elements of a power system.
2. The protective zones are designed in such a way that they cover the complete power system collectively, leaving no portion of the system exposed.
Q12. Draw the circuit diagram of basic protection scheme.
Ans.
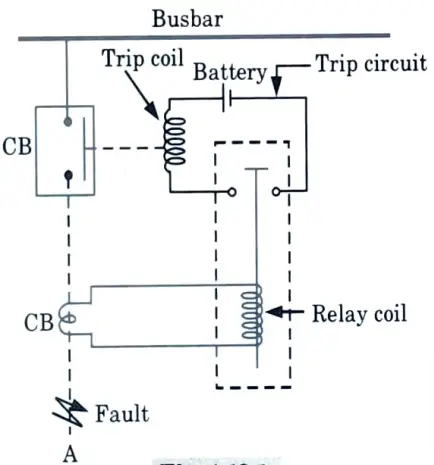


Unit-II: Relays (Short Question)
Q1. What do you understand by relay ?
Ans. A relay is an automatic device that allows an electrical circuit to be controlled indirectly and is guided by a change in the same or another circuit.
Q2. Name different types of electromagnetic attraction relays.
Ans. Electromagnetic relay is of two types :
- 1. Attracted armature relay: Attracted armature relays are of three types :
- i. Plunger relays
- ii. Balanced beam relay
- iii. Polarized relay.
- 2. Induction type relay: Induction relays are of two types:
- i. Induction disc type
- ii. Induction cup type.
Q3. Discuss problems related with the attracted armature type relays.
Ans.
- 1. The directional feature is absent.
- 2. The working can be affected by the transients.
- 3. Due to the presence of moving parts, the response is not very quick due to inertia of the parts, compared to modern static relays.
- 4. Due to moving parts, frequent maintenance is required. The bearing friction and contact troubles may exist.
Q4. Explain time setting of overcurrent relay.
Ans. The operating time of the relay is determined by the time setting. The relay operation time can be raised or lowered proportionally by adjusting the time setting.
Q5. Compare the time-current characteristics of very inverse relay with that of IDMT relay.
Ans.
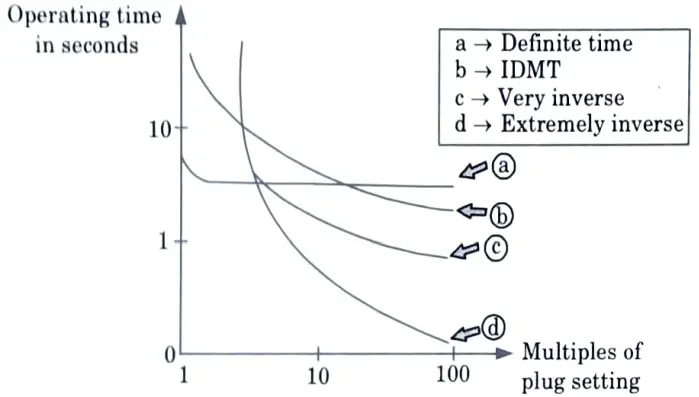


Q6. What is an amplitude comparator ?
Ans. It compares the magnitude of two quantities without considering its angles.
Q7. Briefly state the applications of over current relaying.
Ans. 1. It is used for the protection of distribution lines.
2. It is used for the protection of industrial motors.
Q8. Explain the operating principle of differential relay.
Ans. A differential relay is an overcurrent relay that works when the phasor difference of currents at the two ends of a protected element exceeds a certain value.
Q9. Write the different types of distance relay.
Ans. 1. Impedance relays
2. Reactance relays
3. MHO relays.
Q10. Explain briefly reactance relay characteristic of the R-X diagram.
Ans. The diagram in Fig, is shown in a plane having X-axis as R (resistance) while Y-axis as X (reactance), this plane is called R-X plane.
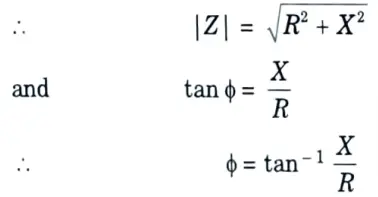
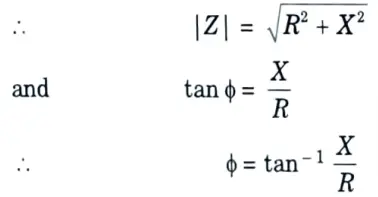
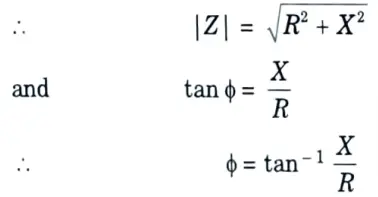
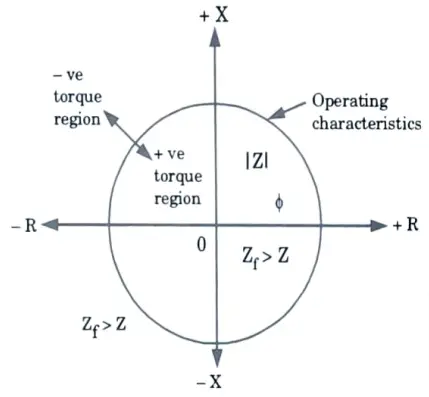


Q11. What are the advantages of distance relays ?
Ans. 1. Simpler to co-ordinate.
2. Less effect of fault levels and fault current magnitude.
3. Permits high line loading.
Q12. Write advantages of static relay.
Ans.
- 1. CT burden is less, so small CT can be employed.
- 2. Instantaneous reset can be achieved easily.
- 3. Accuracy in time-current characteristics.
- 4. Fast operation, absence of mechanical inertia and bouncing of contacts.
Q13. Write the limitations of static relays.
Ans.
- 1. These relays have lower short time overload capacity.
- 2. Additional DC supply is required for various transistor circuits.
- 3. Susceptible to the voltage fluctuations of transients.
- 4. Less robust.
Unit-III: Protection of Components (Short Question)
Q1. Write the different types of fault.
Ans. There are two types of fault
- 1. Symmetrical fault.
- 2. Unsymmetrical fault.
Q2. Classify the generator faults.
Ans. 1. Stator fault
2. Rotor fault
3. Abnormal running conditions.
Q3. What type of protective device is used for the protection of an alternator against overheating of the rotor?
Ans. Thermal relay or overcurrent relay.
Q4. What is magnetizing inrush current ?
Ans. When a power transformer is turned on, the primary can draw a very high peak current from the source. This is referred to as the transformer inrush current or magnetising inrush current.
Q5. What are the various faults possible in transformers ?
Ans.
- 1. Overheating
- 2. Winding faults
- 3. Open circuits
- 4. Through faults
- 5. Overfluxing.
Q6. What are the protective schemes provided in generator ?
Ans.
- i. Stator protection :
- 1. Percentage differential protection
- 2. Protection against stator inter-turn faults
- 3. Stator-overheating protection.
- ii. Rotor protection :
- 1. Field ground fault protection
- 2. Loss of excitation protection
- 3. Protection against rotor overheating because of unbalanced three phase stator currents.
Q7. What do you understand by the term under-reach’ ?
Ans. Failure of distance relay and within set distance is called under reach.
Q8. What is pilot wire ?
Ans. A pilot wire is a wire communication route that allows information to be exchanged between the two end terminals of a transmission system.
Q9. What do you understand by pilot wire protection scheme ?
Ans. 1. In normal operation, the two currents at both ends are equal, and pilot wires carry no current, keeping relays inactive.
2. When there is a defect, the two currents at the two ends are no longer the same, causing circulating current to flow via the pilot wires. This causes relays to trip, causing circuit breakers to trip and isolating the damaged area.
Q10. What are the advantages and limitations of Merz-Price voltage balance system ?
Ans.
- A. Advantages :
- 1. It can be used for parallel as well as ring main system.
- 2. It provides instantaneous protection to the ground faults.
- B. Disadvantages :
- 1. The CTs used must match accurately.
- 2. The pilot wires must be healthy without discontinuity.
Q11. What are the advantages of the Translay scheme ?
Ans. 1. Only two pilot wires are required.
2. The cost is very low.
Q12. List the various possible busbar faults.
Ans.
- 1. Failure of insulation due to material deterioration.
- 2. Failure of circuit breaker.
- 3. Earth fault due to failure of support insulator.
- 4. Flashover due to sustained excessive overvoltage.
- 5. Errors in the operation and maintenance of switchgear.
- 6. Earthquake and mechanical damage.
Q13. What are the schemes of busbar protection ?
Ans. 1. Frame leakage protection of busbar.
2. Circulating current protection of busbar.
3. High impedance differential protection of busbar.
Q14. Why bus bar protection is important in power system?
Ans. It is used to limit equipment damage and to remove bus bar faults prior to back up line protection.
Unit-IV: Circuit Breaking (Short Question)
Q1. What is the purpose of circuit breakers (switchgear) ?
Ans. A circuit breaker is an electrical switch that operates automatically to protect an electrical circuit from harm caused by excess current, which is often produced by an overload or short circuit. Its primary duty is to stop current flow when a defect is identified.
Q2. Define arc extinction.
OR
What is meant by the term arc quenching ?
Ans. Arc interruption (quenching) is the process of interrupting an arc’s route in order to extinguish it. Various methods such as air blast, high air pressure turbulence, and arc splitting are employed for arc interruption.
Q3. Discuss the energy balance theory of are interruption in circuit breaker.
Ans. The rate of heat creation between the circuit breaker contacts is slower than the rate of heat dissipation between the contacts. Thus, if the created heat can be removed at a high rate by cooling, extending, and splitting the arc, the arc can be extinguished.
Q4. What do you understand by recovery and restriking voltage ?
Ans. A. Recovery voltage: The recovery voltage is the power frequency rms voltage that occurs across the circuit breaker contacts after the transient oscillations have died out and the arc has been extinguished.
B. Restriking voltage: Restriking voltage is the transient voltage that emerges across the circuit breaker contacts at the instant of arc extinction.
Q5. Define RRRV.
Ans. It is the rate at which the restriking voltage rises in volts per microsecond. This represents the pace at which the transient recovery voltage increases.
Q6. What do you understand by the term “Current Chopping”?
Ans. 1. There are times when it is important to interrupt tiny inductive currents, such as when removing transformers with no load. A transformer’s no load current is nearly negligible power factor lagging.
2. This current is typically less than the breaker’s regular current rating. Interrupting such a current places a heavy load on the circuit breaker. This is referred to as current chopping.
Q7. Explain short time current rating of a circuit breaker.
Ans. 1. The short time current rating is determined by thermal and mechanical constraints. While another circuit breaker is clearing the fault, the circuit breaker must be capable of carrying short circuit current for a limited amount of time.
2. The rated short time current is the average of the total current that the circuit breaker can safely carry for the specified time period.
Q8. What do you understand by short line interruption ?
Ans. Short line interruption refers to a fault that occurs within a few kilometres to 10 km of the circuit breaker.
Q9. How the air break circuit breaker works ?
Ans. For air blast circuit breaker, the high resistance interruption theory is used. The length of the arc is expanded by utilising arc runners, which raise its resistance to the point when the voltage drop across the arc exceeds the supply voltage and the arc is extinguished.
Q10. Give the classification of circuit breakers based on medium used for arc quenching.
Ans.
| Type | Are Quenching Medium | Voltage range and Breaking capacity |
| Miniature circuit breaker | Air at atmospheric pressure | 400-600 V; for small current rating |
| Air-break circuit breaker | Air at atmospheric pressure | 400 V-11 kV; 5-750 MVA |
| Minimum oil breaker | Transformer oil circuit | 3.3 kV-220 kV: 150-25000 MVA |
| Vacuum circuit breaker | Vacuum | 3.3 kV-33 kV; 250-2000 MVA |
| SF6 circuit breaker | SF6 at 5 kg/cm2 pressure | 3.3-765 kV: 1000-50,000 MVA |
| Air blast circuit breaker | Compressed air at high pressure | 66 kV-1100 kV; 2500-60,000 MVA |
Q11. Why current chopping is not common in oil circuit breaker?
Ans. Current chopping is uncommon in oil circuit breakers since the arc extinguishing power in most oil circuit breakers is proportionate to the size of the interrupted current.
Q12. Write the advantages and disadvantages of air blast circuit breaker.
Ans.
- A. Advantages :
- 1. No power hazards are possible.
- 2. High speed operation is achieved.
- B. Disadvantages :
- 1. The maintenance of compressor and other related equipments is required.
- 2. There is possibility of air leakages at the pipe fittings.
Q13. Give the advantages and disadvantages of SF6 circuit breaker.
Ans.
- A. Advantages :
- 1. Problems connected with current chopping are minimum.
- 2. Size is smaller than conventional breaker of same rating.
- B. Disadvantages :
- 1. Sealing problem arises due to the type of construction.
- 2. Imperfect point leads to leakage of gas.
Q14. Write the advantages and disadvantages of minimum oil circuit breaker.
Ans.
- A. Advantages :
- 1. Small tank size and weight.
- 2. Low maintenance problem.
- B. Disadvantages :
- 1. Higher degree of carbonization as a result of less oil.
- 2. Difficulty in removing gases from the contact space in a timely manner.
Q15. What is resistance switching ?
Ans. 1. The interruption of low inductive currents, as well as the interruption of capacitive currents, causes significant voltage oscillations.
2. The installation of shunt resistance R across the circuit breaker contacts can prevent these high voltage surges during circuit interruption. Resistance switching is the name given to this phenomenon.
Q16. Define breaking capacity of a circuit breaker.
Ans. It is current (rms) that circuit breaker is capable of breaking at given recovery voltage and under specified conditions.
Unit-V: Modern Trends in Protection (Short Question)
Q1. What do you understand by electronic relay ?
Ans. The electronic relay is a sort of electronic switch that uses electronic components to open or close circuit contacts without any mechanical activity.
Q2. What are the advantages of electronic relay ?
Ans. 1. They require low maintenance.
2. The relay has fast response time.
Q3. Give the disadvantages of electronic relay.
Ans. 1. The power consumption in the electronic relay is very high.
2. The relay has the short lifespan.
Q4. Draw block diagram of static relay.
Ans.
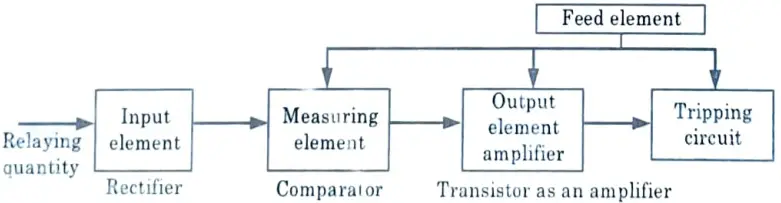


Q5. Write the basic elements of static relay.
Ans. The basic elements are :
- 1. Input element
- 2. Measuring element
- 3. Output element
- 4. Feed element.
Q6. What do you understand by phase comparator ?
Ans. A phase comparator compares two quantities by their phase angle, regardless of their size.
Q7. Define level detector in static relay.
Ans. 1. Level detector circuits are employed in static relays as a final stage before the circuit breaker’s trip coil circuit.
2. The level detector gets its name from the fact that the circuit operates abruptly when the input level exceeds a certain threshold.
Q8. Write the advantages of microprocessor based protective relaying scheme.
Ans. 1. It is very efficient and reliable.
2. It is very fast in operation.
3. Programmable in nature.
Q9. What is static relay ?
Ans. Static relays are those that do not have moving parts and rely on solid-state electronic components such as diodes, transistors, and so on.
Q10. What do you understand by reliability ?
Ans. 1. The primary characteristic of a protective relaying should be dependable. It denotes the relay system’s ability to work under predefined conditions.
2. Every component and circuit engaged in relay operation plays a vital function, and the dependability of a protective system is dependent on the reliability of numerous components such as circuit breakers, PTs, and so on.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Power System Protection Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Power System Protection Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |
