Providing the Important Questions with solution in Fluid Mechanics & Fluid Machines AKTU. Hope you will enjoy that Blog and this Blog help you in your upcoming Exams.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Fluid Mechanics & Fluid Machines : *Unit-01 *Unit-02 *Unit-03 *Unit-04 *Unit-05 *Short-Q/Ans *Question-Paper with solution 21-22
Discuss some physical properties of fluids in brief?
Answer
These are a few of the physical characteristics of fluids:
a. Density or Mass Density:
1. It can be described in terms of mass per unit volume under constant pressure and temperature. It is also known by the name specific mass. It is denoted by p and its unit is kg/m3.
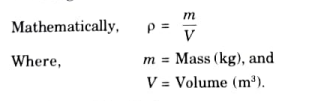
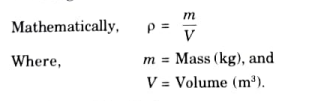
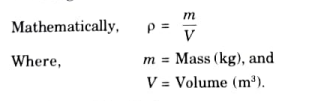
b. Weight Density:
1.It can be characterized as the mass per unit volume at standard pressure and temperature. It also goes by the name “specific weight.” It is denoted by W and its unit is N/m3.
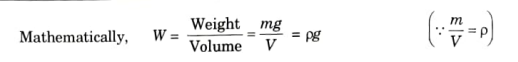
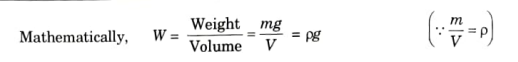
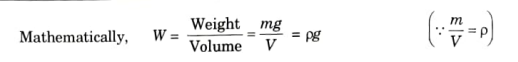
c. Specific Volume:
- It is defined as the volume per unit mass of fluid
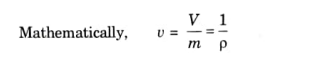
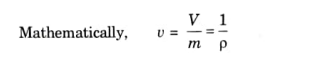
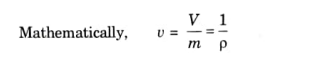
d. Specific Gravity:
It is the ratio of the specific weight of the given fluid to the specific weight of a standard fluid.
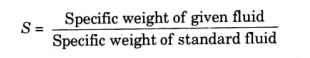
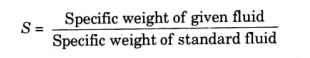
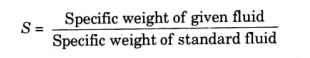
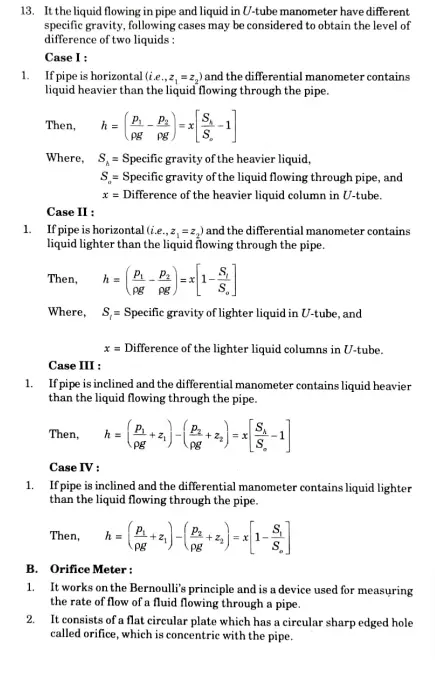
For liquids, standard fluid is pure water at 4 °C and air is standard fluid for gases.
e. Viscosity:
1. It is described as a fluid’s characteristic that affects how resistant it is to shearing forces. Pa-s is its SI unit and poise is its CGS unit.
2. An ideal fluid has no viscosity.
3. Viscosity of fluids is due to cohesion and adhesion.
Explain the following a. Compressibility, b. Surface tension, and C. Incompressible flow.
Answer
a. Compressibility
1. Compressibility is the quality that allows fluids to alter in volume when subjected to external pressure.
2. It is the volumetric strain divided by the compressive stress, which is known as the reciprocal of the bulk modulus of elasticity.



b. Surface Tension:
1. It is described as the tensile force acting between two immiscible liquids or on the surface of a liquid in contact with a gas.
2. It is denoted by sigma (o) and its SI unit is N/m.
3.This occurs due to the force of cohesion at the free surface as shown in Fig. 1.6.1.
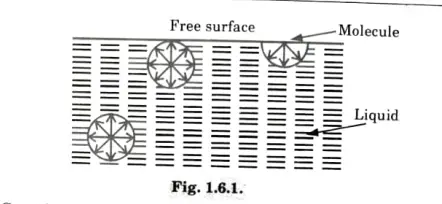


4.Consider a liquid molecule that is in equilibrium and is surrounded by other molecules on all sides.
5.There are no liquid molecules above the surface of a liquid’s free surface to counteract the force of the molecules below it.
6.As a result, the molecule experiences a net inward force that is normal to the surface.
7. As a result, a tiny layer of molecules forms at the free surface, acting as a membrane that allows a thin, little needle to float there.
c. Incompressible Flow:
1.It is that type of flow in which the density is constant for the fluid flow.
2. Isochoric flow, which meaning in the same place or space, is another name for incompressible flow.
3. Since the temperature and pressure of liquids and gases do not change in incompressible flow, these types of flow are simple to model.
Determine the bulk modulus of elasticity and compressibility of a liquid. If the pressure of liquid is increased from 70 N/cm2 to 130 N/cm2. The volume of liquid decreases by 0.15 %.
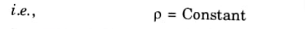
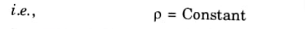
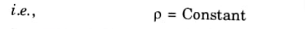
Suggest the device used for the measurement of fluid flow through ducts or pipes. Explain them. OR What are the various applications of Bernoulli’s equation ? Explain them.
Answer
Some of the simple applications of Bernoulli’s equation are as follows:
A Venturimeter:
1. A venturi metre is a tool used to gauge the flow rate of a fluid via a pipe.
2. It consists of three parts, as given below :
i. A short converging part,
ii. Throat, and
ii. Diverging part.
It works on the principle of Bernouli’s theorem.
4. As shown in Fig. 1.12.1, a venturimeter is fitted in a horizontal pipe through which a fluid is flowing.
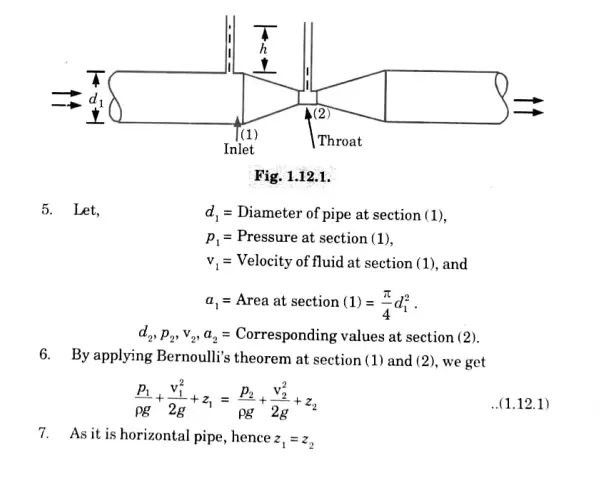







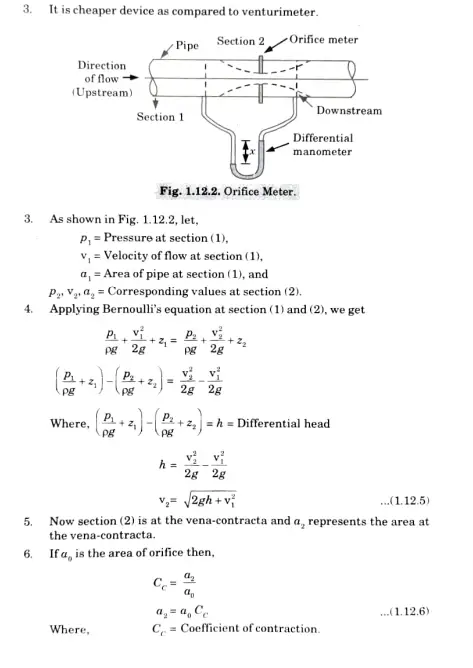


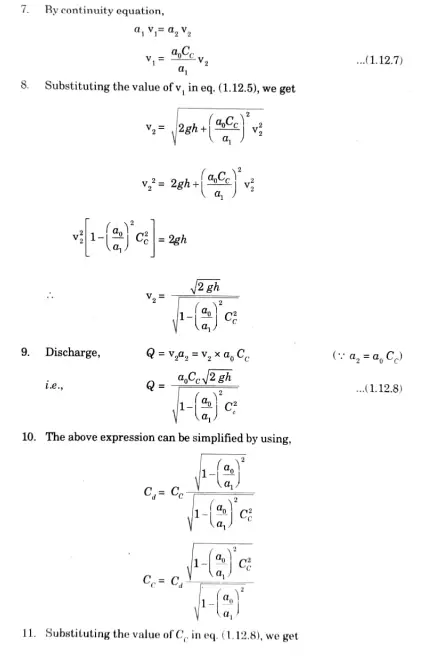





A horizontal venturimeter with a discharge coefficient of 0.98 is being used to measure the flow rate of a liquid of density 1030 kg/m3. The pipe diameter at entry to the venturi is 75 mm and The venturi throat has an area of 1000 mm2. If the flow rate is 0.011 m3/s. Determine the height difference recorded on a U-tube manometer connecting the throat to the upstream pipe. Take the relative density of mercury to be 13.6.






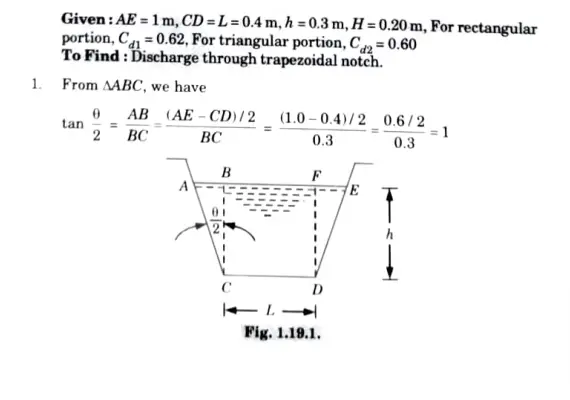
Find the discharge through a trapezoidal notch which is 1 m wide at the top and 0.4 m at the bottom and is 30 cm in height. The head of water on the notch is 20 cm. Assume Cd for rectangular portion = 0.62 while for triangular portion = 0.60.








Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Fluid Mechanics & Fluid Machines Quantum, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Important Unit-1 | Unit-1 |
| Important Unit-2 | Unit-2 |
| Important Unit-3 | Unit-3 |
| Important Unit-4 | Unit-4 |
| Important Unit-5 | Unit-5 |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Fluid Mechanics & Fluid Machines Quantum PDF: | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |

6 thoughts on “UNIT 1 Fluid and Bernoulli’s Equation Important Questions with solution in Fluid Mechanics & Fluid Machines AKTU”