Learn about the Industrial Engineering B.Tech. AKTU Quantum Book Short Question Notes. For effective resource utilisation and productivity increase in industries, investigate optimisation strategies, process management, and system design.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Industrial Engineering: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Overview of Industrial Engineering (Short Question)
Q1. Define production system.
Ans. A production system is a set of actions that allows for the development of value.
Q2. Define productivity and formula to measure it.
Ans. Productivity is defined as the ratio of actual output (production) to what it takes to produce it (inputs).
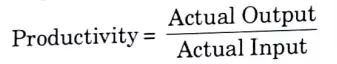
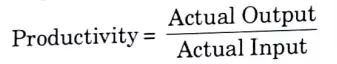
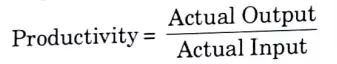
Q3. What are the factors affecting productivity.
Ans. Factors affecting productivity are as follows:
- 1. Human resources,
- 2. Technology and capital investment,
- 3. Government regulation,
- 4. Product and system design, and
- 5. Energy and equipment.
Q4. What are the factors to be considered for selection of site?
Ans. Factors to be considered for selection of site are as follows:
- 1. Raw material availability.
- 2. Proximity to market.
- 3. Labour availability.
- 4. Transport and communication.
- 5. Energy (Fuel/Power).
Q5. What are the objectives of good plant layout?
Ans. Objectives of good plant layout are as follows:
- 1. Integrate the production centres.
- 2. Reduce materials handling.
- 3. Effective space utilization.
- 4. Flexibility.
- 5. Worker convenience and job satisfaction.
Q6. What are the types of production system?
Ans. Types of production system are as follows:
- 1. Mass production system.
- 2. Process production system.
- 3. Job production or project type production system, and
- 4. Batch production system.
Q7. Define intermittent and continuous production system.
Ans. Intermittent production system: With this technique, instead of producing items for stock, they are made specifically to fill customer requests.
Continuous production system: The items are produced under this system for the stock levels rather than for specific orders.
Q8. Differentiate between mass production and job production system.
Ans.
| S. No. | Mass production System | Job Production System |
| 1. | Items are created in enormous quantities under the mass production technique. | Products are manufactured in line with client demand in a job production system. |
| 2. | For example: Newspaper and magazines etc. | For example: Ship building, dam construction etc. |
Q9. Define FMS.
Ans. A highly automated GT machine cell is referred to as a flexible manufacturing system (FMS). It is made up of a number of processing workstations (often CNC machine tools) coupled by an automated material handling and storage system, all of which are under the supervision of a distributed computer system.
Q10. What do you mean by material building?
Ans. The movement, packing, and storage of substance in any form are all part of the art and science of material building. Throughout the manufacturing process, it describes the movement of materials from the storeroom to the machine and from one machine to the next.
Q11. Write the types of plant layout.
Ans. Types of plant layout are as follows:
- 1. Process layout,
- 2. Product layout,
- 3. Combination of process and product, and
- 4. Fixed position layout.
Q12. Write any five important uses of productivity measurement?
Ans. Five important uses of productivity measurement are as follows:
- 1. Productivity boosts production.
- 2. Increased productivity lowers the cost per piece.
- 3. Reduced prices enhance product demand, which in turn boosts business profits.
- 4. A company that makes more money can pay out a larger dividend to shareholders.
- 5. It boosts exports and a nation’s foreign exchange reserves.
Q13. What are the types of materials handling equipment?
Ans. Types of material handling equipments are as follows:
- 1. Lifting and lowering devices.
- 2. Transporting devices.
- 3. Combination devices.
Q14. What are different types of productivity measurement?
Ans. Types of productivity measurement are as follows:
- 1. Land productivity,
- 2. Material productivity,
- 3. Labour productivity,
- 4. Machine productivity, and
- 5. Capital productivity.
Q15. Define product liability.
Ans. Product liability is the term used to describe the responsibility of any or all parties involved in the production of a product for harm brought on by that product.
Q16. What do you mean by operations management?
Ans. Operations management may be summed up as a methodical approach to dealing with all the problems associated with the transformation process that turns some inputs into outputs that are useful and generate income for businesses.
Q17. What is Group Technology (GT)?
Ans. Group technology is a manufacturing strategy in which related items are recognised and put together to capitalise on their similarity in design and production.
Unit-II: Production Planning and Control (Short Question)
Q1. Write the steps involved in production planning and control.
Ans. Steps involved in production planning and control are as follows:
- 1. Forecasting.
- 2. Order writing.
- 3. Product design.
- 4. Routing.
- 5. Leading and scheduling.
- 6. Machine loading.
- 7. Dispatching.
Q2. What do you mean by forecasting?
Ans. Forecasting is the process of estimating the type, volume, and quality of upcoming activities, such as sales, etc. Prediction is a promise made by the sales department and each of its divisions regarding anticipated sales. It becomes a benchmark against which the sales team’s performance will be evaluated.
Q3. Define causal forecasting?
Ans. Causal forecasting makes the assumption that some underlying factors or factors will determine the future.
Q4. What is regression analysis?
Ans. We can use regression analysis to find the relationship between an interest variable and one or more independent variables. For examples, consumption is a function of income.
Q5. What are the methods of aggregate scheduling?
Ans. Methods of aggregate scheduling are as follows:
- 1. Graphical or charting methods.
- 2. Mathematical approaches.
Q6. Write the objectives of MRP.
Ans. Objectives of MRP are as follows:
- 1. Inventory reduction.
- 2. Avoid delays.
- 3. Realistic commitments.
- 4. Increased efficiency.
Q7. Define MRP.
Ans. The master schedule for final products is transformed into a detailed schedule for the raw materials and components utilized in the end products using the computational process known as material requirements planning (MRP).
Q8. What do you mean by MRP II?
Ans. A computer-based system for planning, scheduling, and managing the materials, resources, and supporting activities required to satisfy the master production schedule is known as manufacturing resources planning (MRP).
Q9. Define network scheduling.
Ans. The planning and scheduling of major projects in the industries of construction, maintenance, fabrication, purchasing, computer system installation, research and development design, etc. is done using a technique called network scheduling.
Q10. Define critical path.
Ans. The critical path is the order in which crucial tasks must be completed in a network. The critical path, which defines the shortest amount of time needed to complete the project, is the longest path in the network between the beginning and ending events.
Q11. What are the main features of critical path?
Ans. The critical path has two main features:
- 1. If the project must be shorter, some of the associated activities must as well. If the crucial path is not shortened first, applying more resources to other tasks won’t produce the desired outcome.
- 2. The anticipated completion of the entire project will fully represent the deviation in actual performance from the planned activity duration time.
Q12. What do you mean by project evaluation and review technique (PERT)?
Ans. PERT is the fundamental network technique that entails project planning, monitoring, and control. It is used in the organization and management of a broad range of responsibilities.
Q13. What is optimistic time?
Ans. The shortest amount of time that can be used to complete the task is the optimistic time. The premise is that everything runs very smoothly. It is denoted by t0.
Q14. Define pessimistic time.
Ans. The worst-case scenario shows how long it might take to complete the task. It is the amount of time an action would require if terrible luck were to strike, and it is the worst time estimate.
Q15. What are the requirements for application of PERT?
Ans. Requirements for application of PERT are as follows:
- 1. PERT can be used for project management that is mostly novel or repetitive in nature.
- 2. PERT is typically used for very big, complicated, and specialized projects that have a significant number of interconnected tasks that must be completed either simultaneously or sequentially.
Unit-III: Engineering Economy and Inventory Control (Short Question)
Q1. Define depreciation.
Ans. Depreciation is the measurement of how quickly a depreciable asset loses value due to use, the passage of time, or technological and market developments.
Q2. What are the factors affecting depreciation.
Ans. Factors affecting depreciation are as follows:
- 1. Acquisition cost.
- 2. Estimated life.
- 3. Estimated salvage value.
- 4. Selection of depreciation method.
Q3. Write the assumption in break-even analysis.
Ans. Assumption in break-even analysis are as follows:
- 1. All the units produced are sold in the market.
- 2. Fixed cost remains fixed for any production volume.
- 3. Variable cost increase is linear.
- 4. Selling prices will remain constant at all sales levels.
- 5. Production and sale quantities are equal.
Q4. What do you mean by inventory control?
Ans. Controlling inventory entails ensuring that the requested items are always available to the various departments as needed, in the required amount and quality to fulfil production expectations.
Q5. What is ABC analysis?
Ans. ABC analysis is a method of classifying the content according to the quantity consumed and its relative worth. In the inventory control method ABC (Always Better Control) A category is made up of pricey merchandise, which may be scarce but is exceedingly expensive.
Q6. Why does queuing problem arise?
Ans. Queuing problem arise because:
- 1. There is an excessive amount of waiting time or not enough service facilities due to the excessive demand on the amenities.
- 2. There is either an excessive amount of idle facility time or a surplus of facilities due to a lack of sufficient demand.
Q7. Describe the queuing system.
Ans. A queuing system can be completely described by:
- 1. The input,
- 2. The service mechanism,
- 3. The queue discipline, and
- 4. Customer’s behaviour.
Q8. Define the following terms:
a. Transient state.
b. Steady state.
Ans. a. Transient State: When a system’s operational features rely on time, it is said to be in a transitory state.
b. Steady state: When the behaviour of the system ceases to depend on the passage of time, a steady state condition is said to be in place.
Q9. Give the operating characteristics of a queuing system.
Ans. Some of the operating characteristics of a queuing system are as follows:
- 1. Expected number of customers in the system.
- 2. Expected number of customer in the queue.
- 3. Expected waiting time in the system.
- 4. Expected waiting time in queue.
- 5. The server utilization factor.
Q10. Define the following factors:
a. Queue length.
b. System length.
Ans. a. Queue length: The typical number of clients waiting in line for assistance. This does not include the client being serviced.
b. System length: The usual number of clients in the system, including both those waiting and those being attended to.
Q11. Define the following factors:
a. Waiting time in the queue.
b. Total time in the system.
Ans. a. Waiting Time in the Queue: The typical length of time a consumer must wait in line before receiving service.
b. Total Time in the System: The typical length of time a consumer spends using the system overall, starting when they enter it and ending when they leave it. It is assumed to be the sum of the waiting and service times.
Q12. What are the limitations of queuing model?
Ans. Limitations of queuing model are as follows:
- 1. There is typically not much room for clients to wait.
- 2. The arrival rate could vary by state.
- 3. The customer population might not be limitless, and the first-come, first-served rule might not always apply.
Q13. In which situation the queuing theory is best suited?
Ans. The best applications of queueing theory occur when there is only one random arrival channel and a consistent service time.
Q14. Give the applications of queuing models.
Ans. Applications of queuing models are as follows:
- 1. Scheduling of mechanical transport fleets.
- 2. Scheduling distribution of scarce war material.
- 3. Scheduling of jobs in production control.
- 4. Minimizing of congestion due to traffic delay at tool booths.
- 5. Solution of inventory control problems.
Unit-IV: Work System Design (Short Question)
Q1. Define work study.
Ans. Work study is a method for analyzing human activity and identifying the elements that influence a worker’s accuracy and productivity. Work study aids in completing a task or job as effectively as feasible.
Q2. What is the scope of work study?
Ans. Applications for work study in businesses include marketing (sales and distribution), offices, retail spaces, building construction, transportation, hospitals, the military, and agriculture, among others.
Q3. Define method study.
Ans. Method study is the systematic recording and critical analysis of existing and planned work practises with the goal of creating and implementing simpler, more efficient workflows while also lowering costs.
Q4. Define work measurement.
Ans. Eliminating ineffective time and establishing time standards for a job are two goals of work measurement. Work measurement is a method for determining how long it takes a skilled worker to complete a given task at a specific level of performance.
Q5. What are the objectives of motion study?
Ans. Objectives of motion study are as follows:
- 1. Removal of unwanted motions.
- 2. Increase the efficiency of all activities.
- 3. Improve the proper motion of activities.
- 4. Enhancing the material handling process.
Q6. What do you mean by standard time?
Ans. The total amount of time required to execute the task with standard performance is known as standard time.
Q7. Define the term ergonomics.
Ans. In order to address issues that arise from the interaction between people and machines, the field of ergonomics applies anatomical, physiological, and psychological concepts.
Q8. What are the methods of job evaluation?
Ans. Methods of job evaluation are as follows:
- 1. Ranking method.
- 2. Job classification/grading method.
- 3. Factor comparison.
Q9. Define merit rating.
Ans. Merit rating is the systematic assessment of an employee’s performance in relation to the work criteria and determining if a candidate is qualified for positions with greater responsibility.
Q10. What are the objectives of merit rating?
Ans. Objectives of merit rating are as follows:
- 1. Merit ratings boost output and lessen tension between the employer and employee.
- 2. Identifies a person’s advantages and disadvantages.
- 3. Encourages rivalry and the drive for advancement.
- 4. Allows management to assess the need for training.
Q11. What is the importance of wages and incentives?
Ans. Incentives and wages have an impact on management-employee relations. It contributes significantly to economic efficiency, production rate growth, and peacekeeping.
Q12. What is standardization?
Ans. By combining the knowledge of all people who are interested in the issue, standardization is the temporary crystallization of the most acceptable solution to a recurrent problem. It is subject to review and revision by general agreement, and everyone should adhere to it.
Q13. Define simplification.
Ans. Reducing the variety of products made is the process of simplification (known as variety reduction). It is worried about the narrowing of the product variety, as well as the assemblies, parts, and design.
Q14. What is diversification?
Ans. The addition of new products or the launch of a well-established product into a new market are examples of diversification. Because consumers occasionally like variation in product kind, size, colour, and number, this tends to make manufacturing processes more complex.
Q15. Discuss value analysis.
Ans. Value analysis (VA) focuses on already-available products. A team must examine and assess an existing product in order to cut costs, enhance functionality, or do both.
Unit-V: Operational Analysis (Short Question)
Q1. Define LPP.
Ans. According to the generic LPP, an objective function, which is a linear function of variables, must be optimized while being subject to a set of constraints or restrictions, which can be either linear equations or inequalities.
Q2. What are the fundamental conditions of simple methods?
Ans. The basis of the simple method consists of two fundamental conditions:
- 1. The feasibility condition, and
- 2. The optimality condition.
Q3. What is basic feasible solution?
Ans. It is a straightforward answer that also complies with the prohibitions against negativity. All variables in a basic feasible solution are ≥ 0. Every extreme point of the convex set of viable solutions is a basic feasible solution of the set of constraints, and every extreme point is a basic feasible solution to the problem.
Q4. What is sensitivity analysis?
Ans. The investigation that deals with changes in the optimal solution due to changes in the parameter (aij, bi and cj) is called sensitivity analysis.
Q5. Define duality.
Ans. Each linear programming problem has a twin that can be thought of as the primal counterpart to it, with the remaining problems being the dual counterparts.
Q6. What do you mean by assignment problem?
Ans. It is a unique instance of the transportation problem where the goal is to allocate a certain amount of resources to a certain number of activities while keeping costs to a minimum.
Q7. Explain the reduced matrix method?
Ans. The idea of opportunity cost is the foundation of the reduce matrix approach. Opportunity costs highlight the relative drawbacks of allocating resources to a task rather than choosing the most advantageous or economical option. Making the best assignment will be attainable if we can shrink the cost matrix to the point where each row and column has at least one zero.
Q8. Write the methods of solving assignment problem.
Ans. An assignment problem can be solved using the following four methods:
- 1. Complete enumeration method,
- 2. Transportation method,
- 3. Simplex method, and
- 4. Hungarian method.
Q9. Why is an activity assigned to a resource with zero opportunity cost?
Ans. While completing an assignment, use a resource with no opportunity cost since the goal is to reduce the overall cost.
Q10. How is a maximization assignment problem transformed into a minimization problem?
Ans. By deducting each profit matrix member from the highest element of the matrix, the maximization assignment problem is converted into a minimization problem.
Q11. What is the purpose of a dummy row or column in an assignment problem?
Ans. In an assignment problem, a dummy row or column is used to achieve balance between all activities and all resources.
Q12. Define transportation problem.
Ans. The challenge in transportation is to move varying quantities of a single homogenous commodity that are initially held at diverse origins to numerous destinations while keeping the overall transportation cost to a minimum.
Q13. What are the methods of finding an optimal solution?
Ans. Methods of finding an optimal solution of the transportation problem will consist of two main steps:
- 1. To find an initial basic feasible solution.
- 2. To find the best answer by incrementally improving the first, workable basic solution until there is no more room for cost-savings in the transportation system.
Q14. What are the methods of finding an initial basic feasible solution in transportation problem?
Ans. Methods of finding an initial basic feasible solution in transportation problem are as follows:
- 1. North-west corner method,
- 2. Least-cost method, and
- 3. Vogel’s approximation method.
Q15. Define simulation.
Ans. Simulation is the portrayal of reality using a model or other tool that will behave realistically under a specific set of circumstances.
Q16. What are the types of simulation?
Ans. Simulation is mainly of two types:
- 1. Analogue simulation, and
- 2. Computer simulation.
Q17. Give the advantages of simulation.
Ans. Advantages of simulation are as follows:
- 1. Simulation techniques are simpler to use than strictly analytical techniques.
- 2. The understanding of a system acquired via planning and running the simulation.
- 3. It helps us to evaluate potential risks associated with new policies prior to their implementation.
Q18. Give any three limitations of simulation.
Ans. Limitations of simulation are as follows:
- 1. Simulation creates a method for evaluating solutions, but it does not create the strategies for solving problems.
- 2. Not all circumstances can be assessed using simulation. Only doubtful simulations are taken into account.
- 3. Simulation is a time-consuming exercise.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Industrial Engineering Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Industrial Engineering Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |
4 thoughts on “Quantum Book Industrial Engineering KME-503 Aktu Btech Short Question”