We’ve come to investigate the AKTU’s universal human values. The top most important questions and human values notes, Btech, that may appear in your upcoming exams such as Btech, MCA, and others. HERE Human Value UNIT-3
Guys 🤔.. You desire additional relevant information on the same. Don't forget to read this as well. Important Questions For Universal Human Values : *Unit-01 *Unit-02 *Unit-03 *Unit-04 *Unit-05 *Short-Q/Ans *Question-Paper with solution 21-22
Q1. What is the meaning of justice in human relationships? How does it follow from family to world family?
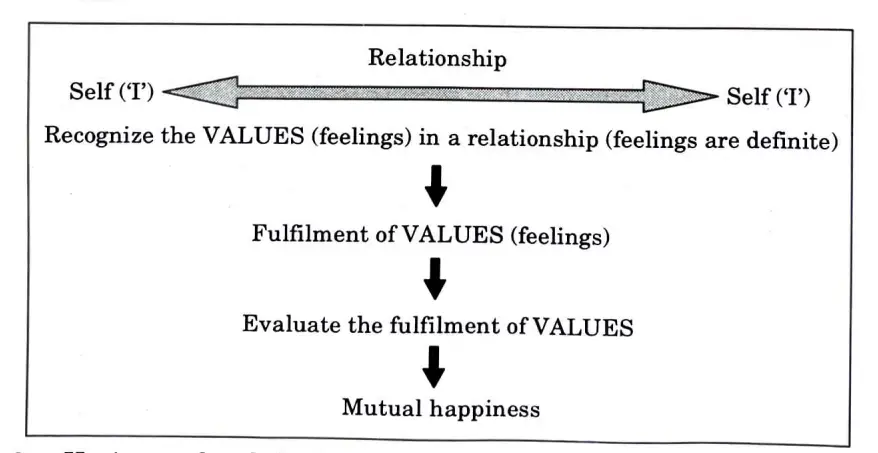
Ans. 1. Justice: Justice is the acceptance of values (the distinct sensations) in a relationship, their fulfilment, and the accurate assessment of the fulfilment leading to enjoyment for both parties. The appropriate arranging of people and things within a society is what justice is concerned with.
2. Elements of Justice: There are four elements:
i. Recognition of values.
ii. Fulfillment.
iii. Evaluation.
iv. Mutual happiness ensured.
When all the four are ensured, justice is ensured.
3. Justice is defined by mutual fulfilment, and justice is essential in all relationships. Justice begins with the family and gradually spreads to the global family. In the family, the child develops an understanding of justice. With this understanding, he enters society and interacts with others.
4. If justice is understood in the family, there will be justice in all of our interactions in the world at large.
5. We are governed by our petty prejudices and conditionings if we do not understand the values in relationships. We may classify people as high or low based on their physical appearance (specific caste, gender, race, or tribe), wealth, or belief systems. All of this is a source of injustice and leads to a fractured society, despite our natural acceptance of an undivided society and universal human order.


6. We can now investigate harmony in the family after investigating harmony in humans. This allows us to comprehend the harmony that exists between society and nature/existence. And in this way, the harmony in our lives grows, and we gain the ability to live in harmony with all human beings.
Q2. Explain the feelings of ‘care’ and ‘guidance’, ‘reverence’ and ‘gratitude’.
Ans. 1. Under Evaluation: When someone is given a lower rating than they deserve. The object under consideration appears pitiful. Underestimating someone means disrespecting them because it demonstrates that their abilities have been overlooked. This can lead to feelings of dissatisfaction.
2. Otherwise Evaluation: When we judge someone based on what they are not. It can mean overestimating someone or, in some cases, underestimating someone.
3. Care: The sensation of nurturing, caring for, and protecting our family and those around us. It is a natural feeling that parents have for their children.
4. Guidance: The desire to assist others and share your knowledge and experience. It is a feeling expressed by family elders and often by teachers towards their students.
5. Reverence: It means to respect and honour something or someone. It is a sense of honour and respect for someone who has achieved success in life.
6. Glory: People who have been able to live exemplary lives are rewarded. When someone works hard to achieve excellence and succeeds. Their lives become a model for future generations to follow. This creates a sense of glory.
7. Gratitude: It is a sense of gratitude and honour for those who have made significant contributions to our lives.
8. Love: It is a sense of affection, and relatedness to people around us.
Q3. Differentiate between intention and competence. How do we come to confuse between the two?
Ans. Trust:
1. The foundational value in all relationships is trust, or vishwas. “Being assured that each human being inherently wants oneself and the other to be happy and prosperous” is what trust entails.
2. Mutual trust is the shared belief that we can rely on one another to achieve a common goal. People expect to be able to rely on our word when they trust us. It is built on trust and consistency in relationships.
3. There are two aspects in trust:
i. Intention (wanting to our natural acceptance)
ii. Competence (being able to do).
Difference Between Intention and Competence:
1. Intention is what we strive for (our natural acceptance), and competence is the ability to achieve that goal.
2. Every human being intends to do the right thing; however, competence may be lacking, which must be developed through proper understanding and practise.
3. But today, when we judge ourselves, we are judging on the basis of our intention, whereas when we judge others, we are judging them on the basis of their competence.
4. We trust our own intentions but are hesitant to trust the intentions of others. The same is true for others. We discover that while we are certain of our own intention, we are unsure of the intention of others. We are observing their competence and drawing conclusions about their intent.
5. As a result, mistrust develops, and we reject the relationship. We rarely consider our own competence and the intentions of others. It is critical to distinguish between intention and competence. If we have faith in the other person’s intentions, we feel connected to him and begin to help him improve his competence if he lacks it.
Q4. What are the dimension of trust? Explain.
Ans. Trust:
1. The foundational value in all relationships is trust, or vishwas. “Being assured that each human being inherently wants oneself and the other to be happy and prosperous” is what trust entails.
2. Mutual trust is the shared belief that we can rely on one another to achieve a common goal. People expect to be able to rely on our word when they trust us. It is built on trust and consistency in relationships.
3. There are two aspects in trust:
i. Intention (wanting to our natural acceptance)
ii. Competence (being able to do).
To develop trust we need to:
1. Be Consistent in our Actions: Consistency in action will help to dispel any suspicion.
2. Faith in Competencies: We should not doubt the capabilities of the people we trust.
3. Do not Keep Secrets: In any relationship, secrets erode trust. When we hide information, people make assumptions about our actions; we would have to lie to keep our secrets hidden. Lies and incorrect assumptions can harm a relationship.
4. Do not Pretend: When we are true to ourselves, it is easier for those around us to believe and interact with us. If we are true to ourselves, all of our relationships will be strong.
Ans. The programme required to achieve comprehension human goals is right understanding among human beings and to facilitate the fulfilment of the basic aspirations of all human beings in society.
There are following comprehensive human goals:
1. Right Understanding (Samadhan): It has been observed that right understanding is the most important need for every human being in order to escape from all contradictions among humans and create harmony among them.
2. Prosperity (Samridhi): Prosperity is critical in the family. It’s a good feeling to have more than enough physical space. Family members must identify their needs and be able to produce/achieve more than what is required. This is referred to as Prosperity.
3. Fearlessness or Trust (Abhay): This goal is appealing to the family, society, and the individual. Trust in society implies that every member feels/realizes a connection to everyone else in the society. They are fearless. As a result, people in society are feeling fearless and free to do whatever they want.
4. Co-Existence (Sah-Astitiva): If there is coexistence in nature, it means that there is a relationship and compatibility between all of the entities in nature. Human beings are also among them. They are devoid of all creeds, castes, religions, and cultures.
The programs needed to achieve these comprehensive human goals are:
1. Education – Right living (Shiksha-Sanskar) :
Education: Meaning to comprehend harmony at all four levels: individual, family, society, and nature.
Sanskar : Refers to live in harmony at all four levels of living.
2. Health Self Regulation (Svasthya-Sanyam) :
Health: When the body is fit to act in accordance with the needs of ‘I,’ and all of the body’s parts are in harmony.
Sanyam : A sense of responsibility for nurturing, protecting, and properly utilising one’s body. It is the foundation of svasthya.
3. Justice – Preservation (Nyaya-Suraksha) :
Justice: It refers to being fair with all human beings
Preservation: It refers to the harmony that exists between humans and the rest of nature.
4. Production Work (Utpadan-karya) :
Production: It refers to the output/physical produce that is obtained by human efforts.
Work: The labour that human does.
5. Exchange – Storage (Vinimaya-kash):
Exchange: It means that the exchange of physical facilities between members of the society.
Storage: It refers to the storage of physical facilities.
Thus, these are the programs needed to achieve the comprehensive human goal.
Q6. What is Universal Human Order? How it can be realized?
Ans. Universal Human Order:
1. The Universal Human Order is defined as living in harmony with oneself from the individual level to the level of the entire order or existence.
2. Only right understanding can bring about Universal Human Order. Except for the human being, the entire existence and all orders create harmony. The Universal Order reveals all aspects of human behaviour, education, and health in a fragmented society. The transition from family to world family is referred to as undivided society.
Family → Family Cluster → Village →Village Cluster → World Family.
3. It is possible with the proper understanding. Work in universal order is required. It is only right understanding that provides us with the foundation for a humanistic constitution, which is required to provide clear guidelines and policies framework conductive to the development of an undivided human society and a universal human order. Working toward comprehensive human goals and developing human ethical competency will be among the salient principles of universal human order.
4. Nowadays, human society is divided into many castes, races, religions, and nationalities, each with its own set of goals and efforts. Our primary focus is on resolving these conflicts and contradictions. Human beings expend a lot of effort and resources preparing for war in order to ensure peace. This is solely due to a lack of understanding on our part.
5. Therefore, we must carry out our responsibilities in a proper manner to preserve an unbroken community.



Important Question Unit wise…🤔
Such a Great Idea😍
Now Exam Made Easy…😊
Important Questions For Universal Human Values -B.Tech AKTU
| Important Question | Question Links |
|---|---|
| human values notes – Unit-1 | UNIT-1 |
| human values notes – Unit-2 | UNIT-2 |
| human values notes – Unit-3 | UNIT-3 |
| human values notes – Unit-4 | UNIT-4 |
| human values notes – Unit-5 | Unit-5 |
| human Values Short Questions | short-questions |
| human values Question-paper | 2021-22 |
AKTU Important Links
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |

3 thoughts on “Universal human values notes – AKTU (Unit-3)”