Discover B.Tech AKTU Quantum Book Short Artificial Intelligence Question Notes. Discover the fundamentals of machine learning and neural networks, as well as insights into intelligent problem-solving and automation.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Artificial Intelligence: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 4th Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Introduction Artificial Intelligence (Short Question)
Q1. What do you mean by intelligent agent ?
Ans. An intelligent agent is a self-contained creature that operates on its surroundings utilising sensors and actuators to achieve its objectives. To attain their objectives, intelligent agents may learn from their surroundings.
Q2. Describe how can we use artificial intelligence in natural language processing ?
Ans.
- 1. Al enables computers to take spoken words as dictation or to follow voice commands via software.
- 2. AI programs can communicate with humans in a natural manner because natural language is one of the most significant communication mediums.
- 3. To comprehend natural language, a programme must be well-versed in its structure, including what words are and how they mix to form phrases and sentences.
Q3. What are goals of AI?
Ans. Goals of AI are:
- 1. To create expert systems: The systems which exhibit intelligent behavior, learn, demonstrate, explain, and advice its users.
- 2. To implement human intelligence in machines: Creating systems that understand, think, learn, and behave like humans.
Q4. Define learning agent with the help of architecture.
Ans. A learning agent is an AI technology that can learn from its experiences. Learning agents may complete tasks, analyse performance, and seek new ways to improve on those tasks.
Architecture of learning agent :
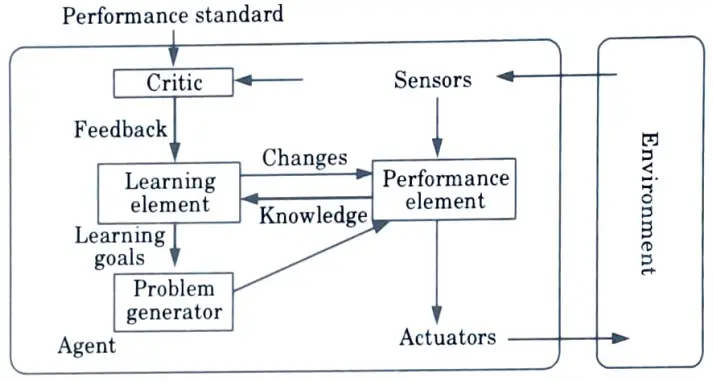


Q5. Design the PEAS measure for Satellite Agent”.
Ans. The PEAS measures for satellite agent are:
Performance measure : Correct image categorization.
Environment : Downlink from orbiting satellite.
Actuators : Display categorization of scene.
Sensors : Colour pixel arrays.
Q6. List down the characteristics of agent.
Ans. Characteristics of learning agent :
- 1. Situatedness
- 2. Autonomy
- 3. Adaptivity
- 4. Sociability
Q7. What are the four components to define a problem ?
Ans. The four components to define a problem are:
- 1. Initial state
- 2. A description of possible action
- 3. The goal test
- 4. A path cost function
Q8. What are the job roles in AI career ?
Ans. Job roles in Al career are :
- 1. Software analyst and developers.
- 2. Computer scientist and computer engineers.
- 3. Algorithm specialist
- 4. Surgical technicians working with robotic tools.
Q9. What are the two main kinds of problem formulation ?
Ans. Two main kinds of problem formulation :
- 1. Incremental formulation
- 2. Complete state formulation
Q10. Write the history of artificial intelligence.
Ans. History of AI:
- 1. Beginning of AI (1943).
- 2. AI knowledge-based expert system (1970).
- 3. Machine learning (1998).
- 4. Supervised learning (2004).
- 5. Unsupervised learning (2010).
- 6. Genetic programming (2010)
- 7. Vaccines development, autonomous vehicles, language processing, and quantum computing (2021 onwards).
Unit-II: Problem Solving Methods (Short Question)
Q1. List some of the uniform search technique.
Ans. Uniform search technique is of following types:
- 1. Breadth First Search
- 2. Depth First Search
- 3. Uniform cost search
Q2. Justify the use of searching in game.
Ans.
- 1. Search algorithm (searching) is used in games to figure out a strategy.
- 2. The algorithms search through the possibilities and pick the best move.
- 3. Consider the following parameters: speed, accuracy, complexity, and so forth.
- 4. These algorithms assess all accessible actions at the time and then evaluate their future moves in light of these alternatives.
- 5. The purpose of these algorithms is to determine the best series of moves to help them get to the end result.
Q3. Define uninformed search.
Ans. Uninformed search is employed by search procedures that investigate all options during the search process. They lack domain knowledge. They just require the initial state, the final state, and a set of valid operators.
Q4. Write down the time and space complexity of DFS search strategies.
Ans. The time complexity of the depth first search (DFS) is O(bd). The space complexity of depth first search (DFS) is Od).
Q5. Give the desirable properties of search algorithms.
Ans. Properties of heuristic search algorithms are :
- 1. Completeness
- 2. Space complexity
- 3. Time complexity
- 4. Optimality
Q6. What are problems in hill climbing ?
Ans. Problems in hill climbing:
- i. Local maxima
- ii. Plateau
- iii. Ridge
Q7. What is constraint satisfaction procedure ?
Ans. Constraint satisfaction is a search process that operates on constraint sets in a space. The constraints specified in the problem description are included in the starting state.
Q8. Define alpha-beta pruning.
Ans. The min-max method has been improved to include alpha-beta pruning. It is a way for optimising the min-max algorithm.
Q9. What are the advantages of local search algorithm ?
Ans. Advantages of local search algorithm are:
- 1. They use very little and constant amount of energy.
- 2. They have the ability to find reasonable solution for finite state spaces.
Q10. Define the term game.
Ans. The term game refers to a type of conflict in which n persons or groups (referred to as players) take part.
Q11. What are the characteristics of game playing ?
Ans. Factors affecting the state space graph complexity are :
- 1. Branching factor.
- 2. Depth of goal node.
- 3. Maximum length of path.
Q12. How do we evaluate performance of problem solving method ?
Ans. Problem solving algorithm’s performance can be evaluated on the basis of following four factors:
- 1. Completeness.
- 2. Optimality.
- 3. Time complexity.
- 4. Space complexity.
Q13. What are the basic methods available for game playing ?
Ans. The basic methods available for game playing are :
- 1. Minimax strategy.
- 2. Minimax strategy with alpha- beta cutoffs.
Q14. What is heuristic function ?
Ans. A heuristic function is a function in search algorithms that ranks alternatives depending on available information at each branching step to determine which branch to pursue.
Q15. Describe optimal problem with suitable example.
Ans.
- i. An optimization problem is the problem of finding the best solution from all feasible solutions. An optimization problem is given as:
- 1. A set of variables, each with an associated domain.
- 2. An objective function that maps total assignments to real numbers.
- 3. An optimality criterion is to find a total assignment that minimizes or maximizes the objective function.
- ii. The aim is to find a total assignment that is optimal according to the optimality criterion.
Example: TSP (Travelling Salesman Problem).
Q16. What are the basic methods available for game playing ?
Ans. The basic methods available for game playing are:
- 1. Minimax strategy
- 2. Minimax strategy with alpha-beta cutoffs.
Unit-III: Knowledge Representation (Short Question)
Q1. List various issues in knowledge representation.
Ans. Issues in knowledge representation :
- 1. Important attributes
- 2. Relationship among attributes
- 3. Choosing granularity
- 4. Set of objects
- 5. Finding right structure
Q2. List various schemes of knowledge representation.
Ans. Various schemes of knowledge representation:
- 1. Simple relational knowledge
- 2. Inheritable knowledge
- 3. Inferential knowledge
- 4. Procedural knowledge
Q3. Define inference.
Ans. In artificial intelligence, we need clever computers that can generate new reasoning from old logic or from evidence, therefore inference is the process of producing conclusions from evidence and facts. Inference rules are the typical patterns of inference that can be used to construct chains of conclusions that lead to the intended aim. Modus Ponens is the most well-known rule.
Q4. State soundness property of inference.
Ans. An inference procedure ⊢ is sound if whenever p ⊢ q then it is also the case that p ⊨ q.
In logic, the concept of soundness is used. We employ the syntax of the knowledge representation language whenever we develop a knowledge-based programme, we assign semantics in some fashion, and the reasoning mechanism describes the inference methods.
Q5. What are the types of variable in FOC?
Ans. There are two types of variables in First order logic :
- 1. Free variable: A variable is said to be a free variable in a formula if it occurs outside the scope of the quantifier. For example: ∀ x Ǝ (y)[P (r, y, 2)], where z is a free variable.
- 2. Bound variable: A variable is said to be a bound variable in a formula ifit occurs within the scope of the quantifier. For example: ∀ x [A(x) B(y)], here x and y are the bound variables.
Q6. Differentiate between forward and backward chaining.
Ans.
| S. No. | Forward chaining | Backward chaining |
| 1. | Forward chaining is a data driven method. | Backward chaining is a goal driven method. |
| 2. | It uses planning, monitoring and controlling method. | It uses diagnosis method. |
| 3. | It uses bottom-up processing. | It uses top-down processing. |
| 4. | Forward chaining looks for possible conclusions that are supported by supplied information. | Backward chaining finds facts that support a given hypothesis. |
| 5. | Forward chaining is similar to breadth-first search. | Backward chaining is similar to depth-first search. |
| 6. | For example: CLIPS. | For example: PROLOG. |
Q7. What are main features of Prolog ?
Ans. Main features of Prolog are :
- 1. Rule-based programming
- 2. Built-in pattern matching
- 3. Backtracking execution
Q8. Define unification.
Ans. Unification is the process of identifying substitutes for lifted inference rules that can make diverse logical expressions appear similar (same).
Q9. What is resolution ?
Ans. In predicate logic, resolution is a proof, a procedure that performs a particular action, or the variety or processes involved in reasoning about claims.
Q10. What is ontological engineering ?
Ans. Ontological Engineering is described as the process of describing abstract concepts such as actions and time that are tied to real-world domains.
Q11. Define semantic network.
Ans. A semantic network is a graph that has nodes that represent objects and their categories and arcs that show interactions between things.
Q12. What are the inference techniques used in description logic?
Ans. Inference techniques used in description logic are :
- i. Subsumption
- ii. Classification.
- iii. Consistency
Q13. Write down the properties of forward chaining.
Ans. Properties of forward chaining :
- 1. It is a down-up approach, as it moves from bottom to top.
- 2. It is the process of reaching a conclusion based on known facts or data, beginning with the initial state and progressing to the desired state.
- 3. The forward chaining strategy is also known as data-driven since we achieve our aim by utilising accessible data.
Q14. Define universal generalization.
Ans. Universal generalization is a valid inference rule which states that if premise P(c) is true for any arbitrary element c in the universe of discourse, then we can have a conclusion as ∀ x P(x).
Q15. What are the properties of first order logic ?
Ans. Properties of first order logic :
- 1. It can express facts about some or all of the universe’s objects.
- 2. It enables the representation of real-world legislation and rules.
- 3. It is useful in the domains of mathematics, philosophy, and artificial intelligence.
- 4. It represents facts in a more realistic way than just true or false statements.
Unit-IV: Software Agents (Short Question)
Q1. Define intelligent agent ?
Ans. An intelligent agent is an Al agent that can take flexible autonomous action to achieve its design goals.
Q2. What is logic based agent architecture ?
Ans. The classic method to developing artificially intelligent systems holds that intelligent behaviour can be formed in a system by supplying it with a symbolic representation of its environment and desired behaviour, and then manipulating this representation syntactically.
Q3. Write down the advantages of reactive agent ?
Ans. The major advantages of reactive approaches are:
- 1. Simplicity
- 2. Economy
- 3. Computational tractability
- 4. Robustness against failure
Q4. Define the term “belief” in BDI architecture ?
Ans. Beliefs represent the agent’s informational state, or its beliefs about the world (including itself and other agents).
Q5. Write down the advantages of BDI architecture.
Ans. Advantages of BDI architecture :
- a. Easy to understand.
- b. Clear functional decomposition.
Q6. Write down the characteristics of multi-agent system.
Ans. Characteristics of multi-agent system :
- 1. Each agent has just incomplete information and is restricted in its capabilities.
- 2. The system control is distributed.
- 3. Data is decentralized.
- 4. Computation is asynchronous.
Q7. What are the attributes of negotiation mechanism ?
Ans. Attributes of negotiation mechanism are:
- 1. Efficiency
- 2. Simplicity
- 3. Distribution
Q8. What is TMS in multi-agent system ?
Ans. A truth maintenance system (TMS) in a multi-agent system is designed to ensure the integrity of an agent’s knowledge, which should be stable, properly found, and logically consistent.
Unit-V: Applications (Short Question)
Q1. Define speech recognition.
Ans. Speech recognition is the process by which a computer recognises and responds to spoken words before converting them into a machine-readable format. Depending on the end purpose, the machine may subsequently convert it into another kind of data.
Q2. Define natural language processing.
Ans. Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the study of the challenges inherent in the processing and manipulation of natural language in order to make computers understand human-written assertions.
Q3. What are the applications of speech recognition ?
Ans.
- 1. Automotive
- 2. Technology
- 3. Healthcare
- 4. Sales
Q4. Write down the applications of NLP.
Ans. Applications of NLP:
- a. Natural language interfaces to databases.
- b. Machine translation.
- c. Advanced word-processing tools.
- d. Explanation generation for expert systems.
Q5. Define machine translation.
Ans. Machine translation is the process of automatically transforming text from one language to another.
Q6. What are the types of machine translation system ?
Ans. Types of machine translation system :
- 1. Bilingual MT System: Bilingual MT systems produce translations between two particular languages.
- 2. Multilingual MT System: Multilingual MT systems can generate translations between any two languages. They can be either unidirectional or bidirectional.
Q7. What are Robots?
Ans. Robots are artificial agents that operate in the real world. Robots are designed to manipulate objects by perceiving, picking, moving, adjusting the physical qualities of the object, destroying it, or having an effect, so releasing people from repetitive tasks without becoming bored, distracted, or weary.
Q8. What are types of locomotion ?
Ans. Following are various types of locomotion :
- 1. Legged Locomotion
- 2. Wheeled Locomotion
- 3. Slip/Skid Locomotion
Q9. Define robot locomotion.
Ans. Locomotion is the mechanism that makes a robot capable of moving in its environment.
Q10. What are the Applications of artificial intelligence?
Ans. Following are the applications of artificial intelligence :
- 1. Gaming
- 2. Natural language processing
- 3. Expert systems
- 4. Vision systems
Q11. Write down various types of models ?
Ans. Following are various types of models :
- 1. State machines
- 2. Rule
- 3. Logic
- 4. Probabilistic models
Q12. Define information retrieval.
Ans. The process of distributing documents/text/data in which the user is interested is known as information retrieval.
Q13. What are the characteristics of information retrieval ?
Ans. Characteristics of information retrieval:
- 1. A huge data/document collection.
- 2. A format of query with standard query language.
- 3. The generated result model.
- 4. Displaying results model.
Q14. What is information extraction ?
Ans. Information extraction is the technique of creating database entries.
Q15. Define mobile robot.
Ans. A mobile robot is nothing more than a collection of hardware and computational components.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Artificial Intelligence Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Artificial Intelligence Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |
