Learn about the B.Tech AKTU Quantum Book Short Question Notes on Mobile Computing. Dive into wireless communication concepts, mobile application development, and portable computer technologies.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Mobile Computing: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 4th Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Introduction Mobile Computing (Short Question)
Q1. Define the term mobile computing.
Ans. It is a computing environment that prioritises physical mobility. The computing environment is mobile and follows the user around. It enables a person to complete a task from any location and at any time using a computing device.
Q2. Write the names of mobile computing.
Ans. Some common names of mobile computing are:
- i. Nomadic computing
- ii. Anywhere, anytime information
- iii. Virtual home environment
- iv. Pervasive computing
- v. Global service portability
Q3. Discuss the term mobility.
Ans. The physical movement of both the user and the terminal is referred to as system mobility. There are two types of mobility:
- i. User mobility
- ii. Device mobility
Q4. Give a list of various mobile computing devices.
Ans.
- i. Portable computer
- ii. Tablet PC
- iii. PDA
- iv. Smart phone
- v. Wearable computer
Q5. Describe any one characteristic of mobile computing environment.
Ans. User mobility: The user can relocate from one physical location to another while still using the same service. For example, suppose a user relocates from Delhi to Mumbai and utilises the internet to access corporate applications in the same way he would at home or in the office.
Q6. Write down the goals of mobile computing.
Ans. Goals of mobile computing are:
- i. Improving customer service.
- ii. Attracting and maintaining a high quality workforce.
- iii. Provide real time analysis.
- iv. Reducing cycle time and speeding decision making.
Q7. What are the challenges involved in mobile computing ?
Ans. There are number of technical challenges that mobile computing faces and overcome them, some of these are:
- i. Wireless communication
- ii. Mobility
- iii. Portability
- iv. Low power
- v. Risk to data
- vi. Small user interface and storage capacity
Q8. Give a list of standards associated with mobile computing.
Ans. There are many standard bodies that generate and provide standards, some of them are:
- i. ISO
- ii. IETF
- iii. IEEE-SA
- iv. ITU
- v. W3C
- vi. ANSI
Q9. Discuss software issues in mobile computing.
Ans. Software issues in mobile computing are:
- i. Mobile systems have fewer resources than static parts.
- ii. Because of mobility, tracking of user calls and updating of user position must be done on a regular basis. Introduction
- iii. Mobile systems are location-aware. Mobile elements’ location is their point of attachment to the fixed network, which changes as they travel.
Q10. What are the applications of wireless communication ?
Ans.
- i. Security systems
- ii. Television remote control
- iii. Cellular telephone (phones and modems)
- iv. Wi-F
- v. Wireless energy transfer
Q11. Give a brief description of third generation (3G) technology.
Ans. 3G refers to a type of next-generation mobile network that operates at a higher frequency bandwidth and has a greater channel bandwidth. This allows 3G networks to offer extremely high data rates of up to 2 Mbps. The term 3G refers to the radio network and RF technology, not the switching core.
Q12. Define multiplexing as a technique.
Ans. Multiplexing is a communication system mechanism that specifies how multiple users can share a media with little or no disturbance. It can be of four types:
- i. Space division multiplexing
- ii. Frequency division multiplexing
- iii. Time division multiplexing
- iv. Code division multiplexing
Q13. What do you understand by the cellular system ?
Ans. A cellular system is a high-capacity mobile system in which the available frequency spectrum is partitioned into discrete channels that are assigned to geographic cells in groups that cover a cellular geographic service (GSA).
Q14. Write down the advantages of small cell.
Ans. There are several advantages of keeping small cells in the cellular systems, some of them are:
- i. Higher capacity
- ii. Less transmission power
- iii. Local interference only
- iv. Robustness
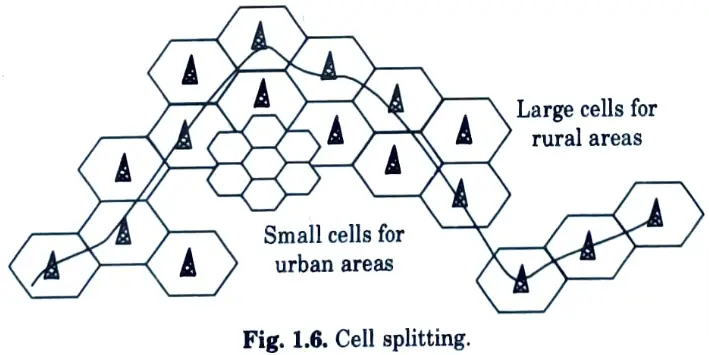
Q15. Discuss the method of cell splitting.
Ans. The concept of establishing entire systems with many small sections was unworkable due to economic considerations. To address this issue, system administrators devised the concept of cell splitting.
Q16. What do you understand by roaming ?
Ans. Most cellular service providers provide roaming, which allows users to access cellular service when travelling outside of their home service area. When an MS leaves their home region and comes within range of another cellular system, the ROAM indicator on their phone will illuminate to indicate that they are in range.
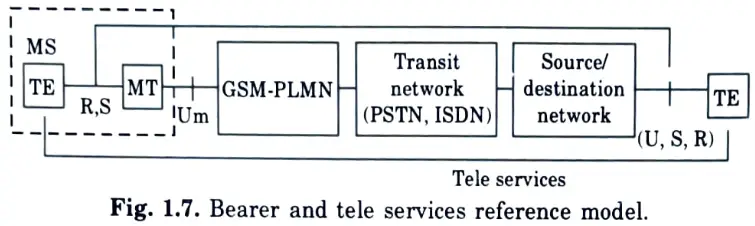
Q17. Describe the bearer services of GSM.
Ans. Bearer services enable synchronous or asynchronous data transport, both transparent and non-transparent. Transparent bearer services solely employ physical layer functions to transport data. Transparent bearer services do not attempt data recovery.
Q18. Briefly describe network and switching sub-systems (NSS).
Ans. It is the GSM system’s brain. It is in charge of connecting the wireless network to conventional public networks, performing handovers between different BSSs, and performing some additional activities such as roaming, localisation, and so on.
Q19. What are traffic channels ?
Ans. Traffic channels are used to carry the encoded user data or speech, in both uplink and downlink directions. Two basic categories of TCHs have been defined i.e.,
- i. Full rate TCH (TCH/F)
- ii. Halfrate TCH (TCHH)
Q20. What do you mean by mobile station roaming number (MSRN)?
Ans. The temporary address, such as TMSI, conceals the name and location of the subscriber. MSRN assists the HLR in locating a subscriber for an incoming call.
Q21. Define visitor location register.
Ans. The VLR is a temporary database store, and there is typically one VLR per MSC. This record contains information about mobile users who are now in the MSC of VLR service area.
Q22. What are the security services offered by GSM?
Ans.
- i. Access control and authentication
- ii. Confidentiality
- iii. Anonymity
- iv. Authentication
- v. Encryption
Q23. Define hard handoff.
Ans. A hard handoff occurs when the channel in the source cell is released first, followed by the channel in the target cell. As a result, the connection to the source is severed before the connection to the target is established.
Q24. Write down the various channel allocation methods used in cellular system.
Ans.
- i. Fixed channel allocation
- ii. Borrowing channel allocation
- iii. Dynamic channel allocation
- iv. Hybrid channel allocation
Q25. Write a short note on GPRS.
Ans. General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a mobile device-based packet-based communication service that allows data to be delivered and received through a mobile telephone network. It is a mobile data service that is available to GSM and IS-136 phone customers.
Q26. Represent diagrammatically the frequency division multiplexing (FDM).
Ans.
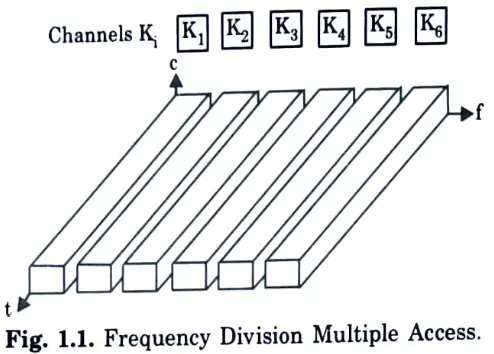


Q27. Depict the figure of wired network with wireless network.
Ans.
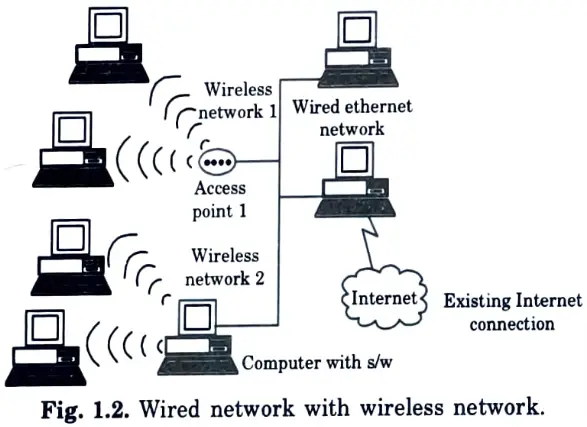


Q28. Show diagrammatically location updating in call routing in GSM?
Ans.
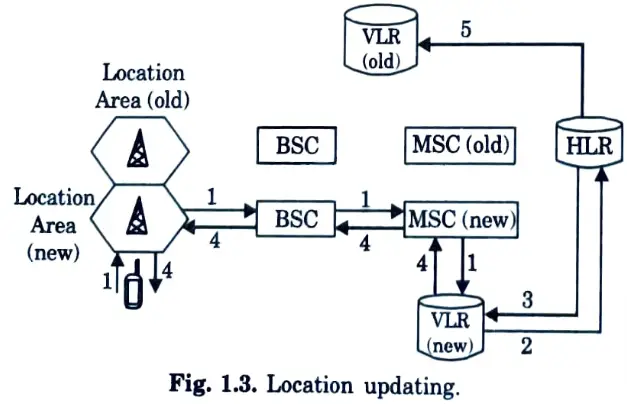


Q29. Give the architecture of GPRS.
Ans.
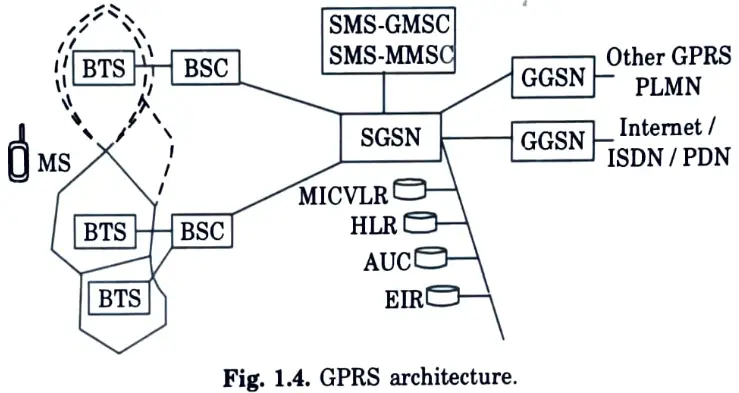


Q30. Depict the structure of time division multiplexing (TDM).
Ans.
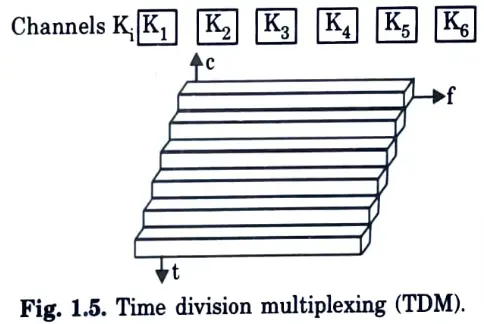


Q31. Draw the structure to show cell splitting is done ?
Ans.


Q32. Give the model of bearer and tele services reference model.
Ans.


Unit-II: Wireless Networking (Short Question)
Q1. Discuss wireless LAN.
Ans. A wireless LAN (WLAN) connects two or more devices utilising a wireless dispersed technique (for example, speed spectrum or OFDM radio) and typically provides access to the internet via an access point. This allows users to roam around inside a limited coverage area while remaining connected to the network.
Q2. What is wireless WAN ?
Ans. Wireless wide area network (WWAN) networks typically span huge outside regions. These networks can be used to connect business branch offices or to provide public internet access. They are often deployed in the 2.4 GHz frequency. Base station gateways, access points, and wireless bridging relays are common components of a conventional system.
Q3. Write down the advantages of wireless networking.
Ans. Advantages of wireless networking are:
- i. Using a wireless network, information might be transferred worldwide more efficiently and reliably.
- ii. It is a cheap and quick way to connect to the internet in nations and regions with weak telecom infrastructure.
Q4. Give the merits for wireless network.
Ans.
- i. Easy to set up Wireless Networking
- ii. Coverage
- iii. Unlimited users
- iv. Convenience, flexibility and efficiency
- v. Cost
Q5. What are the disadvantages of WLAN?
Ans. i. Quality of service
ii. Restrictions
iii. Safety and security
iv. Proprietary solutions
Q6. Describe briefly the robust transmission technology for WLAN.
Ans. WLANs function in more demanding settings than conventional networks. Hair dryers can interfere with radio transmission and many other electrical devices, such as vacuum cleaners, because they employ radio communication. In a typical office or factory environment, the WLAN transceivers cannot be adjusted for flawless transmission.
Q7. Give the disadvantages of radio transmission.
Ans. i. Radio transmission can interfere with other senders.
ii. Electrical devices can destroy data transmission via radio.
iii. Radio transmission is only permitted in certain frequency bands.
iv. Very limited ranges of license-free bands are available worldwide.
Q8. Describe the near and far terminal scenario
Ans. Terminals A and B send with the same transmission power in the near and distant terminal scenarios, however as the signal intensity diminishes proportionately to the square of the distance, terminal B’s signal drowns out terminal A’s signal. As a result, C will be unable to receive A’s communication.
Q9. Give a brief description of distribution system of IEEE 802.11 infrastructure.
Ans. The distribution system (DS) is the mechanism that allows one AP to communicate with another in order to exchange frames for stations in their BSSs, forward frames to follow mobile stations from one BSS to another, and exchange frames with the wired network.
Q10. Write short note on IEEE 802.11a.
Ans. Itis an extension to 802.11 that applies to wireless LAN’s and provide upto 54 Mbps in the 5 GHz band. 802.11a uses an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) encoding scheme. The protocol also supports data rates of 6, 9, 12, 18, 24,36 and 48 Mbps. The 802.11a specifications are applied to wireless ATM systems and are used to access hubs.
Q11. What do you understand by frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) ?
Ans. FHSS allows various networks to coexist in the same area by dividing them with distinct hopping sequences. FHSS PHY operates on the 2.4 GHz radio frequency spectrum, with data rates of 1 or 2 Mbps.
Q12. What are functions of MAC layer ?
Ans. Medium access control layer fulfills several functions such as:
- i. Control medium access.
- ii. Exchange of data packets without delay.
- iii. Provides asynchronous data services.
- iv. Time bounded service.
- v. Supports roaming authentication and power conservation.
- vi. Support broadcast and multicast.
Q13. What is bluetooth ?
Ans. Bluetooth is an open wireless technology standard for sharing data over short distances (through short wavelength radio transmission) between stationary and mobile devices, resulting in highly secure personal area networks (PANs).
Q14. Define piconct.
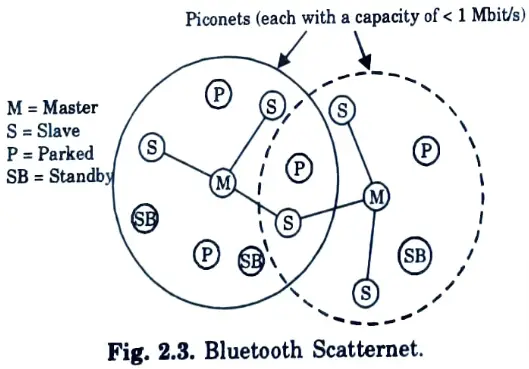
Ans. A piconet is a loosely connected network of Bluetooth devices. One device in the piconet serves as the master (M), while all other devices linked to it serve as slaves (S). Each piconet has one master and up to seven simultaneous slaves, implying that a master Bluetooth device can communicate with up to seven devices.
Q15. Write down the name of bluetooth layers.
Ans.
- i. Radio layer (Physical layer)
- ii. Baseband layer (MAC layer)
- iii. Link manager protocol layer (LMP layer)
- iv. Logical link control and adaption protocol layer (L2CAP layer)
- v. Service discovery protocol layer (SDP)
Q16. Give the functions of frame of IEEE 802.11.
Ans. The functions of frame are:
- i. Synchronization
- ii. Start frame delimiter: The 16-bits indicate the start of the frame and provide frame synchronization.
- iii. PLCP signaling field (PSF): This 4-bit field indicates the data rate of payload.
- iv. Header error check: This field contains the results of a calculated frame check sequence from the sending station.
Q17. What are different types of local channels of L2CAP ?
Ans. L2CAP provides three different types of local channels:
- i. Connectionless: These unidirectional channels are typically used for broadcast from master to its slaves.
- ii. Connection oriented: Each channel of this type is bidirectional and supports flow specifications for each direction.
- iii. Signaling: This type of logical channel is used for exchanging signaling messages between L2CAP entities.
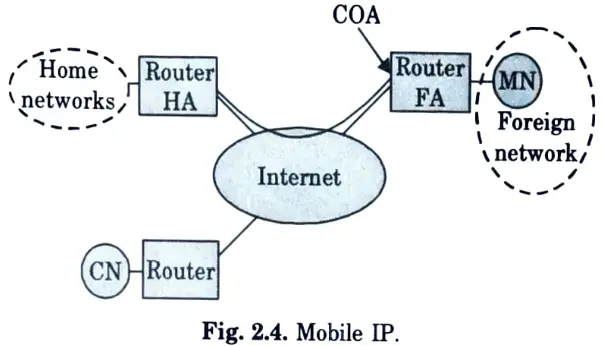
Q18. Describe briefly the mobile IP.
Ans. Mobile IP (or IP mobility) is a standard communication protocol that allows mobile device users to move from one network to another while keeping their IP address constant. This protocol allows IP datagrams to be routed on the internet regardless of their location.
Q19. Write a short note on wireless application protocol.
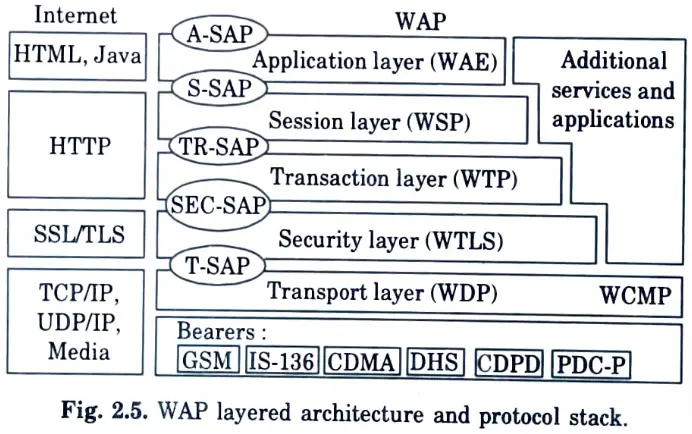
Ans. Wireless application protocol (WAP) connects mobile and wireless devices to the internet. WAP’s purpose is to offer internet content like web pages and phone services to digital cellular phones and other wireless terminals like laptops and PDAs.
Q20. Give a brief description of wireless session protocol (WSP).
Ans. Wireless session protocol (WSP) serves as an interface between the application layer and the transaction layer, providing all features required for wireless communications. It facilitates content sharing for client-server applications by initiating a session from client to server and then releasing the session in an orderly fashion.
Q21. What are the WAP applications ?
Ans. Some of the applications of WAP are as follows:
- i. Handling information of all types.
- ii. Access to e-mail and chat.
- iii. Weather information.
- iv. Information about currency rates.
- v. Online music support of WAP multimedia etc.
Q22. Give a list of major elements of the WAE model.
Ans. The major elements of the WAE model include:
- i. WAE user agents
- ii. Contents generators
- iii. Standard content encoding
- iv. Wireless telephony application (WTA)
Q23. Discuss the application layer of protocol stack of WAP.
Ans. The wireless application environment (WAE) is the topmost layer in the WAP stack. WAE provides an ecosystem for mobile operators and content creators by containing device specs and programming languages for content production. WAE defines a set of content formats that includes user agents for photos, phone book records, and calendar data.
Q24. What do you understand by tunneling ?
Ans. A tunnel connects a tunnel entrance and a tunnel endpoint by creating a virtual pipe for data packets. Packets entering a tunnel are forwarded within the tunnel and leave unmodified. Encapsulation is used to achieve tunnelling, or sending a packet through a tunnel.
Q25. Write down the list of entities of mobile IP.
Ans. Entities involved in mobile IP are as follows:
- i. Mobile node
- ii. Home agent
- iii. Foreign agent
- iv. Care of address (COA)
- v. Correspondent node
- vi. Foreign network
- vii. Home address
- viii. Tunnel
Q26. Illustrate diagrammatically the packet transmission in MACA.
Ans.
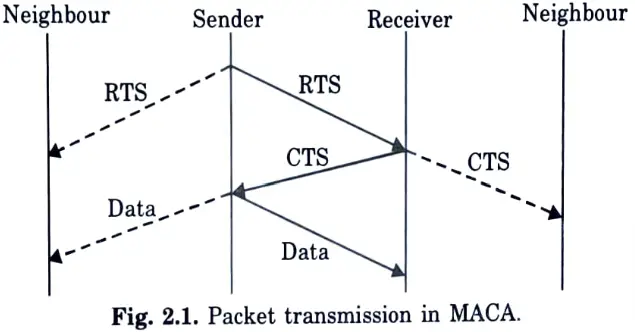


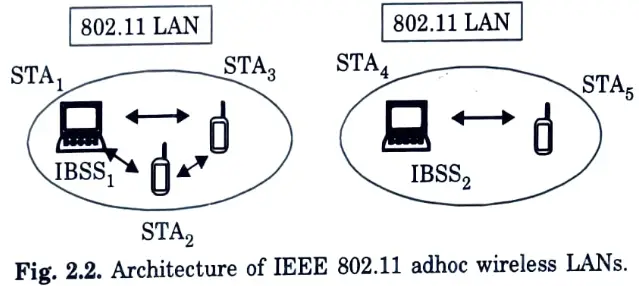
Q27. Represent the architecture of IEEE 802.11 adhoc wireless LANS.
Ans.


Q28. Draw the structure of bluetooth scatternet.
Ans.


Q29. Give the architecture of mobile IP.
Ans.


Q30. Illustrate the architecture of wireless application protocol (WAP).
Ans.


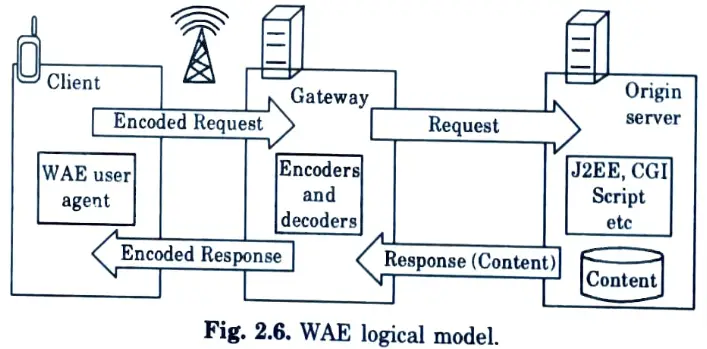
Q31. Represent the logical model of wireless application model.
Ans.


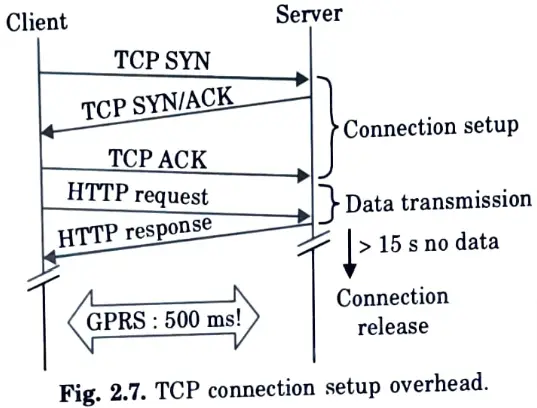
Q32. Illustrate with the help of diagram how the TCP works and gets connected.
Ans.


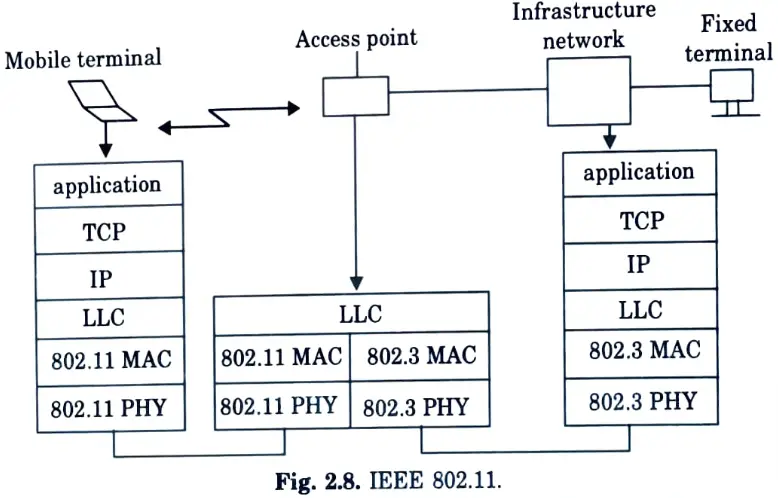
Q33. Sketch the protocol architecture of IEEE 802.11.
Ans.


Unit-III: Data Management Issues (Short Question)
Q1. Define data management.
Ans. Data management is the practise of treating data as a useful resource for an organisation or business. According to the Association for Data Management, data management is the process of establishing and executing data-related designs, practises, and procedures on a regular basis.
Q2. What are the various issues in data management ?
Ans. There are various issues in data management:
- i. Mobility (location management)
- ii. Wireless medium
- iii. Cache consistency and data replication
- iv. Transaction management
- v. Portability of mobile devices
- vi. Wireless security issues
Q3. Describe caching in brief.
Ans. Caching is a widely used strategy for enhancing the performance and availability of data access. Caching frequently accessed data in the local storage of mobile nodes can reduce energy and bandwidth consumption, as well as query latency.
Q4. What are the advantages of mobile database ?
Ans. Advantages of mobile database are:
- i. Portability of service.
- ii. Access for multiple parties.
- iii. Mobile backup and data recovery.
Q5. Discuss data replication in brief.
Ans. Data replication creates and manages numerous copies of data at one or more locations, allowing a corporation to exchange corporate data across its organisation. It acts as a backup mechanism in the event of a system failure. It is a strategy used in conventional dispersed environments to improve system performance and boost data availability.
Q6. Define asynchronous replication.
Ans. Asynchronous replication is a method of copying data between databases (or file systems) in which the system being duplicated does not wait for data to be recorded on the duplicate system before continuing. It has the advantage of being faster.
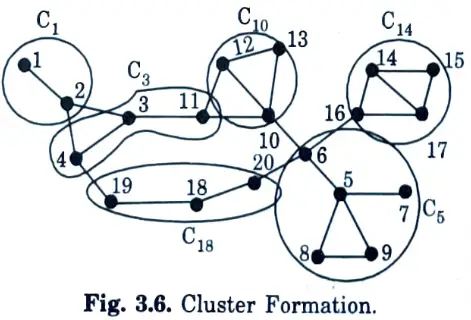
Q7. What is clustering ?
Ans. The process of organising data objects into groups whose members are related in some way is known as clustering. A cluster is thus a group of items that are similar in kind and those that are dissimilar in type and belong to other clusters.
Q8. Write down the requirements of clustering
Ans. The main requirements that a clustering algorithm should satisfy are:
- i. Minimal requirements for domain knowledge to determine input parameters.
- ii. High dimensionality.
- iii. Scalability.
- iv. Discovering clusters with arbitrary shape.
- v. Dealing with different types of attributes.
Q9. Give the application areas of clustering.
Ans. Application areas of clustering are:
- i. Biology
- ii. Library
- iii. Marketing
- iv. City planning
- v. WWW
Q10. Give the need for mobile database.
Ans. i. Mobile users must be able to work without a wireless connection due to poor or even non-existent connections.
ii. Application must provide significant interactivity.
iii. Bandwidth must be conserved.
iv. Limited life of power supply.
Q11. Discuss adaptive clustering briefly.
Ans. Adaptive clustering operates on quick and deployable wireless network infrastructure. It was completely asynchronous and used a distributed architecture. Multihopping is one of the characteristics of adaptive clustering.
Q12. Give the objective of clustering algorithm.
Ans. The clustering algorithm’s goal is to divide the network into numerous clusters. The optimal cluster size is determined by the tradeoff between channel spatial reuse and delay minimization. The radio transmission power determines cluster size.
Q13. What is CODA file system ?
Ans. Constant data availability (CODA) is the successor of AFS and offers two different types of replication: server replication and caching on clients. CODA is successor of AFS which was designed to support the entire CMU community
Q14. How does the communication in CODA works?
Ans. CODA communicates using remote procedure call (RPC) and RPC2 technologies. Each time a remote procedure is invoked, the RPC2 client code creates a new thread that sends an invocation request to the server and waits for an answer.
Q15. Write short note on file identifiers in CODA.
Ans. The shared file collection is replicated and dispersed among multiple vice servers. CODA has both physical and logical volume. A logical volume includes a replicated physical volume as well as a replicated volume identification. The file system is given a 96-bit file identification by CODA.
Q16. What are the features of CODA ?
Ans. CODA has following features:
- i. It is freely available under a liberal license.
- ii. Server replication
- iii. Good scalability
- iv. Security model for authentication, encryption and access control.
Q17. Describe the disconnected operations in CODA.
Ans. Disconnected operation is a style of operation that allows a client to continue accessing vital data even while the shared data repository is temporarily unavailable. In a file system, disconnected operation is indeed practical, efficient, and usable. The key premise is that data caching, which is commonly used to improve performance, may also be utilised to improve availability.
Q18. Give the factors responsible for implementation of hoarding.
Ans. i. Disconnections and reconnections are often unpredictable.
ii. Cache space is finite so the availability of less critical objects may have to be sacrificed in favour of more eritical objects.
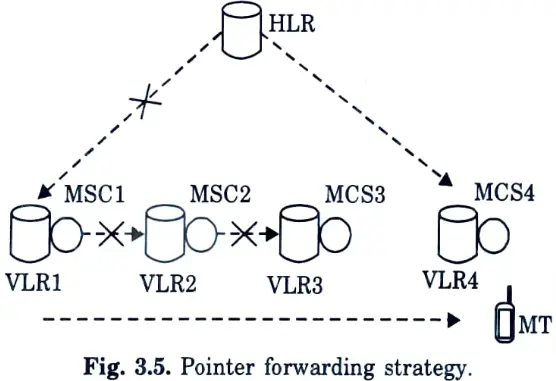
Q20. Write the basic principle of pointer forwarding strategy.
Ans. The primary idea behind the pointer forwarding technique is that instead of reporting a position change to the HLR every time the MT moves to a different VLR’s area.
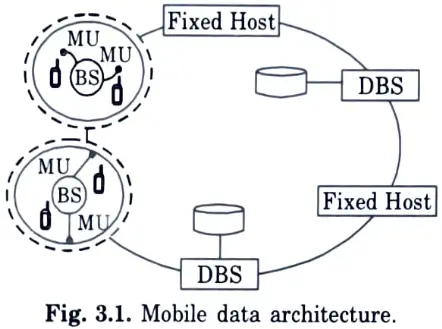
Q21. Depict the architecture of mobile database.
Ans.


Q22. Illustrate the structure of the successor of Andrew File System, i.e., Constant Data Availability (CODA).
Ans.
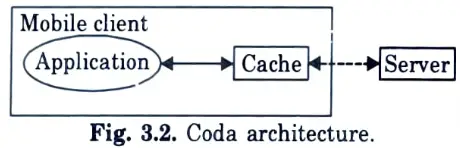


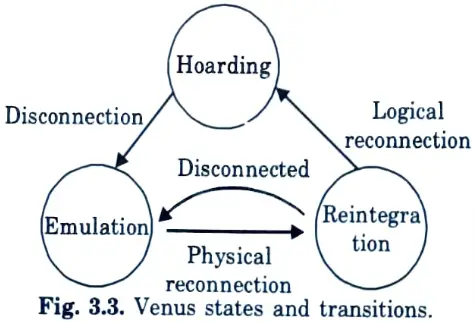
Q23. Represent diagrammatically the various venus states for disconnected operation.
Ans.


Q24. Draw the overall organization of Andrew File System (AFS).
Ans.



Q25. Give the structure by showing the basic idea of the pointer forwarding strategy.
Ans.


Q26. Illustrate the structure of formation of clusters.
Ans.


Q27. Depict the structure of Multihopping where when base station B fails.
Ans.
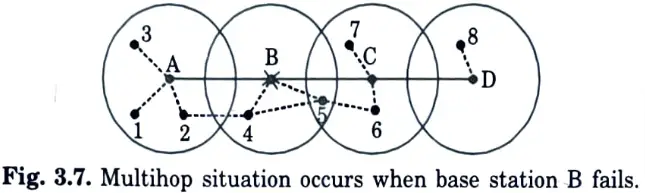


Unit-IV: Mobile Agents Computing (Short Question)
Q1. Define mobile agent.
Ans. An agent is someone whose duty it is to represent or handle the affairs of others. Software agents are programmes that conduct specific tasks on the user’s behalf. A mobile agent is a piece of computer software and data that can transfer from one computer to another and continue running on the destination computer.
Q2. What are the properties of mobile agents ?
Ans. Mobile agents have the following unique properties:
- i. Adaptive learning: Mobile agent can learn from experience and adapt themselves to the environment.
- ii. Autonomy: Mobile agents can take some decisions on its own.
- iii. Mobility: Mobility agents have the ability to move from one host to another in the network.
Q3. Give a brief description about protocol encapsulation.
Ans. Protocols allow distributed system components to interact and coordinate their operations. Protocols evolve throughout time, and new features such as improved security may be added to the protocols. Mobile agents, which can encapsulate the protocol, provide a solution to this difficulty.
Q4. Give a list of advantages of mobile agents.
Ans.
- i. Reduction in network load.
- ii. Overcome network latency.
- iii. Protocol encapsulation.
- iv. Asynchronous and autonomous execution.
- v. Fault tolerance.
Q5. Write down the limitations of mobile agents.
Ans. i. The biggest disadvantage of mobile agents is the security risk associated with their use.
ii. Mobile agent tools are still in their infancy and may have undiscovered security issues and vulnerabilities.
iii. Mobile agents are a young technology, with most agent building tools in alpha or beta stages.
Q6. What are the events in the life cycle of a mobile agent ?
Ans. A mobile agent experiences the following events in its life cycle:
- i. Creation
- ii. Dispatch
- iii. Cloning
- iv. Deactivation
- v. Disposal
- vi. Communication
Q7. Discuss flexibility as a characteristic of mobile agent.
Ans. Flexibility can be defined to include the following properties:
- i. Responsive: It refers to an agent ability to perceive its environment and respond in a timely fashion to changes that occur in it.
- ii. Proactive: Agents are able to exhibit goal driven behaviour.
- iii. Social: Agents should be able to interact with other agents.
Q8. Write down the various applications of mobile agents.
Ans. Applications of mobile agents are:
- i. Parallel computing
- ii. Data collection
- iii. E-commerce
- iv. Mobile computing
Q9. Describe briefly agent TCL as a mobile agent system.
Ans. Agent TCL provides an agent execution environment in which agents written in secure languages such as safe TCL and Java can travel across the network and communicate with local and remote agents. The agent TCL system is a transportable agent support model.
Q10. List down the classes into which threats to security can be categorized.
Ans. i. Disclosure of information.
ii. Denial of service.
iii. Corruption of information.
Q11. What are types of threat ?
Ans.
- i. Threats stemming from an agent attacking an agent platform.
- ii. An agent platform attacking an agent.
- iii. An agent attacking another agent on agent platform.
- iv. Other entities attacking the agent system.
Q12. Define masquerading.
Ans. Masquerading occurs when an unauthorised agent assumes the identity of another agent. In order to acquire access to services and resources to which it is not entitled, the masquerading agent may pretend as an authorised agent.
Q13. What is eavesdropping?
Ans. The eavesdropping threat entails intercepting and monitoring private communications. Agent platforms can monitor not only communications but also every instruction implemented by the agent, all unencrypted or public data it brings to the platform, and all subsequent data generated on the platform when eavesdropping.
Q14. Write down the security requirements in mobile agent.
Ans. i. Confidentiality
ii. Integrity
iii. Accountability
iv. Availability
Q15. Define signed code.
Ans. Signing code or other things with a digital signature is a fundamental strategy for safeguarding an agent system. A digital signature confirms the validity of a thing, its origin, and its integrity.
Q16. What are the types of attack on static assets ?
Ans.
- i. Virus and worms
- ii. Denial of service
- iii. Intrusion
- iv. Replay attack
- v. Buffer overflow attack
Q17. Discuss briefly symmetric key cryptography.
Ans. The same key is used for both encryption and decryption in symmetric key cryptography. This is analogous to a lock that uses the same key to lock and unlock. It is also referred to as a secret key algorithm.
Q18. Define the term transaction.
Ans. A transaction is a modelling abstraction that unites many database accesses as an atomic unit for recovery, concurrency, and consistency. A mobile transaction is a distributed transaction in which some computations are performed on mobile hosts and others on non-mobile hosts.
Q19. What do you understand by transaction processing ?
Ans. Transaction processing is the division of information processing into discrete and unseen operations known as transactions. It is intended to keep databases in a known, consistent state by ensuring that all interdependent operations on the database are either completed successfully or cancelled effectively.
Q20. Give the features of transaction processing.
Ans. Features of transaction processing are:
- i. Rapid response
- ii. Reliability
- iii. Inflexibility
- iv. Controlled processing
Q21. Discuss mobile transaction in brief.
Ans. A mobile transaction is a distributed transaction in which some computations are performed on mobile hosts and others on non-mobile hosts.
The utilisation of wireless media, as well as the mobility of data users and providers, have a variety of effects on transaction processing.
Q22. Describe Kangaroo mobile transaction model.
Ans. i. It captured both data and the movement of mobile unit.
ii. The model is based on a split transaction and enforces the ACID properties.
iii. Upon initiation of a Kangaroo transaction, a base station creates a JT for its execution.
iv. A KT, when initiate by a MU (mobile unit), the initial BS immediately creates a JT with a unique identity and become responsible for its execution.
Q23. Write down the issue concerned to transaction management.
Ans. Issues of transaction processing in mobile computing environment are:
- i. Data consistency and concurrency control.
- ii. Infrastructure requirements.
- iii. Communication costs.
- iv. Relocation mechanism and user profiles.
- v. Scalability.
Q24. Illustrate diagrammatically the life cycle of mobile agent.
Ans.


Q25. Give the architecture of the agent TCL system model.
Ans.



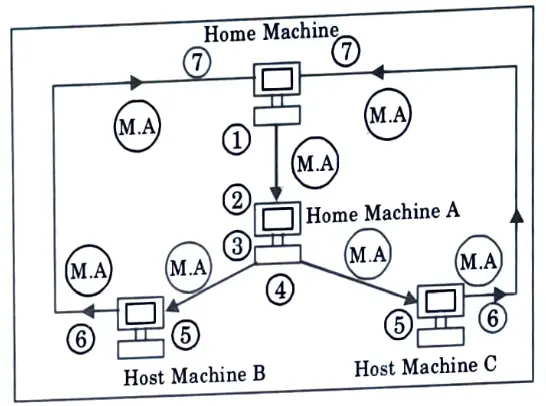
Q26. Represent with diagram how transaction processing can be done in mobile computing environment.
Ans.


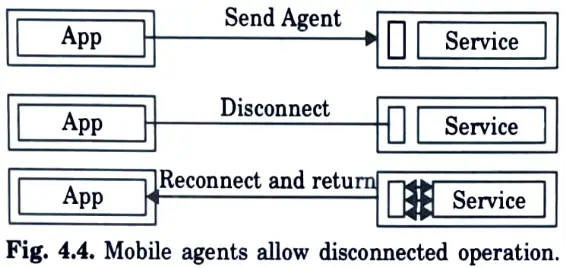
Q27. Draw how the mobile agents execute asynchronously and autonomously.
Ans.


Q28. Illustrate the structure of the Tromoso and Cornell moving agents (TACOMA).
Ans.
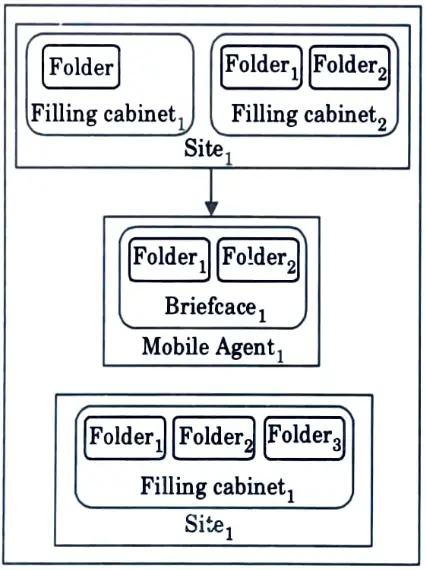


Q29. Depict the agent system model and show only the important aspects that affect security.
Ans.
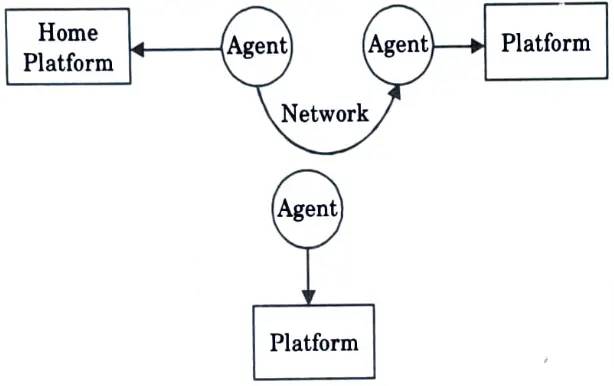


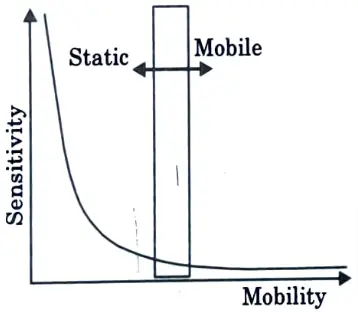
Q30. Represent graphically the degree of mobility v/s sensitivity of agent.
Ans.


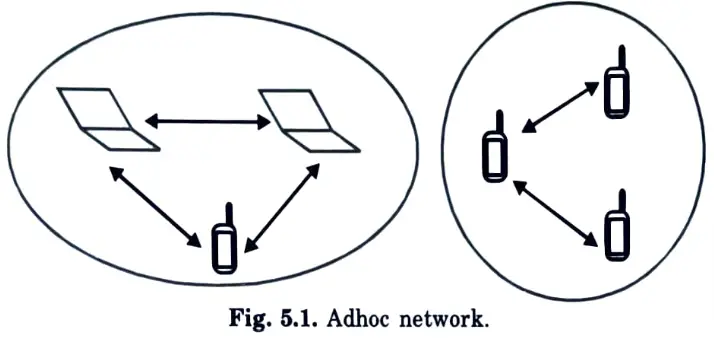
Unit-V: Adhoc Networks (Short Question)
Q1. Define adhoc network.
Ans. An adhoc network is a wireless peer-to-peer network that sends data from one computer to another without the use of a control base station (access point). They are primarily formed amongst individuals and are not connected to the internet.
Q2. Write down the characteristics of adhoc network.
Ans. i. An adhoc network comes up together when needed.
ii. It grew out of packet radio network.
iii. The wireless range is smaller.
iv. Becomes more vulnerable for intrusion.
Q3. Classify the types of wireless adhoc network.
Ans. There are three types of wireless adhoc network:
- i. Mobile adhoc network (MANETs)
- ii. Wireless mesh network (WMN)
- iii. Wireless sensor network (WSN)
Q4. Discuss wireless mesh network briefly.
Ans. A wireless mesh network (WMN) is a communication network made up of radio nodes organised in a mesh topology. It is made up of mesh clients, mesh routers, and mesh gateways. Mesh clients are typically laptops, cell phones, and other wireless devices, whereas mesh routers transfer traffic to and from gateways that may be connected to the internet.
Q5. Write short note on MANET.
Ans. MANET is a wireless ad hoc network of mobile nodes that may be configured on the go. Each node has a router or switch that is linked by a wireless connection. The connection union has an arbitrary topology. The MANET organisation is dependent on the nodes’ location, connectivity, service discovery capability, and ability to find and route messages using nearest node or adjacent nodes.
Q6. Give the applications of MANET.
Ans. i. Conference room attendees sharing documents and other information via laptops and portable computers.
ii. Armed forces establishing a tactical network in unfamiliar territory to facilitate communications and the dissemination of situational awareness information.
iii. Small sensor devices placed in animals and other strategic areas to monitor habitats and environmental conditions collectively.
Q7. List down the problems associated with MANET.
Ans. Some of the problems in MANET are:
- i. Dynamic topologies.
- ii. Bandwidth constrained, variable capacity links.
- iii. Energy constrained operation.
Q8. What are the characteristics of MANET?
Ans. Characteristics of MANET are:
- i. Flexibility.
- ii. Direct communication through nearby node and neighbour discovery.
- iii. Peer-to-peer connectivity.
- iv. No access point requirement.
- v. Data caching, saving and aggregation.
- vi. Computations decentralization.
Q9. Describe flexibility of MANETs as its characteristic.
Ans. MANET allows for the rapid construction of networks. When establishing a new network, the only requirement is to offer a new set of nodes with limited wireless communication range. A node has limited capabilities, in that it can only connect to nodes that are nearby. As a result, it consumes little electricity.
Q10. Write down the need of routing protocols.
Ans. i. Adhoc network nodes are mobile, and the structure of their linkages is dynamic.
ii. When confronted with a highly dynamic connectivity architecture, existing protocols exhibit the least acceptable behaviour.
Q11. Give the goals of adhoc routing protocol.
Ans. i. The protocol should adapt quickly to topology changes.
ii. The protocol should provide multiple routes from the source to destination.
iii. The protocol should require small amount of messages / time to coverage.
Q12. Classify adhoc protocols into classes.
Ans. The adhoc protocols can be divided into three classes:
- i. Proactive routing or table-driven routing protocol.
- ii. Reactive routing or on-demand routing protocol.
- iii. Hybrid (pro-active/reactive).
Q13. Give a list of adhoc protocols that follows the proactive routing protocol.
Ans.
- i. Destination sequence distance vector routing protocol
- ii. Wireless routing protocols
- iii. Fisheye state routing
- iv. Global state routing
- v. Hierarchical state routing
Q14. Compare table-driven and on-demand routing protocols.
Ans.
| S. No. | Table Driven | On-demand |
| 1. | Attempts to keep information consistent and up to date from each node to every other node in the network. | A route is built only when required. |
| 2. | Constant propagation of routing information periodically even when topology change does not occur. | There are no regular updates. Control information is not conveyed unless the topology changes. |
Q15. What is GSR protocol ?
Ans. Link state routing is the foundation of global state routing. It uses the idea of link state routing and enhances it by preventing routing message flooding.
Q16. Discuss Fisheye state routing (FSR) briefly.
Ans. FSR is an enhancement to GSR (both use the link state protocol). The high size of GSR update messages wastes a significant amount of network capacity. This technique was developed to minimise the amount of data needed to depict graphical data.
Q17. Give the advantages of FSR.
Ans. i. FSR is suitable for large and highly network environment.
ii. It is robust to host mobility.
iii. Reduce routing and update traffic.
Q18. Write down the primary objectives of AODV protocol.
Ans. i. To broadcast discovery packets only when necessary.
ii. To distinguish between local connectivity management and general topology maintenance.
iii. To disseminate information about changes in local connectivity to those neighbouring mobile nodes that are likely to need the information.
Q19. What is temporally ordered routing algorithm (TORA) ?
Ans. The TORA routing algorithm is a source-initiated on-demand routing method. It is a highly adaptive, efficient, and scalable distributed routing algorithm that is based on the link reversal notion. This protocol is primarily intended to reduce the impact of topology changes.
Q20. Give the types of packets used in TORA protocol.
Ans. i. QRY packets, used for creating routes.
ii. Update (UDP) packets, used for both creating and maintaining routes.
iii. CLR packets, used for erasing routes.
Q21. Give the list of phases of TORA protocol.
Ans. The TORA protocol has mainly three phases:
- i. Route discovery or route creation.
- ii. Route maintenance.
- iii. Route erasure.
Q22. Define hybrid routing.
Ans. Hybrid routing protocols combine the benefits of both table-driven and on-demand routing techniques. It employs distance vectors for more accurate metrics in determining the optimum paths to destination networks and reports routing information only when the network’s topology changes.
Q23. Write down the list of issues of QOS routing in adhoc networks.
Ans. i. Dynamic varying network topology
ii. Scarce resources
iii. Power limitations
iv. Insecure medium
Q24. What are the objectives of QOS?
Ans. i. To meet Q0S requirements of end users.
ii. To optimize network resource usage.
iii. To gracefully degrade network performance under heavy load.
Q25. Draw the structure how the adhoc network is created.
Ans.


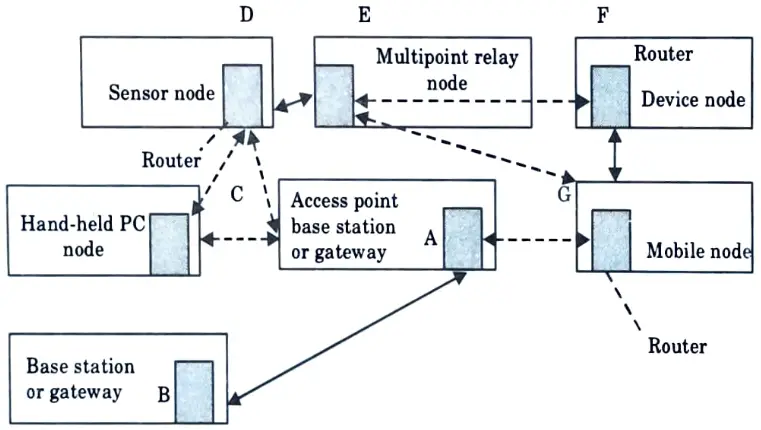
Q26. Depict the architecture of the mobile adhoc network (MANET).
Ans.


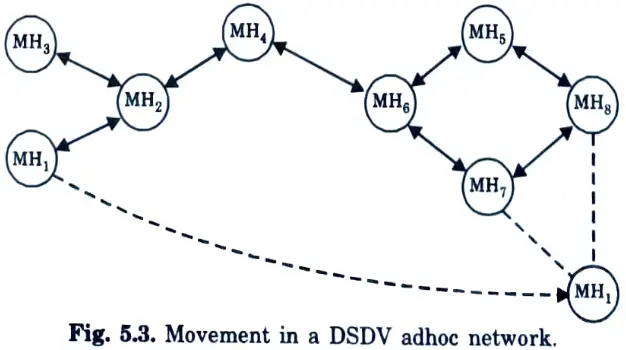
Q27. Represent the structure of the movement of mobile hosts in DSDV adhoc network.
Ans.





Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Mobile Computing Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Mobile Computing Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |
