Learn about Sensor and Transducers Short Question Notes from the B.Tech. AKTU Quantum Book. For precise data collection and analysis, unleash the principles of sensing technology and their applications in a variety of sectors.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Sensor and Transducers: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Sensors and Transducers-I
Q1. Define sensor.
Ans.
- 1. It is described as a component that generates a signal related to the amount being measured in paragraph one.
- 2. It can alternatively be described as “A device that produces an useable output in response to a designated measurand” in definition number two.
Q2. What is transducer?
Ans.
- 1. It is described as an element that, when subjected to a physical change, experiences a related change or as an element that, utilising the transduction principle, transforms a given measurand into a useful output.
- 2. Another definition of it is a machine that changes a signal from one kind of energy to another.
Q3. Give the classification of sensors based on displacement and position.
Ans.
- 1. Potentiometer
- 2. Strain-gauged element
- 3. Capacitive element
- 4. Differential transformers
- 5. Eddy current proximity sensors
- 6. Inductive proximity switch
- 7. Optical encoders
- 8. Pneumatic sensors
- 9. Proximity switches
- 10. Hall effect sensors.
Q4. Classify sensors based on temperature.
Ans.
- 1. Bimetallic strips
- 2. Resistance temperature detectors
- 3. Thermistors
- 4. Thermo-diodes and transistors
- 5. Thermocouples
- 6. Light sensors
- 7. Photo diodes
- 8. Photo resistors
- 9. Photo transistor.
Q5. Give the classification of transducers.
Ans.
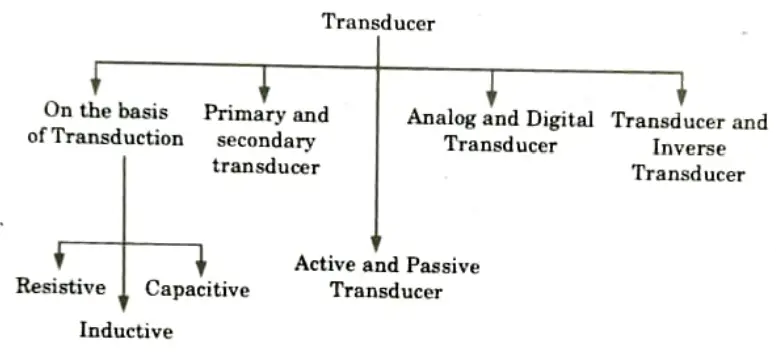


Q6. What are the various advantages of transducers ?
Ans.
- 1. Electrical amplification and attenuation can be done easily.
- 2. No moving mechanical parts.
- 3. Very small electric power required.
Q7. Give the various disadvantages of transducers.
Ans.
- 1. Design is complicated.
- 2. Sometimes the electrical transducer is less trustworthy than the mechanical variety.
Q8. What are the factors to be considered while selecting transducer ?
Ans.
- 1. High input impedance and low output impedance.
- 2. Highly sensitive.
- 3. Small in size.
- 4. High degree of accuracy and repeatability.
- 5. Free from errors.
Q9. What are the applications of transducers in various fields?
Ans. 1. Electromagnetic:
a. Antennas b. Hall-effect sensors
c. Disk read and write heads d. Magnetic cartridges.
2. Electromechanical:
a. Accelerometers b. Pressure sensors
c. Galvanometers d. LVDT
e. Load cells f. Potentiometers.
Q10. What is potentiometer?
Ans. Potentiometers are devices that measure electromotive forces by balancing them against the potential difference created by running a known current through a known variable resistance.
Q11. What is an optical encoder?
Ans. 1. A digital electrical output of an optical encoder is proportional to the angular position of the input shaft. It is an electromechanical device.
2. With optical encoders, it is possible to translate an angular displacement immediately into a digital format. An angular position sensor is an optical encoder.
Q12. What are load cells ?
Ans. A transducer is used in a load cell, a type of force gauge, to provide an electrical signal whose strength is directly proportionate to the force being measured.
Q13. How strain gauge load cell works ?
Ans. 1. To translate the load acting on strain gauge load cells into electrical signals, the strain gauge assembly is positioned inside the load cell enclosure.
2. A strain gauge translates factors like force, pressure, tension, weight, etc. into a change in resistance that can be measured afterwards. This resistance of a strain gauge varies with applied force.
Q14. Explain the characteristics of strain gauges.
Ans.
- 1. They are highly precise.
- 2. They are ideal for long distance communication.
- 3. They require easy maintenance and have a long operating life.
- 4. They require certain precautions while installing.
Q15. Give the applications of strain gauges.
Ans.
- 1. They are employed in failure analysis and machine diagnosis.
- 2. They are employed in proof tests and multi-axial stress fatigue tests.
- 3. They are primarily utilised in automobiles as safety sensors.
Q16. What is piezoelectric sensor or transducer ?
Ans. 1. A piezoelectric transducer, sometimes referred to as a piezoelectric sensor, is a device that converts energy from the piezoelectric effect into an electrical charge in order to measure changes in acceleration, pressure, strain, temperature, or force.
2. A crystal is elastically bent when pressure is applied. This deformation causes an electric charge to flow (which lasts fora period of a few seconds).
Q17. What are the advantages of piezoelectric sensor or transducer ?
Ans.
- 1. No requirement for an outside force.
- 2. Because of its compact size, it is simple to handle and utilise.
- 3. High-frequency reaction.
Q18. Give the disadvantages of piezoelectric sensor or transducer.
Ans.
- 1. It cannot be used for measurements in a static environment.
- 2. The weather has an impact on it.
- 3. Because of the low output, an external circuit is connected to it.
Q19. What are the applications of piezoelectric sensor or transducer?
Ans.
- 1. In microphones.
- 2. It is also used in medical diagnostics.
- 3. It is used in electric lighter used in kitchens.
- 4. It is used infertility treatment.
- 5. It is used in inkjet printers.
Unit-II: Sensors and Transducers-II
Q1. Explain the thermistors.
Ans.
- 1. A thermistor (also known as a thermal resistor) is a type of resistor whose electrical resistance changes as the temperature changes.
- 2. A thermistor is extremely sensitive to temperature change, even though the resistance of all resistors will vary slightly with temperature.
- 3. Thermistors operate under the premise that resistance decreases as temperature rises.
Q2. Give the relationship between resistance and temperature of thermistors.
Ans. The relationship governing the characteristics of a thermistor is given below as,



Q3. What are the applications of thermistors ?
Ans.
- 1. To keep an eye on the engine’s coolant and/or oil temperatures.
- 2. To keep an incubator’s temperature under observation.
- 3. To keep track of the battery packs’ charging-related temperature.
- 4. To keep track on the hot end temperature of 3D printers.
Q4. Discuss RTD.
Ans. A resistance thermometer, also known as a Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD), is a tool that measures the resistance of pure electrical wire in order to calculate the temperature. The term “temperature sensor” refers to this wire.
Q5. Give the characteristics of RTD.
Ans. 1. In factories, the sole option for measuring temperature accurately is the RTD.
2. It exhibits strong linear properties across a broad temperature range.
Q6. What is thermal imaging?
Ans. By detecting an object’s infrared radiation and building an image from it, thermal imaging improves visibility of items in a dark environment.
Q7. Give the types of thermal imaging.
Ans. There are two common types of thermal-imaging devices:
- a. Un-cooled
- b. Cryogenically cooled.
Q8. What is Hall Effect sensors ?
Ans. A tool that is used to gauge the strength of a magnetic field is a Hall Effect sensor. The magnetic field intensity passing through it has a direct correlation with the output voltage.
Q9. What capacitive proximity sensors can detect ?
Ans. Metallic and nonmetallic targets in powder, granulate, liquid, and solid form can all be detected using capacitive proximity sensors.
Q10. Explain photoelectric sensors.
Ans. These sensors, which consist of an emitter (light source) and a receiver, detect things using light-sensitive components.
Q11. What are the types of vibration sensor ?
Ans.
- 1. Accelerometer
- 2. Strain gauge
- 3. Eddy-current.
Q12. How ultrasonic flow sensors work ?
Ans. Ultrasonic flow sensors measure the velocity of a fluid moving in a pipe using sound waves.
Q13. What are the advantages of ultrasonic flow sensors ?
Ans.
- 1. It doesn’t obstruct the passage of fluids.
- 2. The liquid is moving in both directions.
- 3. This metre has a good dynamic response.
- 4. This metre produces data in analogue format.
Q14. Give the disadvantages of ultrasonic flow sensors.
Ans.
- 1. In comparison to other mechanical flow metres, it is pricey.
- 2. Its meter’s design is intricate.
- 3. Once they have rusted, it is unable to measure cement or concrete pipes.
- 4. If the pipe has any holes or bubbles in it, it won’t work.
Q15. What are the applications of ultrasonic low sensors ?
Ans.
- 1. Applications involving wastewater and filthy liquids use these metres.
- 2. These metres are employed in locations that require little maintenance and low pressure drop.
- 3. The velocity is measured using these metres.
Q16. What are the advantages of ultrasonic level sensors ?
Ans.
- 1. Non-contact with product.
- 2. Reliable performance in difficult service.
- 3. No moving parts.
- 4. Measurement without physical contact.
Q17. Give the disadvantages of ultrasonic level sensors.
Ans.
- 1. The product must reflect sound well and not absorb it.
- 2. Unsuitable for use in a hoover or at greater pressures.
- 3. A maximum temperature of 170 °C is allowed.
Q18. What are the advantages of capacitive level sensors?
Ans.
- 1. Relatively inexpensive
- 2. Versatile
- 3. Requires minimal maintenance
- 4. Reliable
- 5. Contains no moving parts
- 6. Easy to clean.
Q19. Give the application of capacitive level sensors.
Ans.
- 1. Powered and granular solids
- 2. Liquefied gases at very low temperature
- 3. Very high pressure industrial processes.
Q20. What are the disadvantages of capacitive level sensors ?
Ans. This system cannot work with materials having varying dielectric materials.
Unit-III: Machine Vision
Q1. What is machine vision ?
Ans. 1. Machine vision systems examine pictures taken by cameras to produce information about image features that help robotic and automated devices comprehend the physical environment.
2. Vision is a sensory input that can generate detailed information that, in many cases, can only be accessed through vision.
Q2. Give the difference between computer and machine vision.
Ans.
| S. No. | Computer vision | Machine vision |
| 1. | It doesn’t depend on machine vision. | It can’t exist without computer vision. |
| 2. | It is a scientific domain. | It is an engineering one. |
| 3. | It has a much greater processing capability of acquired visual data. | It has lesser processing capability of acquired visual data as compared to computer vision. |
Q3. What are the applications of computer vision.
Ans.
- 1. This method is employed to find anomalies in medical scans.
- 2. Based on pattern recognition, computer vision can distinguish between purposeful and unintentional harm.
- 3. Computer vision can be used to automate surveillance.
Q4. Give the applications of machine vision.
Ans. 1. Automatic inspection
2. Quality control
3. Robot guidance.
Q5. What are Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) imaging sensors.
Ans. 1. From digital astronomy to machine vision inspection, the charge-coupled device (CCD) is a technology for image capture.
2. The CCD sensor is made of silicon and has a number of photosensitive spots on it.
Q6. What is full form of CMOS?
Ans. CMOS: Complementary metal oxide semiconductor.
Q7. Compare CCD and CMOS.
Ans.
| Sensor | CCD | CMOS |
| Pixel signal | Electron packet | Voltage |
| Chip signal | Analog | Digital |
| Speed | Moderate – High | High |
| Power Consumption | Moderate – High | Low |
Q8. Explain the tasks included in machine vision system.
Ans. A. Sensing and digitizing image data
B. Image processing and analysis
C. Applications function.
Q9. What is VGR?
Ans. 1. Vision Guided Robots (VGR) are robotic arms with built-in machine vision systems that are typically used in industrial pick-and-place applications.
2. The robot is guided to a desired area for pick and place by the machine vision system, which assists in locating an object.
Q10. Give the applications of VGR systems.
Ans.
- 1. Adding and removing pieces from feeding and conveyor systems
- 2. Assembly, assembling, and packaging
- 3. Stacking and removing racks
- 4. Picking random pieces out of bins.
Q11. What is Animal (AT) Model ?
Ans. The AT robot design paradigm entails a robot that responds verbally to commands to carry out beneficial behaviours and tasks that have been programmed by a human user.
Unit-IV: Signal Conditioning and Data Acquisition Systems
Q1. What is signal conditioning ?
Ans. 1. Signal conditioning is the process of modifying a signal in order to get it ready for the following level of processing.
2. Signal conditioning is the process of getting a sensor or transducer’s signal ready for data gathering equipment to process.
Q2. Give the various functions of signal conditioners.
Ans.
- A. Signal conversion
- B. Linearization
- C. Amplifying
- D. Filtering
Q3. What are various types of signal conditioning?
Ans.
- 1. Amplification
- 2. Excitation
- 3. Linearization
- 4. Filtering
Q4. Give the types of signal conditioners.
Ans.
- 1. Temperature signal conditioner
- 2. Thermocouple signal conditioner
- 3. Thermistors signal conditioner
- 4. RTD signal conditioner.
Q5. Explain amplification process.
Ans. In order to boost (amplify) the signal for recording or digitisation, amplification is used.
Q6. What are the various types of amplifiers ?
Ans.
- 1. Isolation amplifiers
- 2. Current amplifier
- 3. Voltage amplifier
- 4. Operational amplifiers (Op-Amps).
Q7. Give the names of the stages in operational amplifiers.
Ans. 1. Inverting amplifier stages
2. Non-inverting amplifier stages.
Q8. What is the benefit of differential amplifier ?
Ans. The differential amplifier’s capacity to reject any voltages that are shared by both inputs while magnifying the difference voltage is its main advantage.
Q9. What is data acquisition ?
Ans. The process of measuring an electrical or physical phenomenon, such as voltage, current, temperature, pressure, vibration, or sound, using a computer is known as data acquisition (DAQ).
Q10. What are the components of DAQ?
Ans. 1. Sensor
2. DAQ device
3. Computer and software.
Q11. Explain analog to digital converter.
Ans. An electrical integrated circuit known as an analogue to digital converter (ADO) is used to convert analogue signals, such as voltages, to digital or binary form, which consists of 1s and 0s.
Q12. What are the types of analog to digital converter ?
Ans. A. Successive approximation A/D converter
B. Dual slope A/D converter
C. Flash A/D converter.
Q13. What is digital to analog converter (DAC).
Ans. A device called a digital to analogue converter (DAC) converts digital data into an analogue signal.
Q14. Give the types of digital to analog converter.
Ans. A. R-2R ladder network method.
B. Weighted resistors method.
Q15. Why do we need analog to digital converters ?
Ans. 1. Analog signals make up the majority of data in the actual world.
2. In order to use a microprocessor to alter the data, we must convert the analogue signals to the digital signals so that the microprocessor can read, comprehend, and do so.
Q16. Why we use data acquisition system ?
Ans.
- 1. It raises the effectiveness and dependability of procedures or equipment.
- 2. It increases reliance on other applications and data integration.
- 3. It enhances information security.
- 4. Costs for data entry, storage, and retrieval are decreased.
Q17. Discuss counters and timers.
Ans.
- 1. The counter and timer functions count the number of pulses or cycles recorded over the course of a predetermined amount of time, as well as the frequency or period of an input signal.
- 2. A counter can also produce a total number by counting the total number of input events, pulses, or cycles over a specified time period.
- 3. A timer counts the number of cycles of input signals that must occur within a predetermined amount of time.
Unit-V: Smart Sensors
Q1. Explain smart sensors.
Ans. 1. A “Sensing, Monitoring, and Remote Transmission” sensor is the simplest expansion of a smart sensor.
2. It can be defined as a microprocessor-based sensor which can perform one or more number of the functions like logical functions, decision making, two-way communication, etc. It can be simply expressed as:
Sensors + Suitable interfacing circuits = Smart sensors
Q2. Give the features of smart sensors.
Ans.
- 1. Automatic ranging
- 2. Auto calibration of data through an in-built system
- 3. Auto linearization of non-linear functions
- 4. Easy communication through serial bus.
Q3. What are the advantages of smart sensors?
Ans.
- 1. Noneed of bulk cables and connectors
- 2. Enhanced features
- 3. Reliability
- 4. Higher SNR.
Q4. Give the block diagram of smart sensors.
Ans.
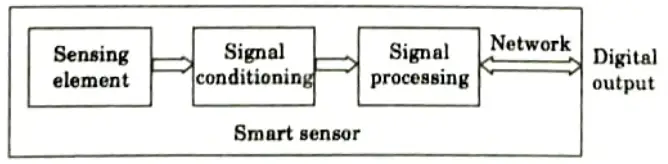


Q5. What are the applications of smart sensors ?
Ans.
- 1. Intelligent accelerometers for measuring acceleration
- 2. Object detection using smart optical sensors
- 3. Food preparation and storage
- 4. Detection of biological hazards.
Q6. What are the characteristics of smart sensors ?
Ans.
- 1. Self-calibration
- 2. Computation
- 3. Communication
- 4. Multi-sensing
Q7. Give the applications of smart sensors in smart cities.
Ans.
- 1. Water management
- 2. Energy management
- 3. Smart streetlights
- 4. Traffic control.
Q8. Which smart sensors used in industrial robots ?
Ans.
- 1. Force torque sensor
- 2. Collision detection sensor
- 3. Safety sensors
- 4. Part detection sensors.
Q9. Which smart sensors are used in electric vehicle ?
Ans.
- 1. Displacement/LVDT sensors
- 2. Inertial sensors
- 3. Wireless sensor networks.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Sensor and Transducers Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Sensor and Transducers Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |
4 thoughts on “Quantum Book Aktu Sensor and Transducers KEE-502 Btech Short Question”