Aktu Btech Quantum Notes can help you gain a deeper understanding of IC Engines, Fuel, and Lubrication. Use these important, commonly requested questions to get ready for your tests. Improve performance right away! Unit-4 Engine Emission and Control
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For IC Engine, Fuel and Lubrication: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Q1. What are the various methods of emission control ?
Ans. Various methods of emission control are as follows:
i. Modification in the Engine Design and Operating Parameters:
A few parameters which improve the emission are:
- 1. Combustion chamber configuration,
- 2. Lower compression ratio,
- 3. Modified induction system,
- 4. Ignition timing, and
- 5. Reduced valve overlap.
ii. Treatment of Exhaust Products of Combustion: To lessen HC and CO emissions, the exhaust gas leaving the exhaust manifold is treated. The devices used for this are:
- 1. After-burner,
- 2. Exhaust manifold reactor, and
- 3. Catalytic converter.
iii. Modification of the Fuels: If gasoline is changed to propane as engine fuel CO emission can substantially be reduced with reduced HC and NOx and in changing from propane to methane the CO as well HC emission touch zero level and only the NOx remains as a significant factor.
Q2. Name the pollutants emitted by gasoline engines and petrol engines into the atmosphere.
Ans. Following are the various pollutants emitted by gasoline engines or petrol engines:
- i. Carbon Monoxide (CO):
- 1. Only engine exhaust contains carbon monoxide.
- 2. It is a byproduct of incomplete combustion caused by a lack of air in the air-fuel combination or by a lack of cycle time for combustion to finish.
- 3. When the engine is idling, carbon monoxide emissions are high, and they are at their lowest during deceleration. At constant speeds, they are at their lowest during acceleration.
- 4. The primary cause of CO creation is the closing of the throttle, which decreases the oxygen supply to the engine.
- ii. Hydrocarbons:
- 1. Uncompleted combustion is the primary cause of unburned hydrocarbon emissions. Several design and operational factors are strongly related to the pattern of hydrocarbon emissions.
- iii. Particulate Matter and Partial Oxidation Product:
- 1. The exhaust gas also contains traces of several partial oxidation products, primarily formaldehyde and acetaldehyde.
- 2. Phenols, acids, ketones, ethers, etc. are additional ingredients. They are essentially byproducts of the fuel’s incomplete combustion.
- iv. Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx):
- 1. Oxides of nitrogen which also occur only in the engine exhaust are a combination of nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
- 2. Nitrogen and oxygen react at relatively high temperatures. Therefore, high temperatures and availability of oxygen are the two main reasons for the formation of NOx.
Q3. Discuss the mechanism of formation of carbon monoxide.
Ans.
- 1. When the mixture is fuel-rich, carbon monoxide (CO) typically forms. Since the mixture contains more and more fuel, a greater amount of CO is produced.
- 2. Despite having a relatively lean fuel mixture, a little quantity of CO will still be released into the atmosphere.
- 3. This is as a result of the products’ passage to the exhaust not establishing balance.
- 4. Because the combustion products are unstable at the high temperature that results, the following reactions occur before the equilibrium is reached.
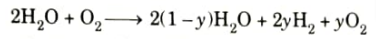
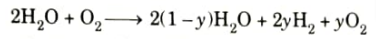
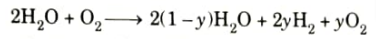
Where, y is the fraction of H2O dissociated.
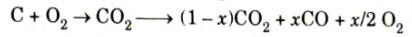
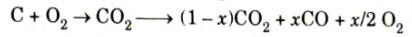
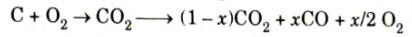
- 5. As the products cool down to exhaust temperature, major part of CO reacts with oxygen to form CO2. However, a relatively small amount of CO will remain in exhaust, its concentration increasing with rich mixtures.
Q4. What is catalytic converter ? Also write the advantages and application of it.
Ans. A. Catalytic Converter:
- 1. Catalytic converters, which are present on the majority of current medium- or large-sized automotive engines, are the most efficient means of lowering engine emissions.
- 2. A catalyst is an element that reduces the amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. As it is not destroyed during the process, it can continue to work forever unless it is damaged by heat, aging, pollutants, or other factors.
- 3. Catalytic converters are installed chambers that the exhaust gases pass through as part of the flow system.
- 4. The catalytic material in these chambers encourages the oxidation of the pollutants present in the exhaust flow.
- 5. Generally, catalytic converters are called three way converters because they are used to reduce the concentration of CO, HC and NOx in the exhaust.
B. Advantages:
- 1. Instead of being achievable at high temperatures like in thermal conversion, the conversion is possible at regular exhaust temperatures.
- 2. Reduction of nitrogen oxides can also be accomplished inside a catalytic converter.
C. Application: Its main objective is to lessen the pollution produced when fossil fuels with hydrocarbon bases are burned in vehicles.
Q5. Explain biogas plant with proper diagram.
Ans. Biogas plants are basically of two types:
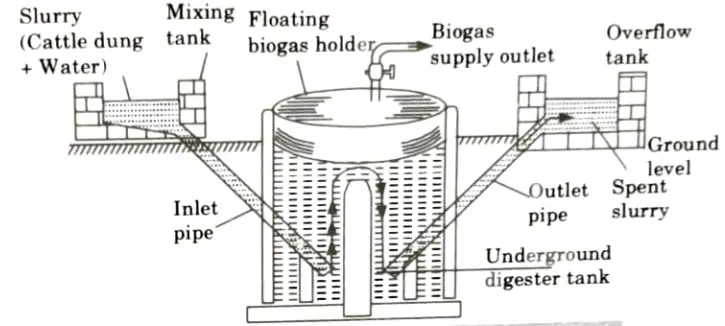
- i. Floating Gas Holder Type Biogas Plant:
- 1. This has a brick-built, well-shaped digester tank that is buried in the ground.
- 2. A steel drum that is upside down floats in the digester tank over the dung slurry to hold the generated biogas.
- 3. The gas exit is controlled by a valve, and the gas container, which is movable, is controlled by a pipe.
- 4. This digester tank has a partition wall, with one side receiving the dung-water combination through an inlet pipe and the other discharging the used slurry through an output pipe.


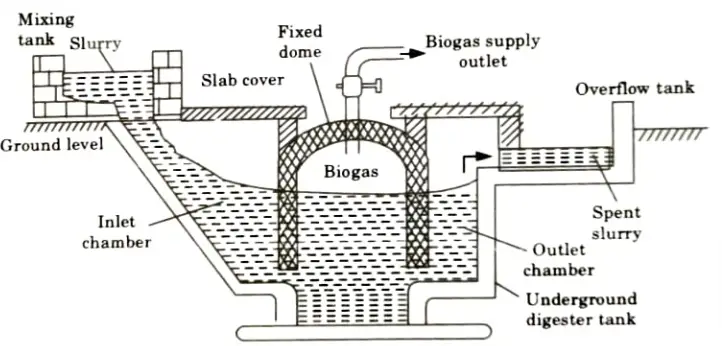
- ii. Fixed Dome Type Biogas Plant:
- 1. The structure resembles a biogas plant with a floating gas holder almost exactly, but the dome-shaped roof is made of cement and bricks rather than a steel gas holder.
- 2. In the primary digester, there is a single unit with intake and exit chambers rather than partitioning.


Q6. Define additives. What are the requirements of additive.
Ans. A. Additives:
- 1. Compounds known as additives are utilized to enhance the efficiency of fuel combustion.
- 2. Surface ignition and knock are the two main combustion issues that develop as operating conditions deteriorate.
- 3. Other methods, such as the enhancement of combustion chamber design, building materials, and fuel and oil quality, can be used to address these combustion issues.
- 4. Using additives is therefore just one strategy among many that can be used to address the combustion issues.
B. Requirements of an Additive:
- 1. It must be resistant to knocks.
- 2. It should consistently dissolve in fuel.
- 3. It shouldn’t affect gasoline negatively.
- 4. It must be liquid at room temperature and volatile to provide quick vapourization in several areas.
- 5. It must not leave behind damaging deposits.
- 6. It must have a low water solubility to reduce handling losses.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
IC Engine, Fuel and Lubrication Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
IC Engine, Fuel and Lubrication Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |
