Explore AKTU B.Tech Quantum Book Short Question Notes on HVAC Systems. Learn about the basics of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, as well as how to build comfortable indoor spaces.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For HVAC Systems: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 4th Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Advanced Vapour Compression Cycles (Short Question)
Q1. Define vapour compression refrigeration system (VCRS).
Ans. 1. It is an upgraded sort of air refrigeration system that employs a suitable operating ingredient known as refrigerant.
2. The refrigerant remains in the system. It is alternately condensed and evaporated and cycled throughout the system.
Q2. Give advantages of vapour compression refrigeration system.
Ans. Advantages of vapour compression refrigeration system are as follows:
- 1. It has smaller size for the given capacity of refrigeration.
- 2. It has less running cost.
- 3. It can be employed over a large range of temperatures.
- 4. The coefficient of performance is quite high.
Q3. What are the types of vapour compression cycles ?
Ans. Types of vapour compression cycles are as follows:
- 1. Cycle with dry saturated vapour after compression.
- 2. Cycle with wet vapour after compression.
- 3. Cycle with superheated vapour after compression.
- 4. Cycle with superheated vapour before compression.
- 5. Cycle with undercooling or sub cooling of refrigerant.
Q4. Define transcritical cycle.
Ans. A closed thermodynamic cycle in which the working fluid passes through both subcritical and supercritical states is known as a transcritical cycle.
Q5. Mention disadvantages of transcritical cycle.
Ans. Disadvantages of transcritical cycle are as follows:
- 1. High pressures involved.
- 2. Systems are normally more complex than traditional ones.
Q6. Define refrigerant.
Ans. Refrigerant is a heat transporting medium that collects heat from a low temperature system and discards it to a higher temperature system during its cycle in the refrigeration system.
Q7. Discuss the nomenclature used for classifying refrigerants.
Ans. The general chemical formula for the refrigerant, either for methane or ethane base, is given as
CmHnClpFq in which n + p + q = 2m + 2
Where,
m = Number of carbon atoms,
n = Number of hydrogen atoms,
p = Number of chlorine atoms, and
q = Number of fluorine atoms.
After finding the values of m, n, q and p, the designation of refrigerant is achieved by the given formula:
R(m -1) (n + 1) (q)
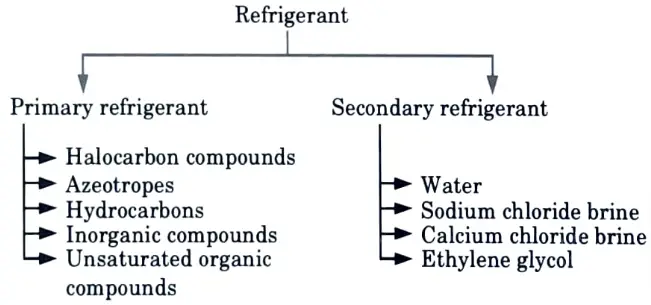
Q8. Classify refrigerants.
Ans.


Q9. Define primary and secondary refrigerant with example.
Ans. Primary Refrigerant: The refrigerants which directly take part in the refrigeration system are called primary refrigerants.
Examples: R-12, NH3 and SO2 etc.
Secondary Refrigerant: Secondary refrigerants are refrigerants that are first cooled by primary refrigerants and then used for cooling.
Examples: H2O, brine solution of NaCl and CaCl2 etc.
Q10. What is an azeotrope ?
Ans. Azeotrope is a stable blend of refrigerants with identical compositions in the vapour and liquid phases over a wide temperature range.
Examples: R-500, and R-502.
Q11. What are common refrigerant used in refrigeration system ?
Ans. The commonly used refrigerants in refrigeration system are ammonia (R-717), air (R-729), carbon dioxide (R-744), sulphur dioxide (R-764), water (R-110), etc.
Q12. Discuss effect of moisture and oil miscibility in refrigerants.
Ans. Effect of Moisture: The presence of moisture is crucial in refrigeration systems working at temperatures below 0 °C. If there is more water present than the refrigerant can dissolve, there is a risk of ice development and subsequent choking in the expansion valve or capillary tube used for throttling in the system.
Effect of Oil Miscibility: It improves lubrication, improves heat transfer, removes oil separation issues, and aids in the return of oil from the evaporator.
Unit-II: Review of Psychrometry (Short Question)
Q1. Define psychrometry.
Ans. Psychrometry is a field of engineering science that studies moist air, which is dry air mixed with water vapour or humidity.
Q2. List psychrometric properties of air.
Ans. Psychrometric properties of air are as follows:
- 1. Humidity,
- 2. Absolute humidity,
- 3. Relative humidity,
- 4. Dry bulb temperature, and
- 5. Wet bulb temperature.
Q3. Explain psychrometric process.
Ans. Psychrometric processes are those that impact the psychrometric qualities of air.
Q4. Define BPF and SHF.
Ans. By Pass Factor (BPF): It is defined as the ratio of actual change in temperature to the maximum change in temperature. It is denoted by x.
Sensible Heat Factor (SHF): The ratio of the sensible heat to the total heat is known as sensible heat factor (SHF) or sensible heat ratio (SHR).
Q5. Define GSHF and ADP.
Ans. GSHF: The grand sensible heat factor (GSHF) is the ratio of total sensible heat to grand total heat that the cooling coil or conditioning apparatus must handle.
ADP: The temperature at which the room sensible heat factor line crosses the saturation curve in a cooling with dehumidification operation is known as the apparatus dew point (ADP).
Q6. Define comfort air conditioning.
Ans. The dry bulb temperature and relative humidity of the air are brought to the required levels for human health, efficiency, and comfort.
Q7. Define industrial air conditioning.
Ans. The dry bulb temperature and relative humidity are kept constant in this for the proper operation of equipment and electrical items.
Q8. Write down advantages of summer air conditioning.
Ans. Advantages of summer air conditioning are as follows:
- 1. Hot air is converted into cold air.
- 2. Used in places where the product has to keep at a cool temperature for a long time.
Q9. Write down advantages of winter air conditioning.
Ans. Advantages of winter air conditioning are as follows:
- 1. Cold air is converted into hot air.
- 2. Used in places where the product has to kept at a warm temperature for a long time.
Q10. Define cooling.
Ans. Cooling is a general phenomena in which one media exchanges heat with another colder medium, either when separated by a barrier or when they mix, resulting in a lower temperature.
Q11. What factors are considered in design of a cold storage ?
Ans. Factors considered in design of a cold storage:
- 1. Storage temperature,
- 2. Relative humidity and air motion,
- 3. Mixed storage,
- 4. Condition of products at the time of entering storage, and
- 5. Product chilling.
Unit-III: Heat Pump and Ventilation (Short Question)
Q1. Define heat pump.
Ans. A heat pump is a device that extracts energy from air and uses it to heat or cool a place.
Q2. What do you understand by industrial heat pump ?
Ans. Industrial heat pumps are a type of active heat-recovery equipment that raises the temperature of a waste-heat stream to a higher, more useful temperature.
Q3. Define ventilation.
Ans. The replacement of indoor air with fresh outdoor air in order to dilute and remove air pollutants (substances that are harmful to humans) inside a structure is known as ventilation.
Q4. Mention advantages of natural ventilation.
Ans. Advantages of natural ventilation are as follows:
- 1. It provides a very high air-change rate at low cost, with a very simple system.
- 2. Low maintenance.
- 3. Improved air quality.
Q5. Define mechanical ventilation.
Ans. Mechanical ventilation systems are thought to be reliable in terms of supplying the intended flow rate, notwithstanding the effects of fluctuating wind and ambient temperature. Because mechanical ventilation is easily integrated into air conditioning, the temperature and humidity of the indoor air may be adjusted.
Q6. Mine ventilation is required why ?
Ans. Mine ventilation is required to provide oxygen to subterranean facilities, remove hazardous compounds such as hydrocarbon methane (CH4), radon, stratum gases, dust, blasting fumes, diesel emissions, and so on, as well as to remove heat and help control humidity.
Q7. What are the components of direct expansion system ?
Ans. Components of direct expansion system are as follows:
- 1. Compressor,
- 2. Condenser,
- 3. Expansion valve, and
- 4. Evaporator.
Q8. Define all water system.
Ans. The fluid employed in the thermal distribution system in all water systems is water, i.e., water transmits energy between the conditioned room and the air conditioning plant.
Q9. Write down advantages of all water system.
Ans. Advantages of all water system are as follows:
1. It can be used for new as well existing buildings (retrofitting).
2. Simultaneous cooling and heating is possible with 4-pipe systems.
Q10. Mention advantages of unitary system.
Ans. Advantages of unitary system:
- 1. There is saving in the installation and assembly labour charges.
- 2. Zoning and duct-work eliminated.
- 3. Only those rooms that require cooling will have units working, whereas the central plant will have to run continuously for the purpose of a few rooms.
Q11. Mention advantages of central system.
Ans. Advantages of central system:
- 1. Low investment cost as compared to total cost of separate unit.
- 2. Better accessibility for maintenance.
- 3. The running cost is less per unit of refrigeration.
Unit-IV: Load Calculation (Short Question)
Q1. What are the requirement of cooling or heating equipment ?
Ans. The key criterion for cooling or heating equipment is that it be able to remove or add heat at the rate at which it is produced or removed while maintaining the specified comfort levels in the room.
Q2. What are the various variables involve in estimation of load ?
Ans. The estimation of load involves the following variables:
- 1. Magnitude and direction of wind velocity.
- 2. Outside humidity and temperature.
- 3. Nature of construction, materials used.
Q3. Define direct radiation.
Ans. The portion of the sun’s radiation that penetrates through the atmosphere and immediately reaches the earth’s surface is referred to as beam or direct radiation.
Q4. Define diffuser or sky radiation.
Ans. The sun’s radiation is scattered, reflected back into space, and absorbed by the earth’s atmosphere in massive amounts. A portion of this radiation is re-radiated and uniformly reaches the earth’s surface from all directions. It’s known as diffuse or sky radiation. It does not generally alter with surface orientation.
Q5. Classify cooling load.
Ans. Cooling load can be classified as follows:
- i. Room Load: Which falls on the room directly.
- ii. Total Load: Which falls on the air-conditioning apparatus.
Q6. Define shading device.
Ans. Shutters, awnings, canopies, blinds, and projecting horizontal and vertical fins are examples of external shading devices.
Q7. Define evaporative cooling.
Ans. Heat is not added to nor taken from the water outside the air washer during the evaporative cooling process. A pump merely circulates the water.
Q8. Define infiltration.
Ans. The flow of outside air into conditioned space through door openings and cracks and interstices surrounding windows and doors is referred to as infiltration.
Q9. What are methods to empirical calculations of heat transfer through walls and roofs?
Ans. Methods to empirical calculations of heat transfer through walls and roofs are as follows:
- 1. Decrement factor and time lag method.
- 2. Equivalent temperature differential method.
Q10. Write down various measures of energy conservation in the air conditioning of buildings.
Ans. Energy conservation in the air conditioning of buildings can be achieved by adopting the following measures:
- 1. Minimisation of solar gain.
- 2. Other building design features and thermal properties of construction materials.
- 3. Minimizing infiltration and ventilation load.
Unit-V: Air Distribution (Short Question)
Q1. What is duct ? Why is it used ?
Ans. Ducts are passages or tubes used in heating and ventilation. Ducts are constructed when the conditioned air cannot be supplied directly from the air conditioning equipment to the spaces to be conditioned.
Q2. Why does pressure of air fall in the duct?
Ans. In the duct, pressure of air falls due to the following factors:
- 1. Frictional losses (due to surface friction), and
- 2. Dynamic losses (due to sudden changes in the direction of air flow, in velocity and eddy current).
Q3. Write the expression for calculating the heat gain through the ducts.
Ans. Expression for heat gain through ducts is given as follows:
QD = UAD (Ta – Ts)
Where,
U = Overall heat transfer coefficient,
AD = Surface area of the duct,
Ta = Temperature of ambient air, and
Ts = Temperature of supply air.
Q4. What are the various method of duct design ?
Ans. Following are the various method of duct design:
- 1. Velocity reduction method,
- 2. Equal pressure drop (or friction loss) method, and
- 3. Static regain method.
Q5. Define diffusers.
Ans. Diffusers are terminal devices that deliver air in several directions by using deflecting vanes.
Q6. Define grilles.
Ans. Grilles are defined as air devices that are typically used to return air back to the fan or to exhaust air from a space.
Q7. Define registers.
Ans. Registers resemble grilles, but they are made up of one-way or two-way adjustable air stream deflectors and dampers that limit the quantity of air flow that must be returned, supplied, or exhausted.
Q8. What are the effects of vibration ?
Ans. The undesirable effects of vibration are:
- 1. Breaking of brazed or soldered joint and consequent loss of charge.
- 2. Transmission of noise through piping and building.
Q9. Classify duct on basis of velocity.
Ans. On basis of velocity ducts classified into 3 basic categories:
- 1. Low velocity systems.
- 2. Medium velocity systems.
- 3. High velocity systems.
Q10. Classify duct on basis of pressure.
Ans. On basis of pressure duct classified into 3 basic categories:
- 1. Low pressure,
- 2. Medium pressure, and
- 3. High pressure.
Q11. What are the basic elements of control system?
Ans. A control system consists of five basic elements:
- 1. Input,
- 2. Process being controlled,
- 3. Output,
- 4. Sensing elements, and
- 5. Controller and actuating devices.
Q12. Define discharge gas lines.
Ans. Discharge gas lines (also known as hot gas lines) allow refrigerant to flow from the compressor’s discharge to the condenser’s input.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
HVAC Systems Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
HVAC Systems Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |