Find out more about B.Tech AKTU Quantum Book Short Question Notes on Energy Conservation and Auditing. Discover the basics of efficient energy utilisation, auditing methodologies, and insights for long-term energy management.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Energy Conservation and Auditing: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 4th Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Energy Scenario (Short Question)
Q1. What are the basic two forms of energy ?
Ans. The basic two forms of energy are:
- 1. Kinetic energy
- 2. Potential energy.
Q2. What do you understand by kinetic energy ?
Ans. Kinetic energy is the energy that an object has because of its motion.
Q3. Define potential energy.
Ans. Potential energy is the energy stored in an object as a result of its position relative to some zero point.
Q4. Write the consumption of energy by different sectors.
Ans. The total consumption of energy by different sectors are:
- 1. Industry sector – 42.69 %
- 2. Domestic sector – 24.01%
- 3. Agriculture sector – 17.67 %
- 4. Commercial sector – 8.04 %
Q5. Define energy intensity.
Ans. Energy intensity is the amount of energy consumed per unit of GDP and shows a country’s level of development.
Q6. Write the objective of energy security.
Ans. The primary goal of energy security is to lessen the country’s reliance on imported energy sources for energy growth.
Q7. What do you mean by energy conservation ?
Ans. 1. Energy conservation is the effort to reduce energy use.
2. This can be accomplished by either using less energy for a steady service or reducing the amount of service consumed (for example, by driving less).
Q8. Write the importance of energy conservation.
Ans. 1. Energy conservation is critical to conserving nonrenewable energy resources.
2. Energy conservation will lower the cost of fossil fuels.
3. Energy saving would boost the economy by giving customers more discretionary income to spend on goods and services.
Q9. Give the various strategies of energy conservation.
Ans. There are three categories of energy conservation strategies:
- 1. Short term strategy
- 2. Medium term strategy
- 3. Long term strategy.
Q10. Discuss the salient features of energy conservation act, 2001.
Ans.
- i. Establish energy usage guidelines and criteria for certain consumers.
- ii. Require commercial building owners to follow energy-saving building codes.
- iii. Energy consumption standards for notified equipment and appliances.
- iv. Prohibit the manufacture, sale, purchase, and import of not-conforming notified equipment and appliances.
Q11. What is BEE ?
Ans.
- 1. The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) is a government of India organization under the ministry of electricity that was established in March 2002 under the provisions of the country’s 2001 Energy Conservation Act.
- 2. Beginning in January 2010, the government proposes making BEE ratings mandatory for all appliances in India.
- 3. The Bureau of Energy Efficiency’s objective is to “institutionalize” energy efficiency service delivery mechanisms in the country and to give leadership in energy efficiency in all sectors of the country.
- 4. The major goal would be to minimise the economy’s energy intensity.
Q12. Discuss some roles of BEE as per energy conservation act 2001.
Ans. This act has provided the bureau of energy efficiency with the following powers:
- i. Encourage the use of energy-saving procedures, equipment, devices, and systems.
- ii. Encourage creative financing for energy efficiency projects.
- iii. Expand consulting services in the field of energy conservation.
- iii. Take appropriate steps to establish recommendations for energy-efficient construction codes.
Q13. Write the different schemes of BEE.
Ans.
- 1. National mission for enhanced energy efficiency.
- 2. Energy conservation building codes.
- 3. Standard and labeling scheme.
- 4. Municipal demand side management scheme.
- 5. Agricultural demand side management scheme.
- 6. Capacity building of DISCOMs.
- 7. State designated agencies.
Q14. Mention the parameters on which the high tension and low tension consumers are charged by electricity boards.
Ans. Generally, high tension consumers are charged based on both demand (kVA) and energy (kWh) while the low tension consumers are charged based on only energy consumed (kWh).
Q15. What is the main objective of electricity Act, 2003 ?
Ans. The objectives of the electricity Act, 2003, is as follows:
- 1. Creating competition in the industry.
- 2. Protecting consumer interest.
- 3. Ensuring supply of electricity to all areas.
- 4. Rationalizing tariff.
- 5. Lowering the cross-subsidization levels.
Q16. Write down the features of electricity act 2003.
Ans. Main features of the act are:
- 1. No license required for new generating station up to a prescribed capacity.
- 2. Compulsory metering of all the consumers.
- 3. Provisions for preventing and eliminating power theft.
- 4. Private companies allowed to build transmission lines for captive use or for common use.
- 5. Open access in transmission.
Q17. What is integrated energy policy ?
Ans. Integrated energy policy:
- 1. The August 2006 integrated energy strategy tackles all areas of energy, including energy security, access and availability, cost and pricing, efficiency, and the environment.
- 2. The strategy strives to meet energy demand “at the lowest possible cost while remaining technically efficient, economically viable, and environmentally sustainable.”
Unit-II: Demand Side Management (Short Question)
Q1. Define demand side management.
Ans. 1. Demand side management is the selection, planning, and execution of initiatives aimed at influencing the demand or customer-side of the electric metre.
2. The DSM programme can lower energy costs for utilities and, in the long run, restrict the need for additional generation capacity augmentation and transmission and distribution system strengthening.
Q2. Write the scope of demand side management.
Ans. 1. Demand side management encompasses all activities that take place on the client side of the energy metre. These activities may be initiated by customers or prompted by the utility.
2. DSM is an essential component of resource planning or cost-cutting planning. The resources are designed to minimise both current and future costs.
Q3. Give the advantage and disadvantage of DSM.
Ans. A. Advantage: It helps in energy conservation.
B. Disadvantage: It requires vast knowledge to execute.
Q4. Name of the various strategies used for DSM.
Ans.
- i. Peak clipping
- ii. Valley filling
- iii. Load shifting
- iv. Strategic conservation
- v. Strategic load growth
- vi. Flexible reliability.
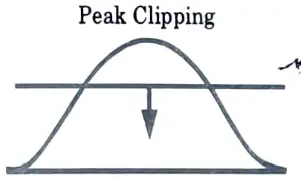
Q5. Define peak clipping.
Ans. It is commonly defined as the reduction of peak load through the utility’s direct control over the consumer’s equipment or through tariff provisions that allow the consumer to reduce his load at particular times of the day.


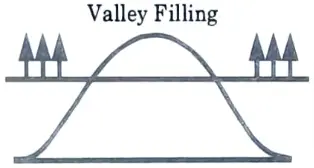
Q6. What is valley filling ?
Ans. It entails raising load during non-peak hours. Valley filling entails constructing OFF-peak loads. This is especially appealing when the long-run incremental cost is less than the average price of electricity.


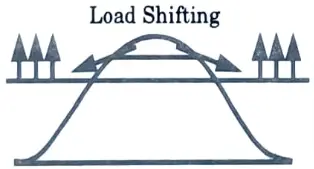
Q7. Discuss load shifting.
Ans. It entails relocating peak loads to off-peak hours. Storage water heating, storage space heating, and coolness storage are all popular applications.


Q8. Discuss strategic load growth.
Ans. It is the change in load form that refers to the overall growth in sales. Load growth may imply a greater market share of loads as a result of the development of new applications.



Q9. Write the customer benefits of DSM.
Ans. These are:
- i. Satisfy electricity demands
- ii. Reduce/stabilize cost
- iii. Improve value of service
- iv. Maintain improve lifestyle and productivity.
Q10. Write the keys to successful implementation of DSM.
Ans.
- i. Start with good programme design.
- ii. Respond to early information in the market place.
- iii. Be flexible with the details of programme delivery.
- iv. Learn from the experience of other utilities in the region.
Q11. What are the different levels of programme implementation of DSM ?
Ans. The various levels are:
- i. Information
- ii. Technical assistance
- iii. Financial incentives
- iv. Direct intervention
Q12. Describe financial incentives.
Ans. Its goal is to lower the cost of adopting energy saving measures for clients. Most energy efficiency methods necessitate additional spending to get financial benefits; however, many customers lack the funds to invest or find the financial returns of energy efficiency less appealing.
Q13. Draw the implementation model of DSM.
Ans.
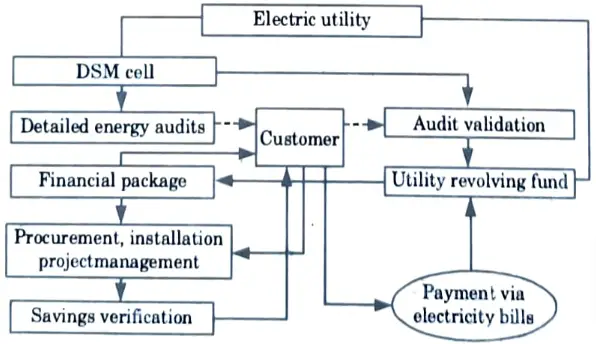


Q14. Define energy monitoring and targeting.
Ans. Energy monitoring and targeting is a method of controlling energy use and reducing energy waste at current levels of usage by improving operating procedures.
Q15. Write the elements of monitoring and targeting.
Ans.
- 1. Recording
- 2. Analyzing
- 3. Comparing
- 4. Setting targets
- 5. Monitoring
- 6. Reporting
- 7. Controlling.
Q16. What do you mean by CUSUM?
Ans. The difference between the base line (anticipated or standard consumption) and the actual consumption points throughout the base line period of time is represented by the Cumulative Sum (CUSUM).
Q17. What is EMIS ?
Ans. A performance management system that helps individuals and organizations to plan, make choices, and take effective actions to manage energy use and costs is known as an energy management information system (EMIS).
Unit-III: Energy Audit (Short Question)
Q1. What is energy audit ?
Ans. 1. An energy audit is an evaluation for improving energy efficiency through study of energy usage. It identifies energy-saving opportunities, which are then examined to determine savings.
2. A general audit is a thorough assessment of prospective energy-saving methods based on meticulous data gathering, in-depth interviews with facility or operations management, and analysis of energy profiles generated by interval metering.
Q2. What are the aims or objectives of energy audit?
Ans. The objectives of energy audit:
- 1. To understand the facility’s energetic behaviour.
- 2. To identify the excess of energy consumed.
- 3. To find out the motive of this excess.
Q3. Write the name of various types of energy audit.
Ans. There are five types of energy audit:
- 1. Envelope audit
- 2. Functional audit
- 3. Process audit
- 4. Transportation audit
- 5. Utility audit.
Q4. What is envelope audit ?
Ans. It inspects the building or factory envelope to evaluate energy losses due to leakage, construction issues, apertures, door and window faults, lack of insulation, and other factors.
Q5. What is the strategy of energy audit ?
Ans.
- i. Establish energy consumption in the organization.
- ii. Estimate the scope for saving.
- iii. Identify the most likely and the easiest areas for attention.
- iv. Identify immediate improvements/ savings.
- v. Set a reference point.
- vi. Identify areas for more detailed study/measurement.
Q6. With diagram explain energy audit team.
Ans.
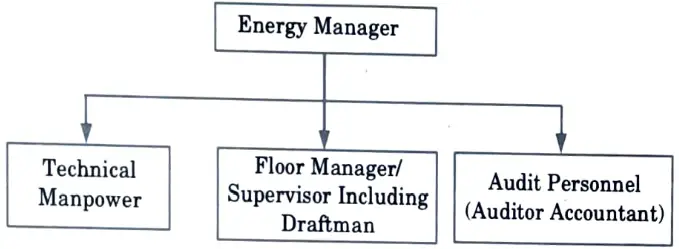


Q7. What are the objectives of energy management ?
Ans. Objectives of energy management team: An energy audit is a component of a larger energy management programme. Energy management is a continuous process that tries to optimise energy input and use over time in order to reduce energy expenditures.
Q8. What are the various steps of energy audit ?
Ans. The various steps are:
- i. Pre audit phase activities
- ii. Detailed energy audit activities
- iii. Post audit phase
Q9. Write the main aims of pre audit phase activities.
Ans.
- i. To finalize energy audit team
- ii. To plan with time frame.
- iii. To create awareness through meetings/programme.
- iv. To identify the instrumentation required for carrying out the audit.
- v. To decide whether any meters will have to be installed prior to the audit.
Q10. Give the data collected during the detailed energy audit.
Ans.
- i. Capacity utilization
- ii. Steam consumption
- iii. Fuel consumption
- iv. Water consumption
- v. Electrical energy consumption
Q11. Which activities are done during post audit phase ?
Ans. i. Action plan, schedule implementation
ii. Follow-up and periodic review
Q12. Briefly explain the energy audit for buildings.
Ans. An energy audit might range from a basic walk-through inspection to one that spans multiple phases. These steps comprise a simple walk-through survey, energy consumption monitoring in building services, and model analysis using computer modelling of building operation.
Q13. What is bench marking ?
Ans. Benchmarking is a useful method for identifying industrial energy consumption patterns and taking necessary measures to improve energy efficiency.
Unit-IV: System Audit of Mechanical Utilities (Short Question)
Q1. What is pump ?
Ans. 1. “A mechanical device, using suction or pressure, to rise or move liquid by mechanical action” is called a pump.
2. It is used to transport various fluids from one point to another. The pump converts the mechanical energy of the fluid into pressure energy (hydraulic energy).
Q2. Write the name of different types of pumps.
Ans. There are basically two types of pumps:
- 1. Positive displacement pumps.
- 2. Rotodynamic pumps.
Q3. Give the applications of pumps.
Ans. 1. It is used in waste water recycling.
2. It is used in chemical industry.
3. Pumping water from the wells.
Q4. What are ways to save energy in pumps ?
Ans. Energy saving in pumps:
- 1. Use constant speed AC induction motors to drive the impellers of pumps.
- 2. Do not use oversized motors (higher hp than required).
- 3. Do not operate the pumps if load is not there.
- 4. Clean pumps regularly to avoid frictional losses.
- 5. Ensure sufficient lubrication.
Q5. Explain blowers.
Ans. Blowers:
- 1. Blowers are the devices which are used for circulation of air and/or gases at low pressures.
- 2. Blowers are used for blowing air/gas in a specific or given area.
Q6. What are the applications of blowers ?
Ans. Application of blowers:
- 1. It is used in dust collector systems.
- 2. It is used in combustion air for burners.
Q7. What do you mean by specific power consumption ?
Ans. The energy required to create a unit of output is defined as the compressor’s specific energy consumption.
Q8. Write the components of compressed air system.
Ans. Compressed Air System and its components:
- 1. Intake air filters
- 2. Inter-stage coolers
- 3. After coolers
- 4. Air-dryers
- 5. Moisture drain traps
- 6. Receivers.
Q9. What is cooling tower ?
Ans. Cooling tower:
- 1. Cooling towers are heat-exchange structures that lower the temperature of circulating hot water.
- 2. A water stream from an industrial process is pushed into a cooling tower via a water inlet valve and meets air in a cooling tower in this operation.
- 3. As soon as the heat is extracted, the water begins to evaporate in small volumes, lowering the temperature of the water and allowing the industrial process to continue.
Q10. Give the different types of water losses in cooling tower.
Ans. There are three types of water losses in the cooling tower:
- 1. Drift loss
- 2. Evaporation loss
- 3. Blow down loss.
Q11. What are the ways of energy saving in compressed air systems ?
Ans.
- 1. Reduction of the inlet air temperature.
- 2. Maximizing allowable pressure dew point at air intake.
- 3. Keep compressor valves in good condition by removing and inspecting them.
- 4. Proper pipe sizing.
- 5. Reduce compressor delivery pressure, wherever possible, to save energy.
Q12. Write the applications of compressor.
Ans.
- 1. It uses in the natural gas plant for gas processing purposes.
- 2. Uses in petroleum refineries.
- 3. Compressor uses in oil refineries.
- 4. It uses in gas turbines.
Unit-V: Energy Efficient Technology (Short Question)
Q1. Give the needs of energy efficient devices.
Ans. Need of energy efficient devices:
- 1. Energy efficient devices are essential to save energy.
- 2. It is also essential to save money.
Q2. What do you mean by life cycle assessment method ?
Ans. A life cycle assessment is a comprehensive review of a product or service’s environmental impact across its full life cycle.
Q3. Write the name of stages in LCA method.
Ans. The LCA consists of four main stages and they are as follows:
- i. Scope and goal
- ii. Analysis of inventory
- iii. Various impact assessments
- iv. Explanation.
Q4. What do you understand by simple payback period ?
Ans. Simple pay- back period:
The simple payback period (SPP) is the number of years required to generate the primary investment (first cost), taking into account total yearly savings.
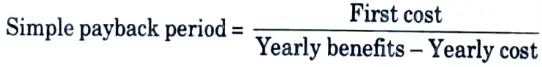
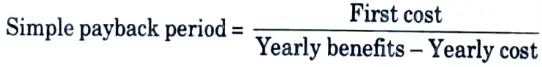
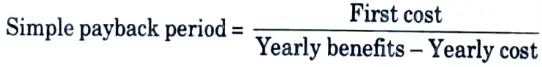
Q5. Write short note on energy efficient motor.
Ans. Energy efficient motors: These motors are very efficient, last longer, require less maintenance, and their life doubles for every 10 °C temperature reduction. These features which can be achieved by:
- 1. Special quality of thinner laminations with little loss. Even at partial loads, this lowers iron loss.
- 2. Thicker conductors and higher copper content reduce copper loss due to decreased resistance.
- 3. Increased core length, as well as a smaller and more uniform air gap between the stator and rotor, to reduce stray losses.
Q6. Give the benefits of energy efficient motors.
Ans. These are:
- i. The efficiency curve of energy efficient motors is practically flat, resulting in significant energy savings because the motor is not always completely loaded.
- ii. These motors are naturally low in noise and vibration, which contributes to environmental conservation.
- iii. The special design features also result in lower operating temperatures, which extends the life of the motor and reduces maintenance expenses.
Q7. Write some motor efficiency testing standards.
Ans. The most common standards are:
- i. IEEE 112-1984 (United States)
- ii. EC 34-2 (International Electrotechnical Commission)
- iii. BS-269 (British)
- iv. JEC-37 (Japanese Electrotechnical Committee)
Q8. Define LED.
Ans. A light-emitting semiconductor diode (LED) emits light in the forward direction or in the direction it is oriented. LEDs are most commonly employed as an indication light in electrical gadgets, traffic signal lights, musical instruments, and dashboards in vehicles and houses, among other things.
Q9. Give the advantages of LED.
Ans. They are:
- i. LED light bulbs consume only 10% of the power of traditional light bulbs.
- ii. LED light bulbs can tolerate a lot of vibration, shock, and temperature changes.
- iii. When compared to incandescent light bulbs, LED bulbs can create a wide range of rich and brilliant colours.
Q10. Write the disadvantages of LED.
Ans. These are:
- i. High initial price
- ii. Temperature dependence.
Q11. Name various energy efficient lighting devices used for energy saving.
Ans. CFLs and LEDs are widely used as energy efficient lighting devices.
Q12. What are the advantages of CFL?
Ans. These are:
- i. Low electrical consumption as compared to conventional
- ii. Long life upto 10,000 hours
- iii. Low cost of maintenance
- iv. High luminous efficiency
- v. It can operate within 130-280 V range.
Q13. What do you understand by energy efficient lighting ?
Ans. Energy efficient lighting:
- 1. Energy efficient lighting reduces electricity demand and is a more cost-effective lighting system than traditional lighting approaches.
- 2. Energy efficient lighting entails using more light from fewer lights by replacing high power consumption lights such as incandescent, high discharge lamps, and so on.
Q14. What is APFC ?
Ans. APFC is an abbreviation meaning “automatic power factor controller.” It is used to increase system power factor through automatic power factor correction and control.
Q15. Write the advantages of APFC.
Ans. 1. Unmanned operation of power factor control.
2. Always maintains very good and accurate power factor.
Q16. What is VFD ?
Ans. 1. A variable frequency drive (VFD) is an electrical device that transforms fixed frequency and fixed voltage sine wave electricity (line power) to variable frequency and variable output voltage to control the speed of a 3-ɸ induction motor.
2. It regulates the speed of a 3-ɸ induction motor by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the motor.
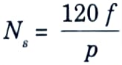
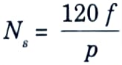
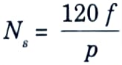
Since the number of pole is constant the speed Ns can be varied by continuously changing frequency.
Q17. How would you incorporate energy efficient features in lighting loads ?
Ans. The best practices are:
- i. Installation of LED panel indicator lamps in place of filament lamps.
- ii. Use of high efficiency light sources for reducing the energy consumption for lighting.
- iii. Installation of compact fluorescent lamps in place of incandescent lamps.
Q18. What are the schemes used to improve performance of motor running on light load.
Ans. 1. The first way utilizes a solid-state controller using thyristors to reduce power input.
2. In the second approach, the input alternating current power is rectified and inverted using a waveform synthesizer to minimise the motor’s power input under any operating situation.
3. The third way involves changing the flux distribution in the core, which reduces the machine’s overall power input. This approach is appropriate for single-phase equipment with lower power ratings and requires retrofitting.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Energy Conservation and Auditing Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Energy Conservation and Auditing Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |
