Table Of Contents
B.Tech AKTU Quantum Book will take you on a journey through the realm of Sensor and Transducers. Access important notes, frequently asked questions, and valuable information for learning this fundamental area. Unit-4 Signal Conditioning and Data Acquisition Systems
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Sensor and Transducers: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Q1. Give the various functions of signal conditioners.
Ans. A. Signal conversion:
- 1. A signal conditioner’s primary job is to capture the signal and transform it into a stronger electrical signal.
- 2. Industrial applications that use a variety of sensors to conduct measurements frequently use signal conversion.
- 3. Because of the many sensors being used, the signals produced might need to be transformed in order for the instruments to which they are connected to be able to use them.
B. Linearization:
- 1. When the signals generated by a sensor do not have a straight line relationship with the physical measurement, certain signal conditioners can conduct linearization.
- 2. This procedure, which is typical for thermocouple signals, is used to interpret the signal from the programme.
- 3. Due to the fact that no sensor is entirely linear, this technique is utilised to achieve higher accuracy.
C. Amplifying:
- 1. The process of boosting the signal for processing or digitizing comes first, and is known as signal amplification.
- 2. Signal amplification can be done in one of two ways: either by improving the input signal’s resolution or by raising the signal-to-noise ratio.
- 3. A variety of amplifiers are used for diverse purposes in signal conditioning, including:
- i. Instrumentation amplifiers: They exhibit high input impedance, high common mode rejection ratio (CMRR), and high gain and are designed for use with DC signals.
- ii. Isolation amplifier: They are used to pass a modest AC or differential signal while isolating strong DC values from the device.
D. Filtering:
- 1. Filtering, which involves reducing the signal frequency spectrum to only contain genuine data and exclude noise, is a crucial function of a signal conditioner.
- 2. Digital algorithms or passive and active components can be used to create filters.
- 3. A passive filter only employs components with a maximum gain of one: capacitors, resistors, and inductors.
- 4. In addition to active components like operational amplifiers and transistors, an active filter also makes use of passive components.
- 5. Modern signal conditioners employ digital filters since they are simple to configure and don’t require any additional gear.
- 6. A digital filter is a mathematical filter that is applied to a signal to control it, such as to pass or block a specific frequency band.
- 7. They make use of logic devices like ASICs, FPGAs, or sequential programmes with signal processors.
E. Evaluation and smart-functions:
- 1. Modern signal conditioners contain additional features for signal evaluation and measurement data pre-processing to offer additional benefits to the user and the process.
- 2. This makes it easier to quickly monitor and assess warnings and alerts directly through an electrical switching output.
- 3. Other smart capabilities, such as an internal computed channel, can handle technological and mathematical procedures, such as the addition of sensor signals.
- 4. These features assist in obtaining a quick-reacting system and lessen the burden on the machine control.
F. Interfaces:
- 1. Signal converters must send sensor signals to the machine control using standardized interfaces and protocols.
- 2. Either analogue or digital interfaces are possible. Typical analogue interfaces include voltage (+/- 10 V) or current (+/- 20 mA) signals, which are simple to handle but require separate wiring for each signal.
- 3. Today’s digital interfaces (PROFINET, EtherCAT, EtherNet/lP) are Ethernet-based bus-interfaces that enable the connection of multiple components with a single cable.
- 4. This saves on wiring and enables the transmission of additional data, such as component diagnostic data, which is crucial for minimizing downtime and accelerating maintenance.
Q2. Why we use data acquisition system ?
Ans.
- 1. Improves the efficiency and reliability of processes or machinery:
- i. Some type of data gathering device that silently monitors some parameter is used in steel mills, utilities, or research labs.
- ii. This data can be used to increase productivity, guarantee dependability, or guarantee that machinery runs safely.
- 2. Problems are analyzed and solved faster:
- i. Measurements are created and shown instantly thanks to real-time data collecting technologies.
- ii. A professional can address any issue more quickly and hasten the machine’s return to peak performance.
- 3. Dataredundancy is reduced: By using a system of this kind, businesses forget about having duplicate data and use technology that makes it easier to analyze the information they have collected because it frees them from distractions that would otherwise impede analysis.
- 4. Decrease update errors:
- i. These systems automate manual data input procedures that were previously carried out.
- ii. By removing human mistake and displacement, automation lowers errors.
- 5. Increased data integration and reliance on other programs:
- i. The more agile a process is, the fewer programmes it will need to interfere in.
- ii. Without relying on other kinds of apps, it makes sure the information is accurate and full.
- 6. Improved access to data for users through the use of host and query languages: These technologies make it simpler to retrieve data from the database for processing and analysis.
- 7. Improves data security: The human aspect is removed from the process of data collection from reality by automating it, lowering the security risks connected with it.
- 8. Data entry, storage and retrieval costs are reduced: These three methods are less expensive since data is entered more quickly, uses less space, and can be retrieved more quickly.
- 9. quality is controlled:
- i. A system of this kind can verify whether a system is satisfying the design requirements and whether a product satisfies the needs of the user.
- ii. In addition, you can examine a product’s quality to see if it meets marketing standards and find any flaws.
- 10. Supervision of processes without human interaction: Such a system allows for faster identification and correction of errors by tracking and monitoring the company’s numerous procedures.
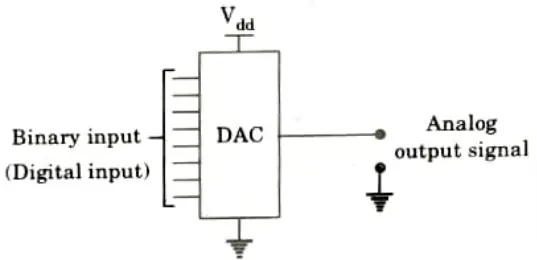
Q3. Explain Digital to Analog Converter (DAC).
Ans.
- 1. A device called a digital to analogue converter (DAC) converts digital data into an analogue signal.
- 2. The Nyquist-Shannon Sampling Theorem states that any sampled data may be precisely recreated using Nyquist criterion and bandwidth.
- 3. A DAC can precisely convert sampled data into an analogue signal.
- 4. Although the digital data may originate from a microprocessor, application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC), or field programmable gate array (FPGA), it must finally be converted to an analogue signal in order to be used in the actual world.


Q4. What is data acquisition ? Give its components.
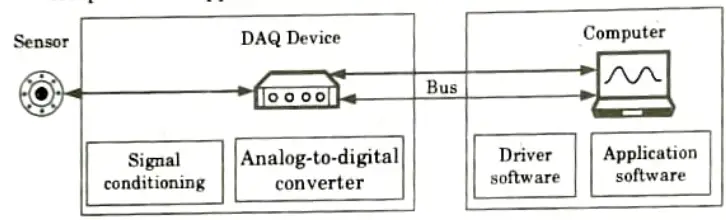
Ans. A. Data acquisition (DAQ) :
- 1. Data acquisition (DAQ) is the process of using a computer to measure a voltage, current, temperature, pressure, vibration, or sound-related electrical or physical event.
- 2. Sensors, DAQ measuring hardware, and a computer running application software make up an DAQ system.


B. Components:
- 1. Sensor: An electrical signal that can be measured, such as voltage or resistance, is produced when a sensor, also known as a transducer, transforms a physical phenomenon, such as temperature or vibration.
- 2. DAQ device: A DAQ device acts as the interface between a computer and signals from the outside world by digitizing incoming analog signals to be computer readable. DAQ devices include three key components :
- a. Signal conditioning circuitry: Transforms noisy real-world signals into forms that may be measured effectively and precisely.
- b. Analog-to-digital converters (ADCs): Digitize real-world analog data into digital representations that can be manipulated by computers.
- c. Computer bus: Enables the DAQ device to transmit data to a computer. Examples include USB, PCIe, or Ethernet.
- 3. Computer and software: A computer with DAQ software is required to process, visualize, and store measurement data.
- a. Driver software: Allows application applications to control your DAQ equipment via menu-driven configuration or a programmable API.
- b. Application software: Provides a ready-made experience for obtaining, evaluating, and presenting data to the user. Menu-driven interfaces are used for configuration.
- c. Programming environment: Users can create their own application to acquire, analyze, and present data by utilizing function libraries (APIs) to access and manage their DAQ device.
Q5. Discuss programmable-gain amplifiers in detail with suitable diagram.
Ans.
- 1. Non-inverting operational amplifiers with a digitally controlled analogue switch coupled to many resistors in the feedback loop are examples of programmable gain amplifiers.
- 2. An external computer or another logic or binary signal controls the analogue switch’s addressable inputs, causing it to select a certain resistor for a specific gain, as shown in Fig.
- 3. The signal conditioners in the data collection system detect the amplitude of the input signal and automatically send the appropriate binary code to the Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA) to increase the gain for a low signal or reduce the gain for a large signal.
- 4. After that, the input signal can be measured and presented without distortion.
Q6. Give the applications of ADC.
Ans.
- 1. They are used in computer to convert the analog signal to digital signal.
- 2. They are used in cell phones.
- 3. They are used in microcontrollers.
- 4. They are used in digital signal processing.
- 5. They are used in digital storage oscilloscopes.
- 6. They are used in scientific instruments.
- 7. They are used in music reproduction technology etc.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Sensor and Transducers Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Sensor and Transducers Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |
