Table Of Contents
With the help of Aktu Btech Quantum Notes, increase your understanding of IC Engines, Fuel, and Lubrication. These important, commonly asked questions will help you study for your tests. Improve your efficiency right now! Unit-5 Engine Cooling and Lubrication
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For IC Engine, Fuel and Lubrication: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Q1. Write the advantages and disadvantages of air and water cooling system.
Ans. A. Advantages of Air Cooling System:
- 1. Water is not needed because heat is transferred directly from the engine to the air.
- 2. Simplified engine design.
- 3. There is no requirement for antifreeze.
- 4. Little heat losses.
- 5. Improved performance during warm-up.
- 6. This cooling system is easier to control than a water cooling system.
- 7. The high mean cylinder temperature results in less carbon deposit.
B. Disadvantages of Air Cooling System:
- 1. Lower volumetric efficiency.
- 2. Not useful for high output engine.
- 3. Greater noise due to use of air fan.
C. Advantages of Water Cooling System:
- 1. Useful for high output engine.
- 2. This can be conveniently located wherever required.
- 3. Fuel consumption of high compression water cooled engine is lower.
- 4. Higher volumetric efficiency.
D. Disadvantages of Water Cooling System:
- 1. The use of a radiator makes the engine heavier and larger.
- 2. Need greater upkeep.
- 3. More climate-sensitive. Antifreeze solutions are used to make cold starting simpler.
- 4. Poor warm-up performance.
Q2. Sketch and explain working principle of a typical thermostat used in engine cooling system.
Ans.
- 1. It is made up of tiny copper tubes that are used as bellows and are partially filled with a volatile liquid, such as ether or methyl alcohol.
- 2. When the volatile liquid reaches the proper operating temperature, it turns into vapour, which generates enough pressure to inflate the bellows.
- 3. When temperature rises, the bellows movement opens the main valve, increasing or decreasing the flow of water from the engine to the radiator.
- 4. As a result, the valve opens and water circulation begins when the engine reaches its typical operating temperature.
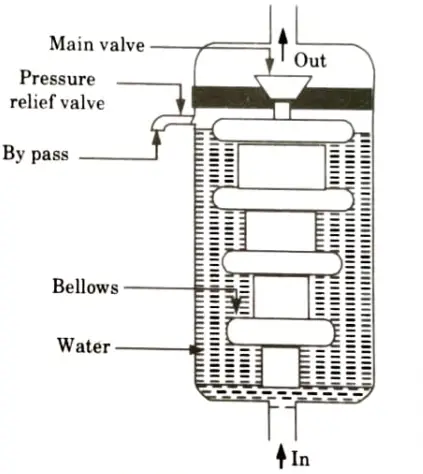


- 5. Gas condenses when the unit is closed, causing the pressure to drop.
- 6. The bellows deflate, the thermostat settles into place, and the airflow around it stops.
- 7. When the engine is running and the thermostat valve is closed, the pressure of the water being pumped increases, causing the pressure relief valve to open.
- 8. As a result, the water has finished moving through the by-pass.
Q3. Describe lubrication principle.
Ans.
- 1. When a proper weight is applied to it, the lubrication operates on the concept of lubricating oil being squeezed out.
- 2. Picture a block laying on a level surface that is coated in lubricant oil. The oil will squeeze out if the block weighs a lot or if the oil is thin. To put it another way, thick oil can support a heavier load than thin oil can Fig (a).
- 3. The lubrication principle can be described in different forms as follows:
- i. Hydrodynamic Lubrication:
- 1. A wedge-shaped oil film (Fig. (b)) forms between the moving block and the surface as the block is moved over it.
- 2. The leading edge of this wedge-shaped film is thicker than the back.
- 3. Hydrodynamic lubrication is the term used to describe this type of lubrication, in which an oil film in the shape of a wedge forms between two moving surfaces.
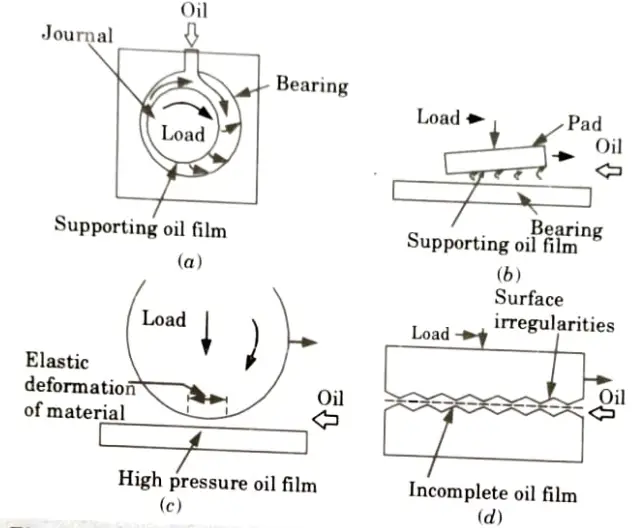


- ii. Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication:
- 1. The material itself deforms elastically Fig. (c) against the built-up oil pressure film when the load on the bearings is very high. Elastohydrodynamic lubrication is the name of this kind of lubrication.
- iii. Boundary Lubrication:
- 1. The lubrication is known as boundary lubrication if the film thickness between the two surfaces in relative motion becomes so thin that hydrodynamic oil film production is not possible and the surface high spots or asperities penetrate this thin film to produce metal-to-metal contact (d).
- 2. An excessive load, a thin oil, or a lack of oil owing to slow movement are possible causes of this problem.
- iv. Hydrostatic Lubrication: A thin oil coating in this lubrication prevents quick oil squeezing out when loads are reversed while moving relatively slowly.
Q4. What is crankcase ventilation and its types ?
Ans. A. Crankcase Ventilation:
- 1. An internal combustion engine’s crankcase can release gases in a regulated way through a crankcase ventilation system, which is a one-way route.
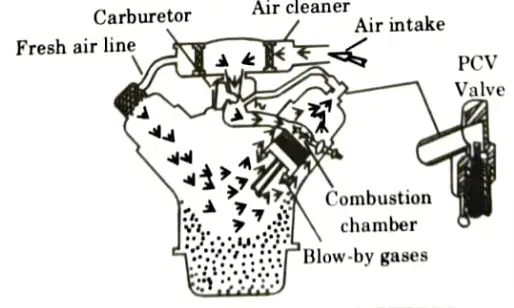


- 2. There are two main reasons due to which we have to adopt the crankcase ventilation:
- i. To get rid of the many impurities, including water, fuel, blow-by gases, etc., that get into the crankcase and could lead to sludge and metal part corrosion.
- ii. To release any pressure that has built up inside the crankcase and could have led to the crankshaft seal leaking.
B. Types of Crankcase Ventilation: There are two type of ventilation system:
- i. Open System:
- 1. This technique introduces fresh air into the crankcase during the compression stroke.
- 2. During the expansion stroke, the entering air picks up the impurities and releases them to the atmosphere.
- ii. Closed System:
- 1. The carburetor is used in this arrangement to transport fresh air to the crankcase.
- 2. To ensure that all of the crankcase gases are burned in the combustion chamber, the air cleaner and breather outlets are connected to the intake manifold using a PVC valve.
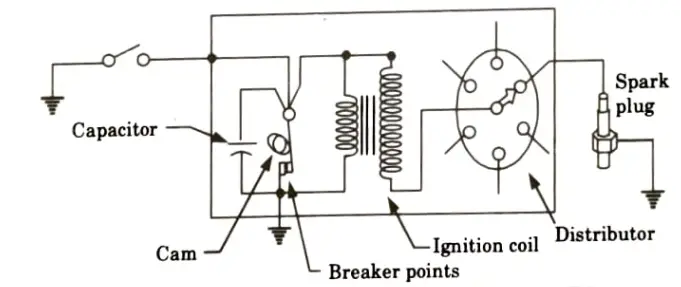
Q5. Describe high tension magneto ignition system with a neat sketch.
Ans.
- 1. The magneto ignition system is conceptually similar to the battery system, with the exception that a spinning permanent magnet creates the magnetic field in the core of the primary and secondary windings.
- 2. The field is produced as the magnet rotates, moving from a positive maximum to a negative maximum and back again.
- 3. When the magnetic field decreases from a positive maximum value, the primary winding induces a voltage and current.
- 4. The primary current generates its own magnetic field, which maintains the overall magnetic field that surrounds the primary and secondary windings at a relatively constant value.
- 5. The breaker points open and the magnetic field around the secondary winding abruptly changes from a high positive value to a high negative value after the permanent magnet has spun enough to make its contribution to the total field significantly negative.
- 6. This causes the secondary winding to generate a high voltage, which the distributor then directs to the appropriate spark plug.


Q6. What is the main function of a spark plug? Draw a neat sketch and explain its various parts.
Ans. A. Function of Spark Plug:
- 1. A spark plug’s primary job is to carry the high potential from the ignition system into the combustion chamber.
- 2. It offers the right space for the spark to be formed when high voltage is used to ignite the fuel in the combustion chamber.
B. Construction of Spark Plug:
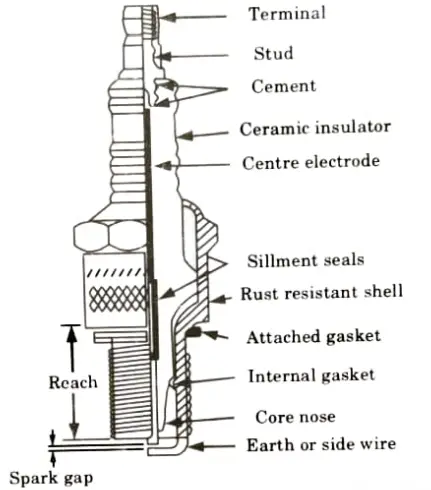


- i. Terminal: It is provided to connect the spark plug to the ignition system.
- ii. Insulator: Its primary purpose is to give the core electrode mechanical support and electrical insulation. Typically, ceramic materials are used to make it.
- iii. Centre Electrode: It is utilized to lessen the emission produced by the sparking and is wired internally to the terminal.
- iv. Seals: These are required to ensure there is no leakage from the combustion chamber.
- v. Metal Case/Shell: They withstand the torque created by lightening the plug, act as the ground for the sparks that travel from the central electrode to the side electrode, eliminate heat from the insulator, and go to the cylinder head.
- vi. Earth Electrode: They are available in order to improve heat conduction. High nickel steel was used to create these.
- vii. Gasket: An external gasket is utilised to seal the joint between the combustion chamber and the shell body, while an interior gasket is used to keep the insulator pressure tight inside the body.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
IC Engine, Fuel and Lubrication Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
IC Engine, Fuel and Lubrication Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |
