Explore the B.Tech AKTU Quantum Book Short Question Notes on Electric Drives. Discover motor control and power electronics concepts, as well as insights into efficient and dynamic electric drive systems for a variety of applications.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Electric Drives: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 4th Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Fundamentals of Electric Drive (Short Question)
Q1. What are electric drives ?
Ans. 1. Motion control is required in a wide range of industrial and home applications, including transportation systems, rolling mills, paper mills, textile mills, machine tools, fans, pumps, robots, and washing machines, among others.
2. Motion control systems are known as drives, and they can use any of the prime movers, such as diesel or gasoline engines, gas or steam turbines, steam engines, hydraulic motors, and electric motors, to deliver mechanical energy for motion control.
3. Electrical drives are those that use electric motors.
Q2. Draw the block diagram of electric drive.
Ans.
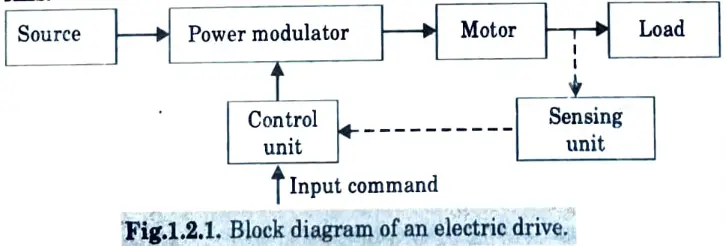


Q3. Write the functions of power modulator in electric drive.
Ans. 1. It limits source and motor current during transient operations such as starting, braking, and spread reversal; excessive current received from the source may overload it or produce a voltage dip.
2. Modulates power flow from the source to the motor such that the motor receives the speed-torque characteristics required by the load.
Q4. Mention the advantages of electrical drives.
Ans. 1. They have adaptable control properties. Electrical drives’ steady-state and dynamic characteristics can be adjusted to meet load requirements. Speed can be adjusted in a variety of ways. Electric braking is an option. Control gear for speed control, starting, and braking is often basic and straightforward to use.
2. Electric motors are highly efficient, have low no-load losses, and can handle significant short-term overloading. They can be built in a variety of designs to be load suitable. They have a longer life, lower noise, less maintenance requirements, and a cleaner operation when compared to other prime movers.
Q5. Differentiate between AC drives and DC drives.
Ans.
| S. No. | DC Drives | AC Drives |
| 1. | The commutator adds bulk, cost, and weight to the motor. Sparking at the brushes renders it environmentally inappropriate in some areas. | Motors are inexpensive, particularly the squirrel cage motor. |
| 2. | The highest speed and design rating are limited due to commutation. | Speed and design rating have no upper limits. |
| 3. | The commutator requires frequent maintenance. | Motor is reliable, requires little maintenance and can be used in all locations. |
Q6. Why switching operations are done ?
Ans.
- 1. For changing motor connections to change its quadrant of operation.
- 2. For changing motor circuit parameters in discrete steps for automatic starting and braking control.
- 3. For operating motors and drives according to a predetermined sequence.
- 4. To disconnect motor when abnormal operating conditions occur.
Q7. What are the forms of drive motors ?
Ans. 1. DC motors fed from DC supply.
2. DC motors fed from AC supply.
3. AC motors fed from AC supply.
Q8. What are the factors on which choice of an electric drive depends ?
Ans. 1. Requirements for steady-state operation: speed torque characteristics, speed regulation, speed range, efficiency, duty cycle, quadrants of operation, speed variation, ratings.
2. Transient operation requirements: Acceleration and deceleration values, as well as starting, braking, and reversing performance.
3. Source requirements: kind of source and capacity, magnitude of voltage, voltage variations, power factor, harmonics and their effect on other loads, ability to receive regenerated power.
Q9. Write the fundamental torque equation in electric drives.
Ans. If, in addition to one load directly coupled to the motor shaft, there are m other loads with translational motion with velocities v1, v2,… vm and masses M1, M2, ….., Mm, respectively then
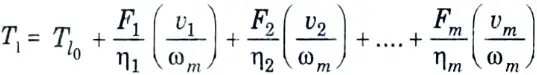
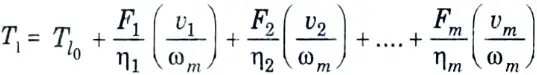
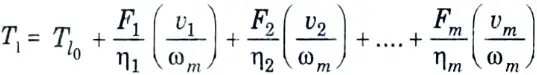
Q10. Give the name of component of motor load dynamics.
Ans. 1. Friction torque TF: Friction will be present at the motor shaft and also in various parts of the load. TF is equivalent value of various friction torques referred to the motor shaft.
2. Windage torque TW: When a motor runs, wind generates a torque opposing the motion. This is known as windage torque.
3. Torque required to do the useful mechanical work TL.
Q11. Show the variation of load torque according to the nature of load.
Ans.
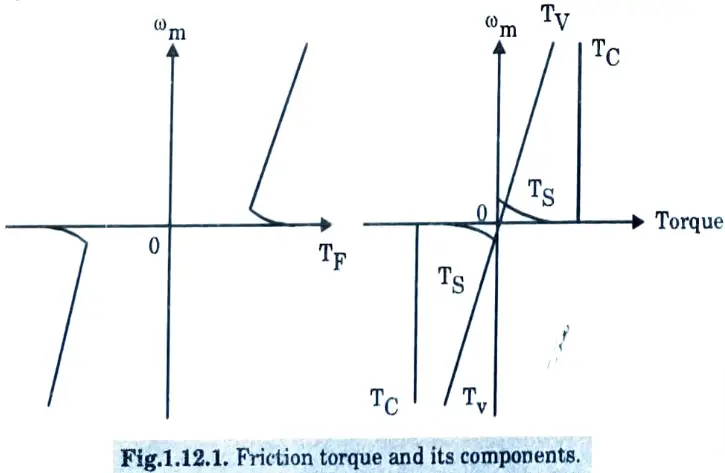


Q12. Write the classification of electric drives.
Ans. 1. Group drive: The system is known as group drive or shaft drive when many groups of mechanisms or machines are organised on one shaft and driven or operated by a single motor.
2. Individual drive: An individual drive is one that uses a single motor to drive or actuate a specific mechanism and performs all of the tasks associated with that load.
3. Multimotor drive: Each operation of the mechanism is taken care of by a separate drive motor.
Q13. Define constant torque drive.
Ans. If the maximum torque capability of a variable speed drive does not change with speed setting, it is referred to as a constant torque drive. Constant torque mode is the corresponding mode of operation.
Q14. What is constant power drive ?
Ans. If the maximum power capability of a variable speed drive does not change with speed setting, it is referred to as a constant power drive. Constant power mode is the corresponding mode of operation.
Q15. Which motors are employed in variable speed drives ?
Ans. 1. Induction and synchronous motors are used, but they are both expensive and inefficient.
2. DC motors.
3. AC motors as a result of the advancement of semiconductor converters that use thyristors, power transistors, IGBTs, and GTOs.
Q16. Give the classification of load torque.
Ans. 1. Active load torque: Active load torques are loads that have the potential to drive the motor under equilibrium conditions.
2. Passive load torque: Passive load torques are torques that always oppose motion and change sign when motion is reversed.
Q17. List out source employed in electric drives.
Ans. 1. Low and medium power motors (ten of kilowatts) are generally fed from 400 V supply
2. For high ratings, motors may be rated at 3.3 kV, 6.6 kV, 11 kV and higher.
3. In case of aircraft and space applications, 400 Hz ac supply is generally used to achieve high power to weight ratio for motors.
Unit-II: Dynamics of Electric Drive (Short Question)
Q1. Define steady-state stability and transient stability.
Ans. 1. Steady-state stability: It is assumed that speed and torque deviations follow the steady-state speed-torque curves of the motor and load. Because the changes are so slow, the energy storage elements have little effect on the variation as it moves from one state of equilibrium to the next. When a motor is slowly or progressively loaded, it can be loaded to its maximum torque or power capacity.
2. Transient stability: The motor cannot achieve this limit for transient loads because the kinetic energy of the rotating parts must also be considered. The understanding of transient stability is required for the effective design of flywheels and other associated controllers.
Q2. What is load equalization ?
Ans.
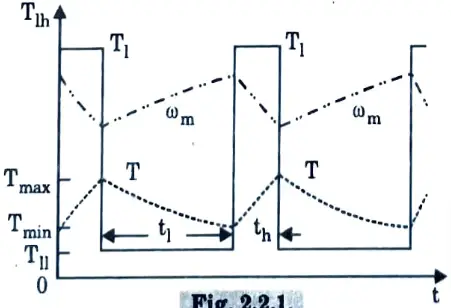


Fig. indicates that the peak torque required by the motor is substantially lower than the peak load torque. As a result, a motor with a far lower rating than the peak load can be utilised, and the peak current drawn by the motor from the source is much reduced.
Fluctuations in motor torque and speed are also reduced. Since power drawn from the source fluctuates very little, this is called Joad equalization.
Q3. Write the objectives for the selection of motor power rating.
Ans. 1. Obtain a suitable thermal model for the machine that may be used to calculate motor ratings for different kinds of motor duty.
2. Classification of load variation with time into specific standard categories known as motor duty classes.
3. To demonstrate methods for computing motor ratings for various duty classes.
Q4. Why it is important to study transient stability ?
Ans. The steady-state speed and torque of the motor and load in a synchronous motor drive may be such that the steady-state stability criterion does not provide any reliable information about its stability. As a result, it is vital to investigate its transient stability.
Q5. Give the expression of mean temperature rise in thermal model of motor for heating and cooling.
Ans. It is given by
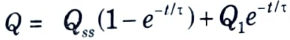
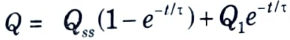
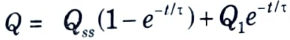
where,
Q1 = Initial temperature rise
QSS = Steady state temperature
𝛕 = Thermal time constant
Q6. Draw the heating and cooling curves of motor.
Ans.


Q7. Write the various classes of motor duty.
Ans.
- 1. Continuous duty.
- 2. Short time duty.
- 3. Intermittent periodic duty.
- 4. Intermittent periodic duty with starting.
- 5. Intermittent periodic duty with starting and braking.
- 6. Continuous duty with intermittent periodic loading.
- 7. Continuous duty with starting and braking.
- 8. Continuous duty with periodic speed changes.
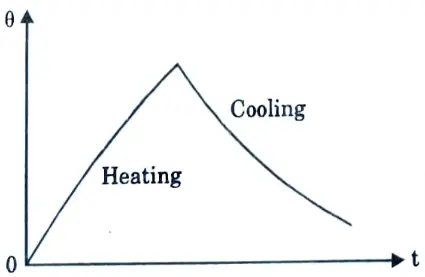
Q8. Discuss continuous duty.
Ans. It describes the operating of a motor at a constant load torque for a long enough period of time for the motor temperature to reach a steady-state value. This task is distinguished by a continual motor loss. Ex: Paper mill drives, compressors etc.
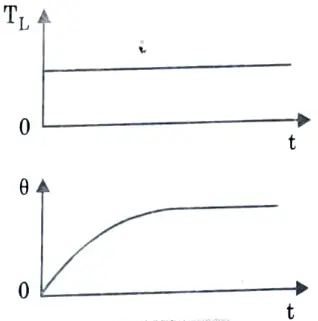


Q9. Briefly explain short time duty.
Ans. The time of drive operation is significantly less than the heating time constant in this case, and the machine is allowed to cool to room temperature before the motor is required to function again.
Ex: Crane drives, turning bridges etc.
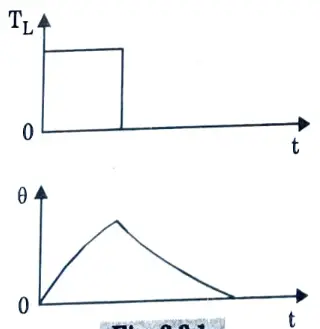


Q10. What is intermittent periodic duty ?
Ans. It is made up of periodic duty cycles, each of which includes a period of constant load and a rest interval. The running period is insufficient to elevate the temperature to a steady state value, and the rest period is insufficient to cool the machine to ambient temperature.
Ex: Pressing, cutting and drilling machine drives.
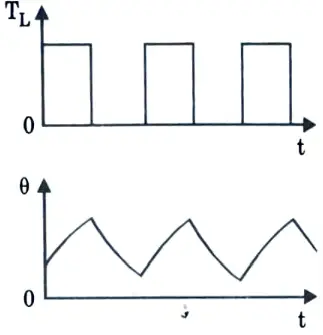


Q11. Discuss intermittent period duty with starting.
Ans. This is intermittent periodic duty, therefore heat losses at startup must be considered. Thus, it comprises of a starting period, a continuous load period, and a rest period.
Ex: Drives for fork lift trucks, mine hoist etc.
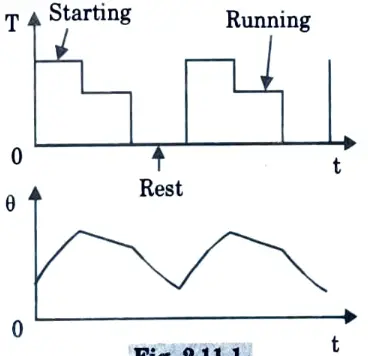


Q12. Give the expression to determine equivalent current, torque and power for fluctuating and intermittent load.
Ans. Equivalent Current, Torque and Power methods for fluctuating and intermittent loads:



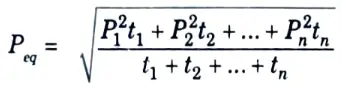
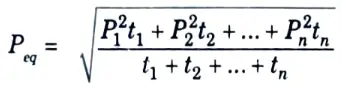
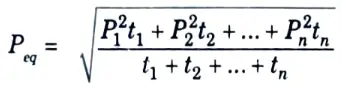
Q13. What is intermittent periodic duty with starting and braking ?
Ans. It comprises of a starting period, a constant load operation period, an electrical braking time, and a rest period.
Example: Billet mill drive, mine hoist etc.
Q14. Define continuous duty with intermittent periodic loading.
Ans. It consists of periodic duty cycles with normal voltage across the excitation winding, each consisting of a period of running at a constant load and a period of running at no load. This task differs from intermittent periodic duty in that a time of running at a constant load is followed by a period of running at no load rather than rest.
Ex: Pressing, cutting, shearing etc.
Q15. Explain continuous duty with periodic speed changes.
Ans. It comprises of periodic duty cycles, each with a period of running at one load and speed and another period of running at a different speed and load, both of which are too short to achieve respective steady-state temperatures. There is no time for rest.
Q16. Write the formula of moment of inertia by load equalization.
Ans. It is given by
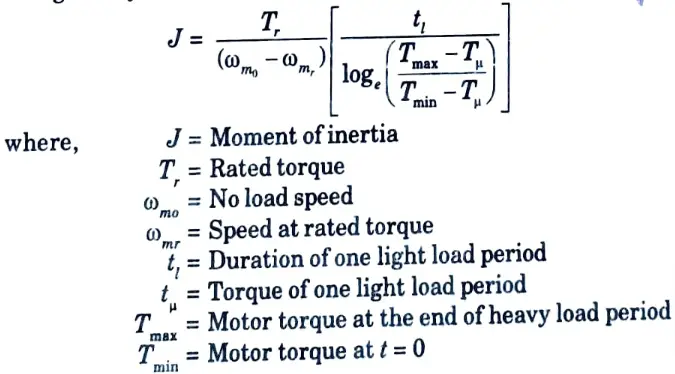


Q17. Why a motor smaller rating can be selected for a short time duty ?
Ans. 1. The time of drive operation is significantly less than the heating time constant in this case, and the machine is permitted to cool to room temperature before the motor is required to function again.
2. During this process, the machine can be overloaded until the temperature at the end of the loading reaches the allowable limit. As a result, for a short period job, a motor with a lower rating can be chosen.
Unit-III: Electric Braking (Short Question)
Q1. What are the disadvantages of mechanical braking ?
Ans.
- 1. Frequent maintenance.
- 2. Replacement of brake shoes.
- 3. Lower life.
- 4. Braking power is always wasted as heat.
Q2. What is the purpose of using electrical braking ?
Ans. The limitations of mechanical braking are overcome by employing electrical braking, in which a motor is configured to function as a generator, converting mechanical energy to electrical energy and providing torque in a direction opposing the motion.
Q3. Give the types of electric braking.
Ans. 1. Regenerative braking
2. Dynamic or rheostatic braking
3. Plugging or reverse voltage braking
Q4. In regenerative braking, generated energy is supplied to the source. Which condition must be satisfied for this ?
Ans. For this,
E > V and the armature current must be negative.
Q5. When plugging is employed for stopping on induction motor, why is it necessary to disconnect it from supply when speed reaches to zero ?
Ans. The direction of the stator field can be reversed by changing the phase sequence of the input to an induction motor. In practise, this is accomplished by switching the power supply between any two terminals of the motor. A brake torque is generated, and the motor comes to a rapid stop. When approaching zero speed, the motor must be disconnected from the power supply. Otherwise, the torque generated accelerates the motor in the other direction.
Q6. Why regenerative braking is not possible in series motor ?
Ans. In series motor, as speed increases, armature current increases and therefore flux decreases. Hence, regenerative braking is not possible in this.
Q7. Enumerate different types of braking of dc motor. Which one is usually employed and why ?
Ans. 1. Regenerative braking
2. Dynamic or rheostatic braking
3. Plugging or reverse voltage braking
Regenerative braking is commonly used because it eliminates the load’s inclination to accelerate the motor. It is also conceivable if the terminal voltage is rapidly reduced.
Q8. Which methods are employed for braking of an induction motors ?
Ans.
- 1. Regenerative braking
- 2. Plugging or reverse voltage braking
- 3. Dynamic braking:It is further categorised as:
- i. ac dynamic braking
- ii. self-excited braking using capacitors
- iii. dc dynamic braking
- iv. zero sequence braking
Q9. Sketch the graph of regenerative braking for induction motor.
Ans.
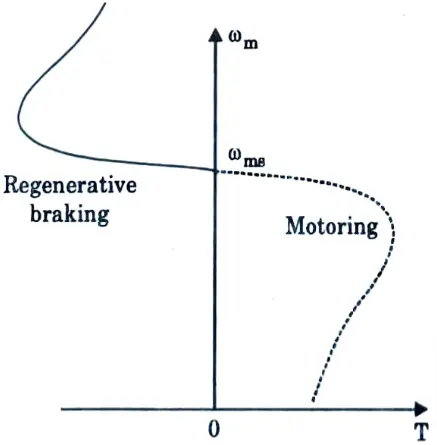


Q10. What is the advantage and disadvantage of regenerative braking of induction motor?
Ans. Advantage: The generated power is usefully employed.
Disadvantage: When fed from a constant frequency source, it cannot be employed below synchronous speed.
Q11. Why regenerative braking is mostly employed ?
Ans. Regenerative braking is commonly used because it eliminates the load’s inclination to accelerate the motor. This can also be used if the terminal voltage is rapidly reduced.
Q12. Why dc series motor is more suited to deal with torque overloads than other DC motor?
Ans. In case of series motor,
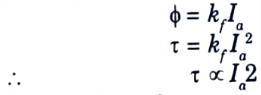
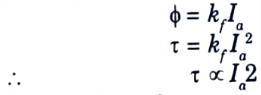
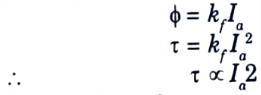
At condition of torque overload, plenty amount of current will be required from mains which may or may not be fulfilled. Hence, DC series motor is more suited to deal with torque overloads than other DC motor.
Q13. Write the features of de dynamic braking.
Ans.
- 1. The heat produced is less than that produced by plugging.
- 2. The motor can be stopped quickly.
- 3. The braking torque is proportional to the dc current squared.
- 4. The amount of energy dissipated by the motor is not affected by the magnitude of the dc current.
- 5. This method is applicable to induction motors with wound rotors or squirrel cage rotors.
Q14. What is the energy loss in a dc motor during transient?
Ans. It is given by
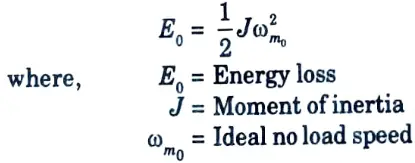
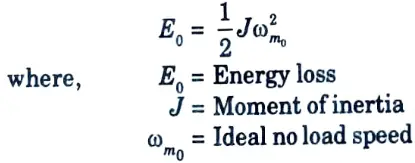
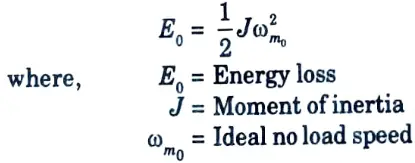
Q15. Mention the methods of reducing energy loss during starting.
Ans. 1. Reducing the moment of inertia of the rotor.
2. Starting of dc shunt motors by smooth adjustment of applied voltage.
3. Starting of multispeed induction motors in discrete steps of speed.
4. Starting of induction motors by smooth variation of supply frequency.
Unit-IV: Power Electronic Control of DC Drives (Short Question)
Q1. What is inversion ?
Ans. When 𝛂 > 90°, Va is negative and rectifier takes power from dc terminals and transfers it to ac mains. This operation of rectifier is called inversion and the rectifier is said to operate as an inverter.
Q2. Explain dual converter.
Ans. A dual converter is made up of two fully-controlled rectifiers that are connected in parallel across the armature.
Rectifier A provides positive motor current and voltage in either direction, allows motor control in quadrants I and IV, rectifier B provides motor control in quadrants III and II, because it gives negative motor current and voltage in either direction.
Q3. Discuss the two methods of control for the dual converter.
Ans. 1. In simultaneous control, both rectifiers are regulated at the same time. To avoid circulating current between the rectifiers, they are set to provide the same dc voltage across the motor terminals.
2. The non-simultaneous or non-circulating current control method controls one rectifier at a time. As a result, no circulating current flows.
Q4. Write the disadvantages which conventional Ward Leonard scheme has as compared to static Ward Leonard scheme.
Ans.
- 1. Higher initial cost.
- 2. Needs more floor space and proper foundation.
- 3. Larger weight and size.
- 4. Requires more frequent maintenance.
- 5. Higher noise.
- 6. Lower efficiency due to higher losses.
Q5. What are the disadvantages which static Ward Leonard scheme has in comparison with conventional?
Ans. 1. No provision is made for load equalization.
2. Has a low power factor, especially at low speeds.
3. It generates a significant number of harmonics, which has a negative impact on the quality of supply and the operation of the generating plant.
Q6. Give necessary expression for chopper control of separately excited dc motors in motoring mode.
Ans. Motoring control: During on-period of the transistor, 0 ≤ t ≤ tON the motor terminal voltage is V. The operation is described by



Q7. Discuss distortion of supply.
Ans. Harmonics exist in the source current of a rectifier. Current harmonics distort source voltage in a weak alternating current source with a high internal impedance. A temporary short circuit of lines during thyristor commutation creates strong current pulses, further distorting source voltage. Source voltage and current distortion can cause interference with other loads connected to the source as well as radio frequency interference in communication equipment.
Q8. Why self commutated devices are preferred over thyristor building choppers ?
Ans. 1. They can be commutated by a low power control signal.
2. They do not need commutation circuit.
3. They can be operated at a higher frequency for the same rating.
Q9. What is duty ratio or duty cycle ?
Ans. It is denoted by δ. Ratio of duty interval tON to chopper period T is called duty ratio or duty cycle.
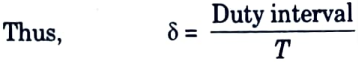
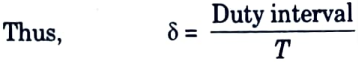
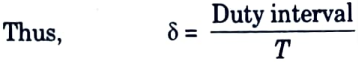
Q10. Sketch the graph of motoring and regenerative braking characteristics of chopper controlled series motor.
Ans.
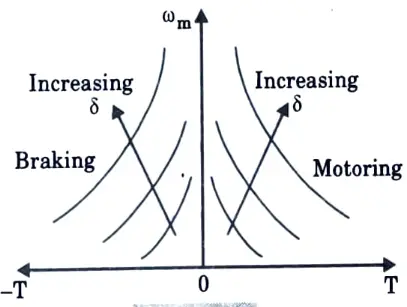


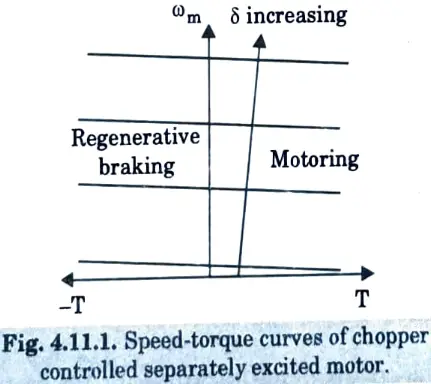
Q11. Sketch speed-torque curve for chopper controlled separately excited dc motor.
Ans.


Q12. Write any two advantages and disadvantages of de drive system.
Ans. Advantages:
- 1. No start-up problems with high torque.
- 2. Insensitivity to system voltage drops.
Disadvantages:
- 1. Motor requires maintenance.
- 2. Generally not suitable for harsh, explosive, or corrosive environments.
Q13. Why half wave converter is not used for supply to the field circuit of dc motor ?
Ans. To maintain constant flux, a field circuit requires continuous power supply, which a half wave converter does not offer. As a result, a half wave converter is not employed to supply the field circuit of a dc motor.
Q14. List any five applications of dc drive system.
Ans. 1. Machine tools
2. Plastic processing lines
3. Paper making and finishing machinery
Q15. What are disadvantages of dc drives due to which the three phase induction motor drive is replacing it ?
Ans.
- 1. The commutator adds bulk, cost, and weight to the motor. Sparking at the brushes renders it environmentally inappropriate in some areas.
- 2. Due to commutation, the highest speed and design rating are limited.
- 3. The commutator must be serviced on a regular basis.
- 4. The converter technology is well proven. The power converter is straightforward and affordable.
Unit-V: Power Electronic Control of AC Drives (Short Question)
Q1. Discuss VSI.
Ans. It is an abbreviation for Voltage Source Inverter. It enables the generation of a variable frequency supply from a de source. It can be used as a stepped wave or pulse-width modulated inverter.
Inverter output line and phase voltages are given by
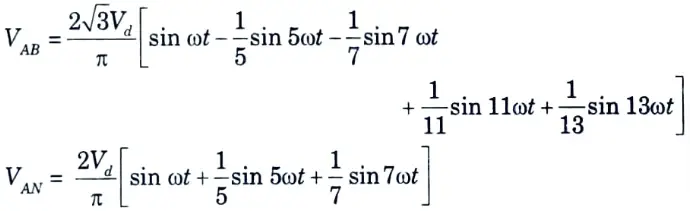
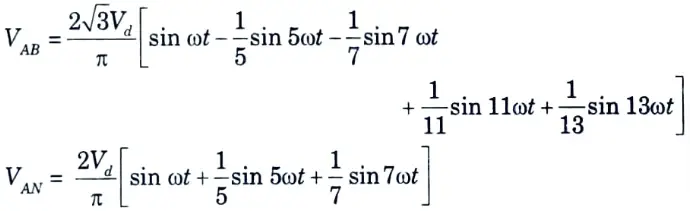
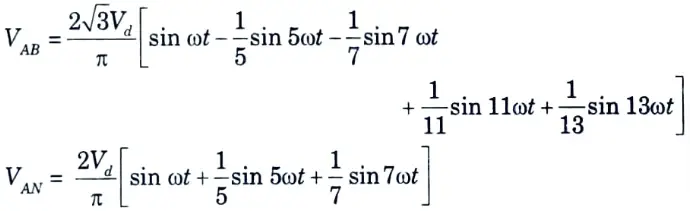
Q2. What are the drawbacks when an induction motor drive is fed from a stepped wave inverter ?
Ans. 1. Because of low frequency harmonics, motor losses rise at all speeds, resulting in motor derating.
2. The motor generates pulsating torques as a result of the fifth, seventh, eleventh, and thirteenth harmonics, resulting in jerky rotor motion at low speeds.
3. At low speeds, the harmonic content of motor current increases.
Q3. Write the applications of cycloconverter. How low speed operation is obtained ?
Ans. They are used in:
- 1. Ball mill
- 2. Cement plant
The low speed operation is achieved by feeding a motor with a large number of poles from a low frequency cycloconverter.
Q4. Why cycloconverter drives are called gearless drives ?
Ans. These are known as gearless drives because, unlike traditional drives, low speed load operation is attained without the use of a reduction gear, hence reducing the associated cost, space, and maintenance.
Q5. Why CSI is more reliable than VSI?
Ans. 1. The CSI drive has a larger cost, weight, and volume due to the huge inductance in the dc connection and big inverter capacitors, as well as a reduced speed range and secure dynamic response.
2. The CSI drive is incompatible with multimeter drives. As a result, each motor is powered by its own inverter and rectifier. A single converter can power multiple VSI motor systems connected in parallel. A single VSI can also power many motors connected in parallel.
Q6. Give the advantages of rotor resistance control.
Ans. 1. Motor torque capability remains unaltered even at low speeds.
2. Cost is very low.
Q7. Why rotor resistance control has low efficiency ?
Ans. It has low efficiency due to additional losses in resistor connected in the rotor circuit.
Q8. Why V/f is kept constant while controlling the speed of a three-phase induction motor ?
Ans.
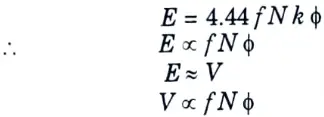
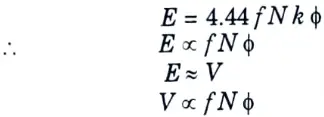
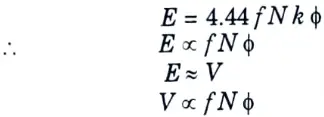
If only V is changed, the value of the flux changes, but the machine is intended for constant flux. V/f is kept constant for managing the speed of a three-phase induction motor in order to maintain flux constant.
Q9. Sketch the torque-speed curves for rotor resistance control.
Ans.
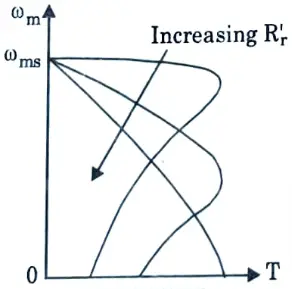


Q10. Mention the advantages of static rotor resistance control.
Ans.
- 1. Smooth and stepless control
- 2. Fast response
- 3. Less maintenance
- 4. Compact size
- 5. Simple closed-loop control
Q11. What is the maximum value of firing angle in static Scherbius drive and what is the reason behind this?
Ans. The maximum firing angle is limited to 165°. It is limited to this value in order to provide safe commutation to inverter thyristors.
Q12. In self-controlled synchronous motor drive employing a cycloconverter, why damper winding is removed ?
Ans. This is because the damper winding reduces the machine’s inductance and so filters out harmonics in the cycloconverter’s output voltage. Because the drive operates in self-control mode, the damper winding is not required for its traditional functions.
Q13. Write the advantages of brushless dc motors.
Ans.
- 1. No maintenance is required.
- 2. Long life.
- 3. High reliability.
- 4. Low inertia and friction.
- 5. Low radio frequency interference and noise.
Q15. Give the applications of brushless de motors.
Ans.
- 1. Record players.
- 2. Tape drive for video recorders.
- 3. Spindle drives in hard disk drives for computers.
- 4. Gyroscope motors.
- 5. Artificial heart pumps.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Electric Drives Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Electric Drives Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |
