Explore B.Tech AKTU Quantum Book Short Question Notes on Optical Network. Discover the fundamentals of high-speed data transfer, fibre optics, and innovative communication technologies based on light signals.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Optical Network: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 4th Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Introduction to Optical Networks (Short Question)
Q1. What is the need for multiplexing ?
Ans. Multiplexing is required because it is more cost effective to transmit data at greater rates over a single fibre than to transmit data at lower rates over numerous fibres.
Q2. How can transmission capacity be increased ?
Ans. Transmission capacity can be increased by using WDM and TDM.
Q3. What is the key driver for second generation optical networks?
Ans. In second generation, data passing from one node to another might be routed in the optical domain, reducing the burden on the underlying electronics at the node dramatically. This is a major motivator for second generation optical networks.
Q4. What is optical layer ?
Ans. The optical layer serves as a server layer for the client layers. This optical layer connects lightpaths to several client layers.
Q5. List the key network elements that enable optical networking.
Ans. The key network elements that enable optical networking are:
- a. Optical line terminals (OLTs).
- b. Optical add/drop multiplexers (OADM).
- c. Optical cross connects.
Q6. Compare CPM and SPM.
Ans.
| S. No. | CPM | SPM |
| 1. | The spectrum broadening is caused by the influence of additional pulses propagating in the same waveguide at the same time. | Spectral broadening occurs due to its own intensity. |
Q7. What is CPM?
Ans. The induced chirp in one channel of a WDM system with many channels is determined by the variation of the refractive index with the intensity on the other channels. This is known as cross phase modulation (CPM).
Q8. What do you mean by scattering effect ?
Ans. Energy is transferred from one light wave to another with a longer wavelength (or lower energy) in scattering effects. The lost energy is absorbed by the medium’s molecular vibrations, called phonons.
Q9. What is optical packet switching?
Ans. Optical packet switching refers to packet switching performed in an optical domain. Optical networks that can conduct packet switching in the optical domain could provide virtual circuit or datagram services similar to IP and MPLS networks.
Q10. List any two reasons for not using optical packet switching commercially.
Ans. a. Lack of optical random access memory for buffering.
b. Relatively primitive state of fast optical switching technology, compared to electronics.
Q11. What is the relation between wavelength, frequency and channel spacing ?
Ans.
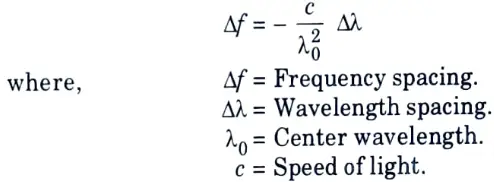
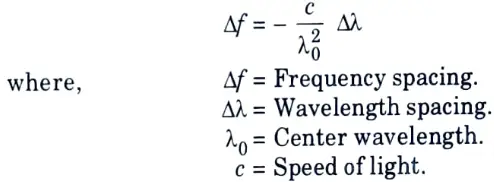
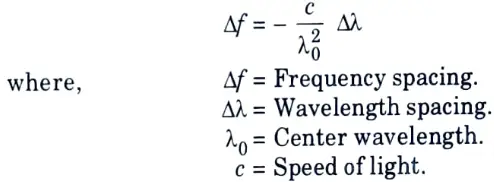
Q12. Why is the 1.55 mm wavelength region used by WDM systems ?
Ans. 1.55 μm wavelength region is used for two reasons:
- a. Inherent loss in optical fiber is the lowest in this region.
- b. Excellent optical amplifiers are available in this region.
Q13. What do you mean by spectral efficiency ?
Ans. The ratio of bit rate to available bandwidth is called spectral efficiency.
Q14. Explain power spectrum.
Ans. The power spectrum, or simply spectrum, is a frequency domain representation of a signal in which the energy of the signal is divided throughout a collection of frequencies.
Q15. What is numerical aperture ?
Ans. A fiber’s numerical aperture is a figure of merit that represents its light gathering capacity. The bigger the numerical aperture, the more light the fibre accepts.
Unit-II: Optical Components (Short Question)
Q1. What do you mean by a coupler ?
Ans. A coupler is simple component used to combine or split optical signals.
Q2. What do you mean by Isolator ?
Ans. An isolator is a device that allows transmission in one direction but prevents transmission in the other.
Q3. What do you mean by circulator ?
Ans. A circulator is a device with several port devices, often three or four, where input is applied to one port and output is obtained on the neighbouring port.
Q4. How can high bit rate transmission on widely deployed fiber be achieved ?
Ans. High bit rate transmission can be achieved through a combination of:
- a. Using pulses narrower than a bit period but much wider than solitons.
- b. Dispersion compensation of the fiber plant at periodic intervals to keep the average dispersion low.
Q5. Define non-reciprocal devices with example.
Ans. These are the devices which work exactly the same way if their inputs and outputs are reversed.
Example: Isolator.
Q6. Define spectral efficiency.
Ans. The spectral efficiency of a digital signal is defined as the bit rate divided by the signal’s bandwidth.
Q7. What is interchannel crosstalk ?
Ans. Interchannel crosstalk occurs when the crosstalk signal is at a wavelength sufficiently different from the target signal’s wavelength that the difference is greater than the receiver’s electrical bandwidth.
Q8. Enlist the ways to reduce the crosstalk.
Ans. a. Using spatial dilation.
b. Using wavelength dilation.
Q9. What do you mean by etalons ?
Ans. Etalons are devices that generate numerous optical signals by repeatedly traversing a single cavity.
Q10. What is use of gratings in WDM communication system ?
Ans. Gratings are employed in WDM communication systems as demultiplexers to separate distinct wavelengths or as multiplexers to combine them.
Q11. List the applications of fiber gratings.
Ans. a. Filtering.
b. Add/drop functions.
c. Compensating for accumulated dispersion in the system.
Q12. What is the difference between short period grating (Fiber Bragg grating) and long period fiber grating ?
Ans.
| S. No. | Short period grating | Long period grating |
| 1. | They have periods that are comparable to the wavelength, typically around 0.5 μm. | They have periods that are much larger than the wavelength. |
| 2. | In the fibre core, energy is linked from the forward propagating mode to the backward propagating mode. | The forward propagating mode in the fibre core couples energy to the other forward propagating modes in the cladding. |
Q13. What is the main advantage of Fabry-Perot filters over other devices ?
Ans. Fabry-Perot filters have the benefit over other devices in that they can be tweaked to choose different channels in a WDM.
Q14. What is finesse of the filter ?
Ans. Finesse is the ratio of free spectral range (FSR) to FWHM and is an approximation of the number of wavelengths that the system can accommodate. It is given by
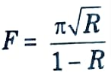
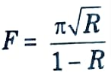
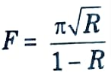
where, R = Reflectivity of mirror.
Q15. List the methods for tuning a Fabry-Perot filter.
Ans. a. By changing cavity length.
b. Using a piezoelectric material within the cavity.
c. By mechanical tuning of filter.
Q16. What is MZI?
Ans. A Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZ) is an interferometric device that resolves distinct wavelengths by using two interfering channels of different lengths.
Q17. What is arrayed waveguide grating ?
Ans. A generalization of the Mach-Zehnder interferometer is an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG). It is a gadget that adds together many copies of the same signal that have been altered in phase by varying amounts.
Q18. What is extinction ratio?
Ans. The extinction ratio of an on-off switch is the ratio of the on-state output power to the off-state output power.
Q19. Write down the applications of optical switching and their switching time.
Ans.
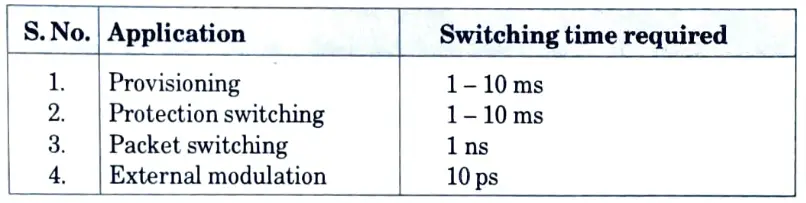


Q20. Write the advantages of lithium niobate switches over mechanical switches.
Ans. The advantage of lithium niobate switches over mechanical switches is that they allow for lower degrees of integration.
Q21. What is wavelength converter ?
Ans. A wavelength converter is a device that transfers data from one incoming wavelength to another.
Q22. What are the disadvantages of wavelength conversion using four-wave mixing ?
Ans. a. The other waves must be filtered out at the SOA output.
b. The conversion efficiency goes down significantly as the wavelength separation between the signal and probe is decreased.
Q23. List the main advantage of wavelength conversion using four-wave mixing.
Ans. The fundamental advantage of four wave mixing is that the effect is totally transparent because it is independent of modulation type and bit rate.
Q24. Define spectral efficiency.
Ans. The spectral efficiency of a digital signal is defined as the bit rate divided by the signal’s bandwidth.
Q25. What is the capacity limit of optical fiber?
Ans. An upper limit on the spectral efficiency and the channel capacity is given by Shannon’s theorem. cis given by
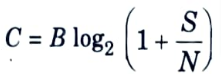
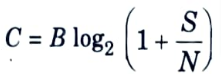
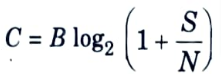
where,
B = Available bandwidth.
S/N = Signal to noise ratio.
C = Channel capacity
Q26. What is inter-channel crosstalk ?
Ans. When the crosstalk signal has a wavelength that is enough different from the target signal’s wavelength that the discrepancy is greater than the electrical bandwidth of the receiver. This type of crosstalk is known as inter-channel crosstalk.
Q27. Enlist the ways to reduce the crosstalk.
Ans. a. Using spatial dilation.
b. Using wavelength dilation.
Q28. Write down two differences between isolator and circulator.
Ans.
| S. No. | Isolator | Circulator |
| 1. | It is two port device. | It has multiple port typically 3 or 4 |
| 2. | Isolators are used in optical amplifier and laser to prevent reflections. | Circulators are used to construct optical add/drop multiplexer. |
Q29. List two features of WDM.
Ans. 1. WDM is technique to increase the capacity.
2. The idea is to transmit data simultaneously at multiple carrier wavelength over a fiber.
Q30. Give the classification of wavelength routing network design problem.
Ans.
- 1. Minimizing the effect (bandwidth loss) due to wavelength continuity constraint.
- 2. Employing wavelength converters, multifibers, and wavelength rerouting.
- 3. Design, reconfiguration, and survivability of virtual topology (optical layer).
- 4. Optical multicasting, control and management.
- 5. Traffic grooming.
- 6. IP-over-WDM.
Unit-III: SONET/SDH (Short Question)
Q1. Enlist the advantages of SONET/SDH.
Ans.
- a. Multiplexing simplification.
- b. Management.
- c. Interoperability.
- d. Network availability.
Q2. What is the function of path layer in SONET/SDH?
Ans. The path layer in SONET/SDH is in charge of connecting nodes end to end and is terminated only at the ends of a SONET.
Q3. Enlist the applications of physical layer interfaces based on the target distance and loss on the link between the transmitter and receivers.
Ans.
- a. Intra-office connection (I).
- b. Short-haul interoffice connections (S).
- c. Long-haul interoffice connections (L).
- d. Very long-haul interoffice connections (V).
- e. Ultra-long-haul interoffice connections (U).
Q4. What is spanning tree protocol ?
Ans. The spanning tree protocol (STP) is a distributed algorithm run by the switches to form the spanning tree.
Q5. What is link aggregation control protocol ?
Ans. Switched Ethernet networks can provide large capacity links by combining numerous parallel lines into a single logical link. This is the link aggregation control protocol (LACP) of Ethernet.
Q6. What do you mean by ATM ?
Ans. Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) is a technology that originated in the 1970s and 1980s with the advent of broadband ISDN. ATM combines multiplexing and switching functions. ATM is intended for high-speed multimedia networking.
Q7. What are the benefits of using ATM?
Ans. The high level benefits delivered through ATM services deployed on ATM technology using international ATM system can be summarized as follows:
- 1. Used in dynamic bandwidth for bursty traffic.
- 2. ATM has smaller header length.
- 3. It can handle mixed network traffic very efficiently.
- 4. Cell network.
- 5. Class-of-service support.
- 6. Common LAN/WAN architecture,
- 7. International standards compliance.
Q8. What do you mean by GFP client-specific aspects and GFP common aspects ?
Ans. 1. GFP client-specific aspects are the mappings of the client signal to GFP frames.
2. The GFP common aspects include the functions of frame delineation, multiplexing, frame scrambling and client management.
Q9. What is flooding ?
Ans. Flooding is a technique used to disseminate (spread) information across the network.
Q10. What is the significance of TCP ?
Ans. IP, as a network layer protocol, does not ensure reliable, in-sequence data delivery from source to destination. This task is carried out via a transport protocol known as the transmission control protocol.
Q11. Define reconfigurability.
Ans. The capacity to select the desired wavelengths to be dropped and added to the signal, rather than needing to plan ahead and deploy necessary equipment, is referred to as reconfigurability.
Q12. List the characteristics of an ideal OADM.
Ans. a. It would be capable of being configured to drop a certain maximum number of channels.
b. It would not require the user to plan ahead as to what channels may need to be dropped at a particular node.
c. It would maintain a low fixed loss.
Q13. What is an OXC?
Ans. An OXC is the essential network element that enables reconfigurable optical networks, in which lightpaths can be added and removed as needed without being statically supplied.
Q14. List the key functions of an OXC.
Ans.
- a. Service provisioning.
- b. Protection.
- c. Bit rate transparency.
- d. Performance monitoring, test access and fault localization.
- e. Wavelength conversion.
- f. Multiplexing and grooming.
Q15. What is transparency ?
Ans. The term “transparency” refers to the fact that the lightpath can transmit data at many bit rates and protocols and can be rendered protocol insensitive.
Q16. What is the significance of optical line terminal (OLT) in WDM networks ?
Ans. OLTs are WDM network elements that are used at either end of a point to point link to multiplex and demultiplex wavelengths.
Q17. Enlist any five key attributes of OADM.
Ans.
- a. Total number of wavelengths that can be supported.
- b. Maximum number of wavelengths that can be dropped/added.
- c. Reconfigurability of OADM.
- d. Complexity of physical layer path design.
- e. Easy is to add and drop additional channels.
Unit-IV: WDM Network Design (Short Question)
Q1. What is RWA problem?
Ans. The routing and wavelength assignment (RWA) problem is the difficulty of implementing the lightpath architecture within the optical layer.
Q2. What is the important component of the optical layer cost ?
Ans. An important component of the optical layer cost is the number of transponders required in the OLT’s and OADMs.
Q3. List the different lightpath topologies that can be deployed over a fiber ring topology.
Ans. a. Point-to-point WDM ring.
b. Hub topology.
c. Full mesh topology.
Q4. What is the objective in LTD problems ?
Ans. The goal of LTD problems is to minimise network costs, which may include bandwidth, port, switching, amplifiers, and regenerators.
Q5. Define the term grooming.
Ans. Grooming is commonly used to refer to the packing of low-speed SONET/SDH circuits into higher speed circuits.
Q6. What do you mean by revertive protection scheme ?
Ans. When the working path is repaired under a revertive scheme, traffic is automatically moved back from the protect path to the working path.
Q7. What is non-revertive protection scheme ?
Ans. In a non-revertive protection scheme, traffic is kept on the protect path until it is manually switched back to the original functioning path, which is normally done by a user via the network management system.
Q8. Compare the different protection schemes in SONET and SDH.
Ans.
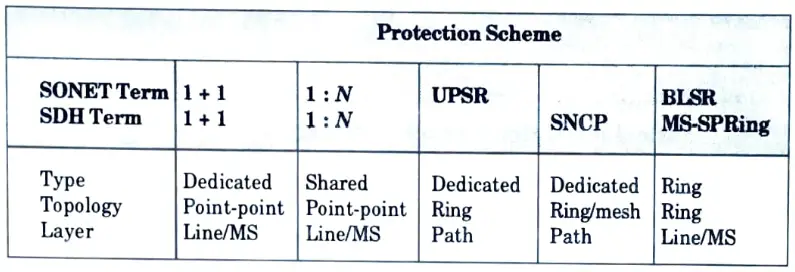


Q9. Why SONET/SDH rings are called self-healing rings ?
Ans. SONET/SDH rings are referred to be self-healing rings because they include protective features that immediately detect problems and rapidly divert traffic away from broken links and nodes.
Q10. Comment on protection in ethernet.
Ans. The spanning tree protocol (STP) provides a built-in protection mechanism in switched ethernet networks. The original STP blocks linkages, forming a spanning tree with the remaining active links. If a tree link fails, STP will create a new spanning tree.
Q11. Why there is a need of optical layer protection ?
Ans. a. Using optical layer protection instead of client layer protection can result in significant cost savings.
b. Networks such as IP networks do not give the same level of security as SONET/SDH networks. Using optical layer protection to protect data networks is one option that can be both cost-effective and efficient.
Q12. Write some limitations of optical layer protection.
Ans. a. All failures cannot be handled by the optical layer.
b. The optical layer may not be able to detect the appropriate conditions that would cause it to invoke protection switching.
c. The optical layer protects traffic in units of lightpaths, and it cannot protect part of the traffic within a lightpath.
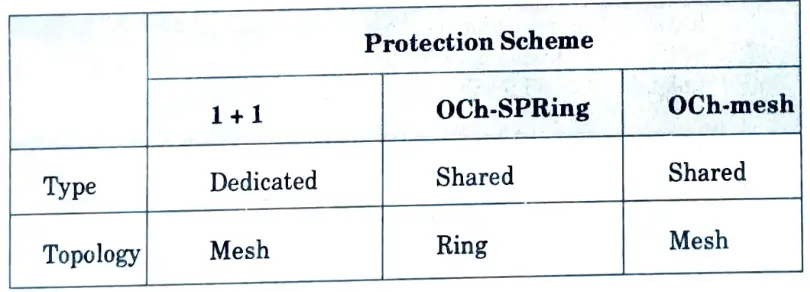
Q13. List the various optical layer protection schemes.
Ans.
- a. 1 + 1 OMS protection.
- b. 1:10 MS protection.
- c. OMS-DPRing.
- d. OMS-SPRing.
- e. 1:N transponder protection.
- f. 1+10 Ch dedicated protection.
- g. OCh-SPRing.
- h. OCh-Mesh protection.
- i. GMPLS protection.
Q14. Compare the optical protection schemes operating in the optical multiplex section (OMS) layer.
Ans.
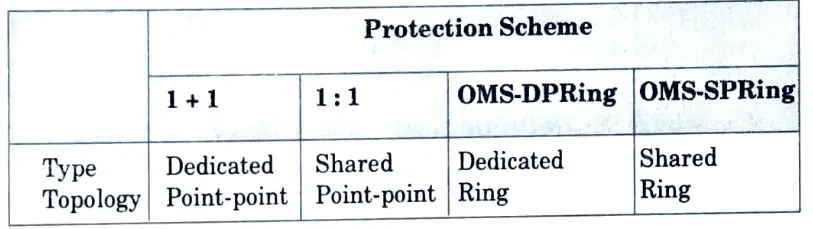


Q15. Compare optical protection schemes operating in the optical channel layer.
Ans.


Q16. List the different types of services that must be supported by an access network.
Ans.
- a. Telephony
- b. ISDN
- c. Broadcast video
- d. Interactive video
- e. Internet access
- f. IPTV
- g. Video-on-demand
- h. Videoconferencing
- i. Business services
Q17. Classify different types of access networks.
Ans.
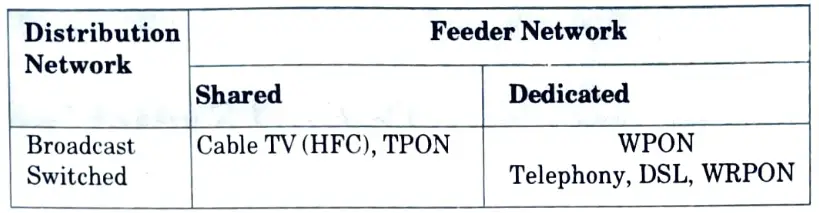


Q18. What is the difference between FTTC and HFC ?
Ans.
| S. No. | HFC | FTTC |
| 1. | It is a broadcast architecture. | It incorporates switched architecture. |
| 2. | Data is broadcasted by using a passive optical star coupler. | Data is transmitted digitally over optical fiber. |
| 3. | It serves 50-500 homes. | It serves 8-64 buildings. |
Unit-V: Optical Switching (Short Question)
Q1. List the two reasons for researching optical packet switching.
Ans. a. Optical packet switches hold the potential for realizing higher capacities than electronic routers.
b. It can improve the bandwidth utilization within the optical layer.
Q2. List the function performed by IP router.
Ans.
- a. Routing.
- b. Forwarding.
- c. Switching.
- d. Buffering.
- e. Multiplexing.
- f. Synchronization.
Q3. What is synchronization ?
Ans. The technique of synchronizing two pulse streams in time is known as synchronization. It might relate to the alignment of an incoming pulse stream and a locally available clock pulse stream in a PPS network, or it can refer to the relative alignment of two incoming pulse streams.
Q4. Name the device used to perform logical AND operation in OTDM.
Ans. a. Nonlinear optical loop mirror.
b. Soliton-trapping AND gate.
Q5. Define the term soliton trapping.
Ans. In soliton trapping, the two pulses shift in opposing directions, so that the group velocity difference caused by the wavelength shift exactly compensates for the group velocity difference caused by birefringence. Because the two soliton pulses travel (and do not weaken), this phenomenon is known as soliton trapping.
Q6. Differentiate between 0TDM and electric TDM.
Ans. The sole difference between optical TDM (OTDM) and electrical TDM is that optical TDM performs multiplexing and demultiplexing fully optically at high rates rather than electronically.
Q7. List the options to deal with contention resolution in an optical switch.
Ans. a. The first option is to provide sufficient buffering in the switch to be able to handle these contentions.
b. Second option is to drop packets whenever we have contentions.
c. Third option is to use the wavelength domain to resolve conflicts.
Q8. Define throughput.
Ans. It is the maximum rate at which new packets can be injected into the network from their sources.
Q9. What is the main difference between burst switching and conventional photonic packet switching ?
Ans. The main difference is that bursts can be fairly long compared to the packet duration in packet switching.
Q10. What is main issue with burst switching ?
Ans. When there is contention, the fundamental challenge with burst switching is determining the buffer sizes required at the nodes to ensure tolerable burst drop probability.
Q11. List the parts of a metro network.
Ans. There are two parts of a metro network:
- a. Metro access network.
- b. Metro interoffice network.
Q12. Why recirculation buffering is more effective than output buffering?
Ans. Recirculation buffering is more effective than output buffering at resolving contentions because the buffers are shared among all outputs, as opposed to having a separate buffer for each output.
Q13. What is the importance of buffering in routers ?
Ans. a. Buffering deals with destination conflicts.
b. Buffers are also used to separate packets based on their priorities or class of service.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Optical Network Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Optical Network Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |
