Aktu Btech Quantum Notes will help you be more prepared for the Geotechnical Engineering test. Your route to success lies in these vital, in-depth resources that address the most frequently asked issues. Improve your knowledge right now! Unit-2 Soil Hydraulics
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Geotechnical Engineering: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Q1. A granular soil deposit is 7 m deep over an impermeable layer. The ground water table is 4 m below the ground surface. The deposit has a zone of capillary rise of 1.2 m with a saturation of 50 %. Plot the variation of total stress, pore water pressure and effective stress with the depth of deposit, e = 0.6 and G = 2.65.
Ans. Given: Depth of soil deposit 7m, Depth of water table = 4 m, Specific gravity, G= 2.65, Degree of saturation, S = 50 * Void ratio, e = 0.6, Capillary rise = 1.2 m
To Find: Plot the variation of
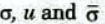
with the depth of deposit.
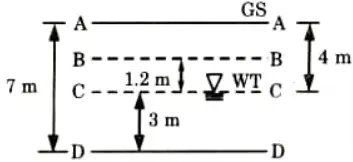


1. Bulk unit weight,



4. At Level A-A :
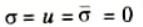
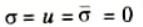
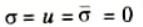
5. At Level B-B (Upper Side):
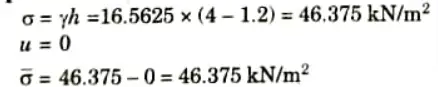
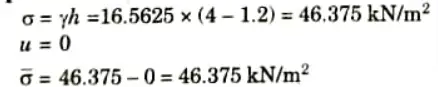
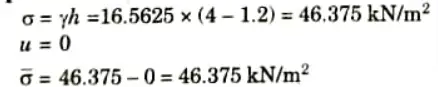
6. At Level B-B (Bottom Side):
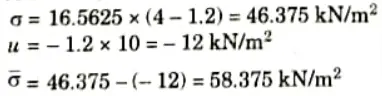
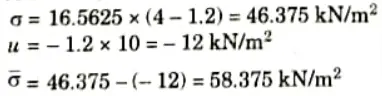
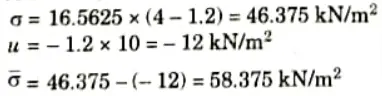
7. At Level C-C:
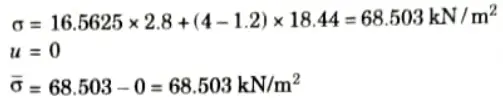
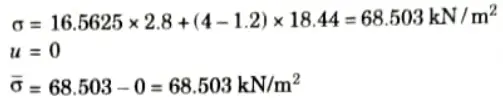
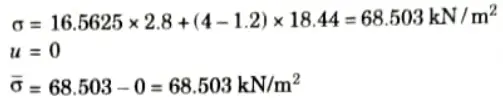
8. At Level D-D:
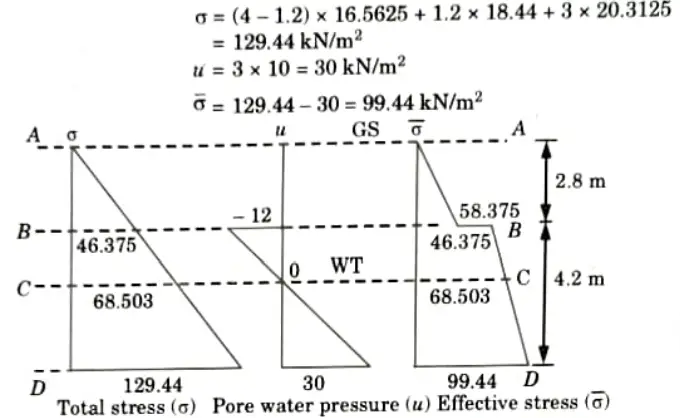


Q2. Describe Darcy’s law and give its validity.
Ans. Darcy’s Law:
- i. Darcy’s law states that there is a linear relationship between flow velocity (v) and hydraulic gradient (i) for any given saturated soil under steady laminar flow conditions.
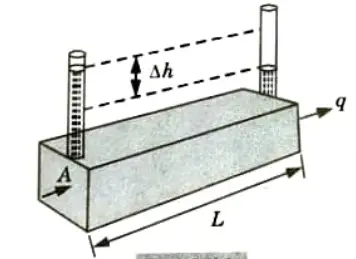


ii. If the rate of flow is q (volume/time) through cross-sectional area (A) of the soil mass, Darcy’s Law can be expressed as:
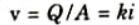
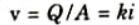
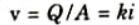
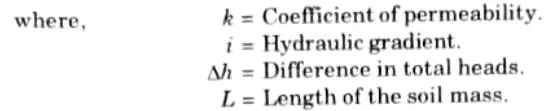
Validity of Darey’s Law:
- 1. If the flow through soils is laminar, Darcy’s law is true.
- 2. It is applicable to the flow of silts, clays, and fine sands. The flow may be turbulent in coarse sands, gravels, and boulders, making Darcy’s law inapplicable.
- 3. The relationship between velocity (v) and hydraulic gradient I must be linear for Darcy’s law to be true.
- 4. The interstices are exceedingly narrow in soils with extremely fine-grained particles, such as colloidal clay. As a result, the velocity is relatively low. The Darcy’s law is invalid on such soils.
Q3. What are different methods for determination of the coefficient of permeability in a laboratory ? Discuss their limitations.
Ans. A. Permeability: It is a characteristic of a porous media that free or gravitational water (or other fluids) can travel slowly through its interconnecting spaces.
B. Laboratory Methods: The coefficient of permeability of a soil can be determined by using the following methods :
1. Constant Head Permeability Test:
- i. For determining the coefficient of permeability of coarse-grained soils with high permeability, such as clean sands and gravel, constant-head experiments are used.
- ii. Fig. shows the arrangement in which the flow is one-dimensional and in downward direction.
- iii. The figure also indicates the head loss (h1) and the corresponding length of soil, L, over which the head loss occurs.
- iv. The experimental data consist of a measured quantitý of discharge Q during a time interval t, under steady state conditions of flow. The head loss hl is also noted.
- v. k can be computed from the formula,





Limitations: Following are the limitations of constant head permeability test:
- i. Equipment expensive.
- ii. Complicated to set up and to use.
- iii. Not suitable for most sites.
- iv. Test duration long.
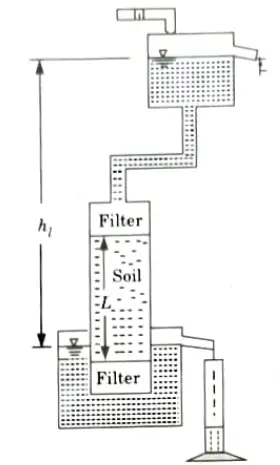
2. Falling or Variable Head Permeability Test:
- i. Falling-head test are used for fine-grained soils with low permeability, such as silty or clayey fine sand, silts, and clays.
- ii. A typical set-up for falling head permeability test is shown in Fig. The water level in the stand pipe is observed from time to time.
- iii. Let A be the area of soil sample, a the area of stand pipe and L the length of soil sample.
- iv. If the head difference at time t1 is h1 and at time t2 is h2, then coefficient of permeability is calculated from the expression.
Limitations: Test specimen cannot be consolidated to expected in-situ effective stress.


Q4. Discuss the factors that influence permeability of soil.
Ans. Following are the factors affecting the permeability of soils:
- 1. Properties of Pore Fluid:
- i. Fluids that fill pores in soil or rock are known as pore fluids.
- ii. Pore fluid viscosity and the unit weight of the pore fluid are inversely correlated with permeability.
- 2. Void Ratio: The area accessible for low thus increases with an increase in the void ratio, increasing permeability for crucial situations.
- 3. Entrapped Air and Organic Impurities: The flow is obstructed by organic contaminants and trapped air, and as a result, the coefficient of permeability is lessened.
- 4. Adsorbed Water:
- i. Adsorbed water refers to the microscopic water layer that envelops each soil particle.
- ii. Because this water cannot travel freely, it limits the effective pore space, which lowers the coefficient of permeability.
- 5. Shape of Particles: While angular soil has a greater specific surface area than round soil, it is less permeable than soil with rounded particles. Permeability is inversely proportional to specific surface area.
Q5. Explain flownet. Describe its properties and its applications.
Ans. A. Flownet: Flownet is a type of grid created by drawing several equipotential and stream lines.
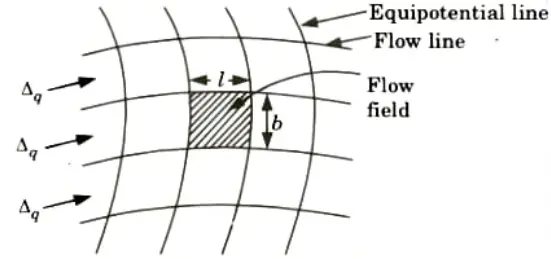


B. Characteristics / Properties of Flownet: Following are the characteristics of a flownet:
- 1. In a flownet, equipotential lines and stream lines cross one another orthogonally.
- 2. Flow cannot cross a flow line, and flow velocity always runs perpendicular to the equipotential line.
- 3. Equipotential drop is the name given to the loss of head between two equipotential lines, which is always the same.
- 4. Flow fields are the area between two equipotential lines and flow lines, and in an isotropic media, they are roughly square; in an anisotropic medium, they are roughly rectangular.
C. Application: Flownet is used to:
- 1. Estimation of seepage losses from reservoir.
- 2. Determination of seepage pressure.
- 3. Uplift pressure below dams.
- 4. To check against the possibility of piping and many others.
Q6. What are the assumption and limitations of Dupuits’s theory ?
Ans. A. Assumptions: Following are the assumptions of Dupuits’s theory:
- 1. Darcy’s law is true because the flow is laminar.
- 2. The soil bulk is homogeneous and isotropic.
- 3. The well reaches all the way down into the aquifer.
- 4. The stream is constant.
- 5. Throughout, the permeability coefficient is constant.
- 6. The flow is horizontal and radial as it approaches the well.
- 7. The normal groundwater cycle is unaffected.
B. Limitations: Various assumptions have been made in the Dupuits theory formulae. n actual practice, however, none of these conditions may get fulfilled; say for example:
- 1. Aquifers are not entirely homogeneous, for one.
- 2. The aquifer may have been only partially penetrated by the well.
- 3. There may be variations in permeability.
- 4. The base of the cone might not be a circular because the ground water table could be sloped.
- 5. It’s possible that the equilibrium conditions weren’t entirely attained.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Geotechnical Engineering Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Geotechnical Engineering Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |