Utilise Quantum Notes to improve your structural analysis coursework. For your Aktu Btech examinations, find important, commonly asked questions. Gain academic success with our assistance! Unit-5 Analysis of Arches
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Structural Analysis: * Aktu Quantum * B.tech-Syllabus * Circulars * B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Q1. Discuss what types of straining actions are sustained by an arch ?
Ans.
- 1. Consider a cross-section PQ of the arch Fig.(c). Let T be the resultant thrust acting through D along the linear arch.
- 2. Thrust T is neither normal to the cross-section nor does it act through the centre C of the cross-section.
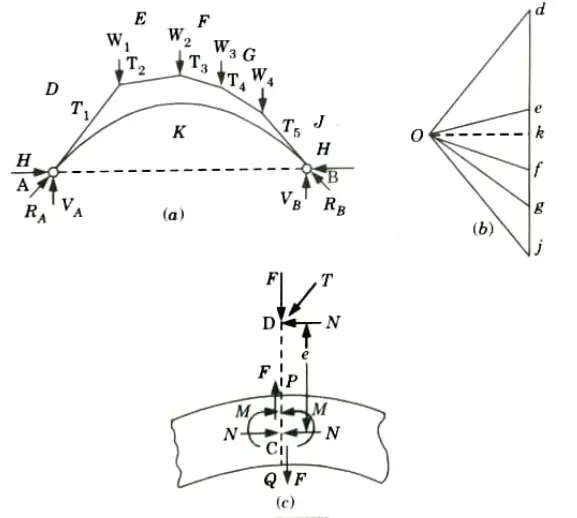


- 3. Resultant thrust T can be resolved normal and tangential to the section PQ.
- 4. Let N be the normal component and F be the tangential component.
- 5. The tangential component F will cause shear force at the section PQ and normal component N acts eccentrically, the eccentricity being equal to CD.
- 6. Thus the action of N acting at D is two fold.
- i. A normal thrust Nat C
- ii. A bending moment, M = N. e at C.
- 7. Hence unlike beams a section of arch is subjected to three straining actions.
- i. Shear force, F
- ii. Bending moment, M
- iii. Normal thrust, N
- Sometimes shear force F is also known as radial shear.
Q2. Show that the parabolic shape is a funicular shape for a three hinged arch subjected to a uniformly distributed load over its entire span.
Ans. 1. Let L = Span of the arch,
h = Central rise, and
w = UDL applied on the arch.
2. From symmetry we have,


3. For horizontal thrust, taking moment about C,
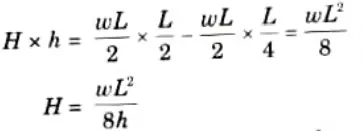
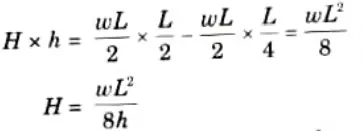
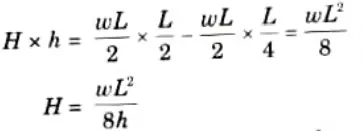
4. Let us now consider any section at distance x from A
Equation of parabola is given by,
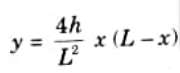
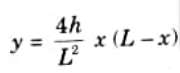
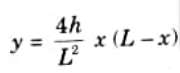
5. The value of bending moment at any section of the arch,
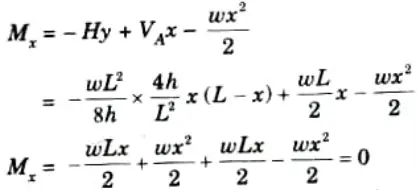
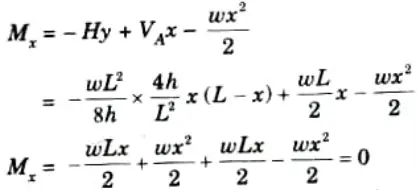
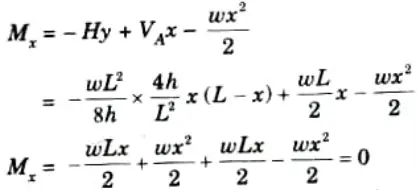
6. A parabolic arch therefore prone to a UDL The bending moment is zero at any point over its whole length. For this reason, a funicular shape is a parabolic shape for a three-hinged arch.
Q3. With a neat sketch describe about spandrel braced arch.
Ans. Spandrel Braced Arch:
- 1. A three hinged spandrel braced arch is shown in the Fig.
- 2. The spandrel of the arch in a spandrel braced arch refers to the area above the arch rib and below the level of the crown.
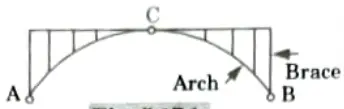


Types of Spandrel Braced Arch: The spandrel braced arch can be of following types:
- 1. Closed Spandrel Arch: The area above the arch rib and below the level of the crown in a closed spandrel arch can be filled.
- 2. Open Spandrel Arch: In an open spandrel arch, a truss-like system can be used to fill the space above the arch rib and below the level of the crown.
- Note: The spandrel is often filled with dirt in the case of concrete and masonry arch bridges with short spans.
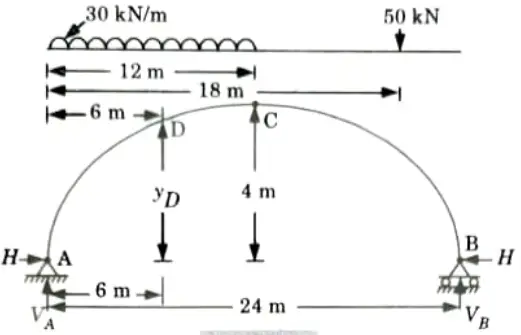
Q4. A three hinged parabolic arch hinged at the supports and at the crown has a span of 24 m and a central rise of 4 m. It carries concentrated load of 50 kN at 18 m from the left support and UDL of 30 kN/m over the left portion. Determine the normal thrust, radial shear at a section 6 m from the left hand support.
Ans. Given: Span of arch, L = 24 m, Central rise of arch, h = 4m
Concentrated load, W= 50 kN, Intensity of UDL, w = 30 kN/m
Distance of section = 6m
To Find: Normal thrust and Radial shear.
1. The arch is shown in Fig. Taking moment about support B, we get
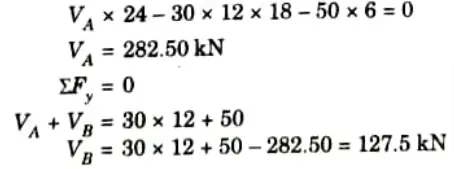
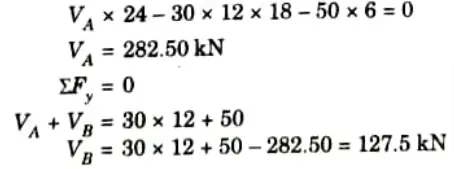
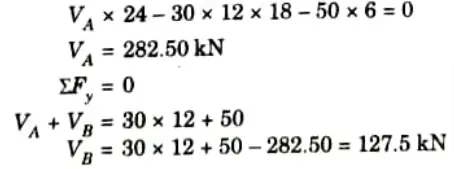


2. Taking moment about crown C (Right part),



Q5. A three hinged parabolic arch of 50 m span and a rise of 10 m is subjected to a uniformly distributed load of 20 kN/m intensity over its left half portion and point load of 100 kN at right quarter span. Calculate the bending moment, normal thrust and radial shear at a section 10 m from the left support.
Ans. Given: Span of arch, L = 50 m, Rise of arch, h = 10 mm
Intensity of UDL, w = 20 kN/m, Point load, W = 100 kN
To Find: BM, Normal thrust and Radial shear.
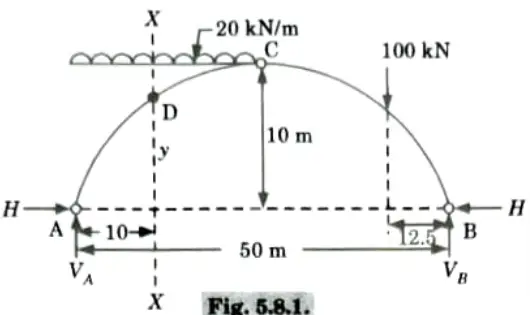


1. Reactions at supports :
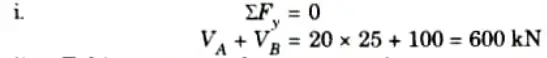
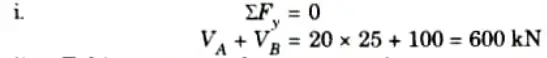
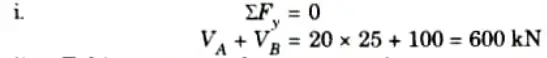
ii. Taking moment about support A,



iii. Taking moment about C,
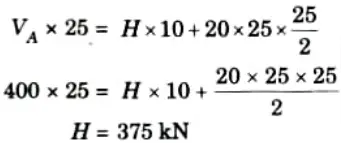
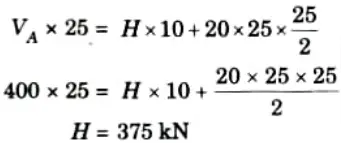
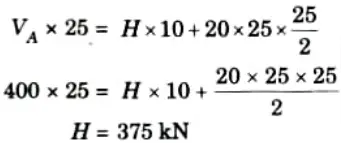
2. Bending Moment at Section D:
i. Let a section X-X at a distance 10 m from A.
Rise of arch at section D,
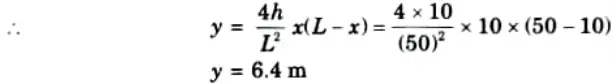
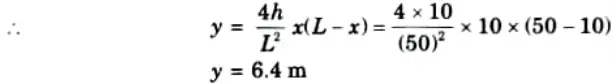
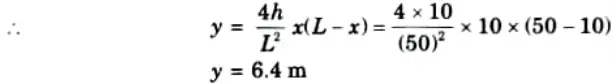
ii. Bending moment at D,
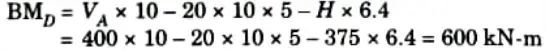
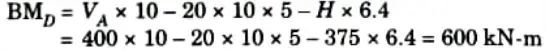
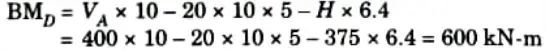
3. Normal Thrust and Radial Shear at Section D:
i. Consider the equilibrium of the part AD of arch.
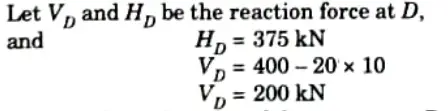
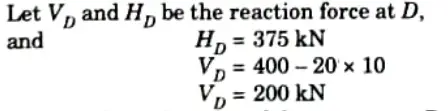
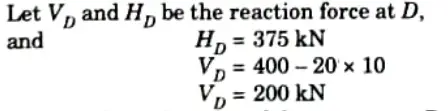
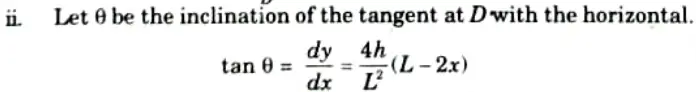
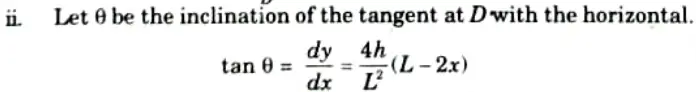
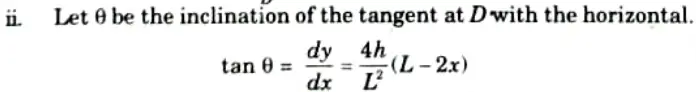
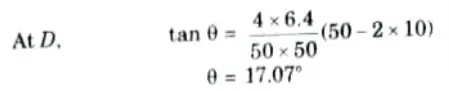
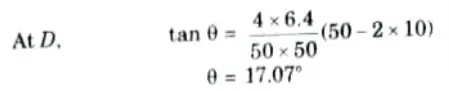
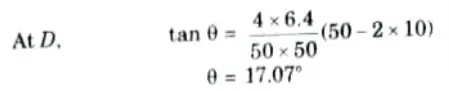
iii. Normal thrust at D,
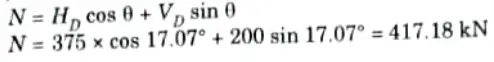
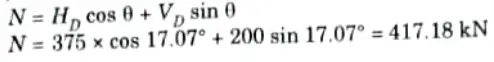
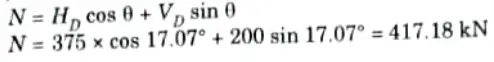
iv. Radial shear at D,
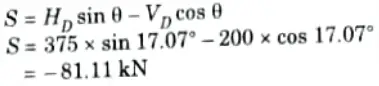
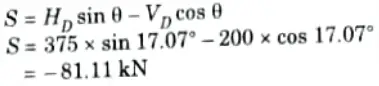
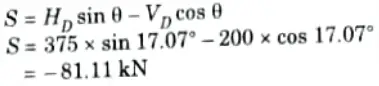
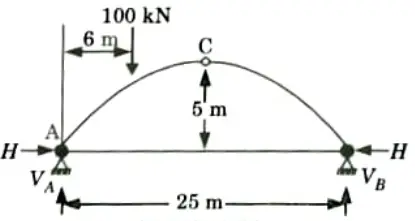
Q6. A circular arch to span 25 m with a central rise 5 m is hinged at the crown and springing. It carries a point load of 100 kN at 6 m from the left support. Calculate:
i. The reactions at the supports.
ii. The reactions at crown.
Ans. Given: Span of arch, L = 25 m, Central rise, h = 5 m, Load = 100 kN
To Find: VA, VB and VC


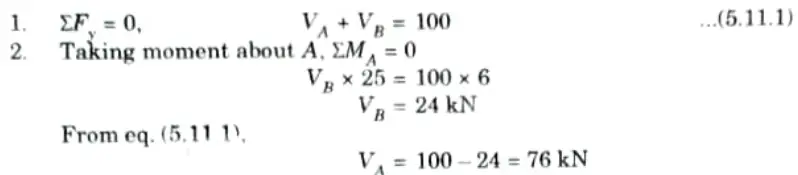
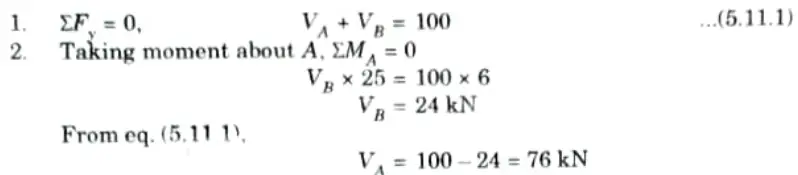
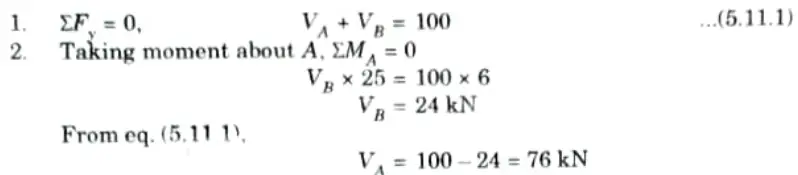
3. Considering right part (CB part) of arch,
Taking moment about point C.
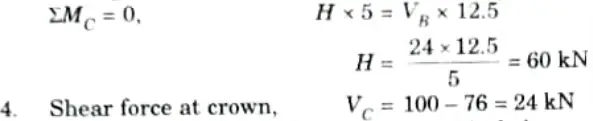
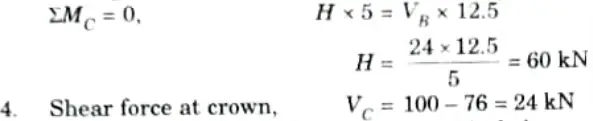
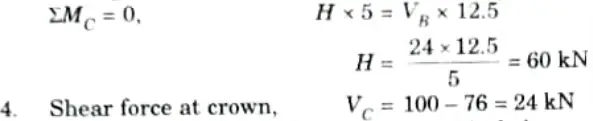
5. Angle between plane of section and vertical plane passing through the crown of circular arch,
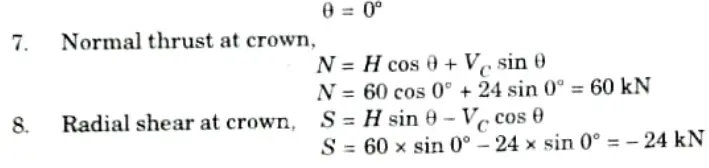
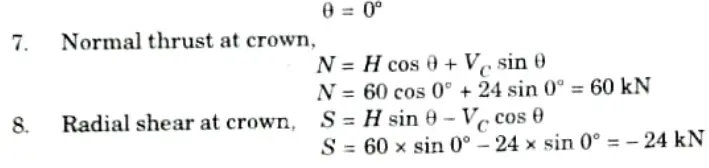
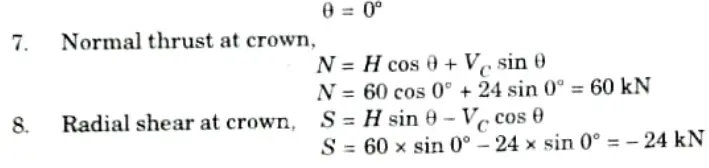



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Structural Analysis Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Structural Analysis Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |
