Internet of Things: Previous year’s question paper with answers for AKTU B.Tech degree includes a diverse range of exam-oriented questions and comprehensive solutions, serving as a valuable resource for IoT-related test preparation.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Internet of Things: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 4th Year
Section A: Short Question Internet of Things
a. Define internet of things.
Ans. The Internet of Things (IoT) is a concept that allows internetworking items and applications to communicate with one another.
b. Illustrate sources of the IoT with example.
Ans. Arduino Yun :
- 1. Arduino Yun board uses microcontroller ATmega32u4 that supports Arduino and includes Wi-Fi, Ethernet, USB port, micro-SD card slot and three reset buttons.
- 2. The board also combines with Atheros AR9331 that runs Linux.
c. Define M2M communication.
Ans. Machine-to-Machine (M2M) refers to the process of communicating a physical object or device at a machine with others of the same sort, mostly for monitoring but also for control purposes. Each machine in an M2M system contains a smart device.
d. List features of value creation using IoT.
Ans. Following are the features of value creation using IoT :
- 1. Addressing to the emergent needs and real-time needs using predictive analytics.
- 2. Information convergence creating new experiences for the current product information.
- 3. Enabling the innovative services.
- 4. IoT enabling value capture and thus enables recurrent revenue.
e. What are communication technologies ?
Ans. Communication technologies that are used in IoT are :
- 1. RFID
- 2. Bluetooth
- 3. Wifi
f. What is data enrichment and consolidation ?
Ans. Data enrichment: Data enrichment refers to adding value, security and usability of data.
Data consolidation: The collection and integration of data from various sources into a single destination is referred to as data consolidation.
g. Compare device centric identity management and hybrid identity management.
Ans.
- 1. Device-centric identity management is the management of numerous contexts, interoperability, and the definition of a common interface for an identity system.
- 2. Hybrid identity management is concerned with hybrid identities such as user and device identities.
h. What is architectural view ?
Ans. Architectural view of IoT consists of three layers. The functionalities of the layers are specified as :
- 1. Perception layer
- 2. Network layer
- 3. Application layer
i. What is conceptual framework ?
Ans. IoT conceptual framework can be given in terms of three equations :
- 1. Physical Object + Controller, Sensor and Actuators + Internet = Internet of Things
- 2. Gather + Enrich + Stream + Manage + Acquire + Organise and Analyse = Internet of Things with connectivity to Data Centre and Enterprise Server (Oracle IoT Architecture)
- 3. Physical Objects + Gather and Consolidate + Connect + Collect + Assemble + Manage = Internet of Things (IBM IoT Foundation)
j. What is M2M communication ?
Ans. Machine-to-Machine (M2M) refers to the process of communicating a physical object or device at a machine with others of the same sort, mostly for monitoring but also for control purposes. Each machine in an M2M system contains a smart device.
Section B : Long Questions in Internet of Things
a. Explain industries can benefit from IoT.
Ans. Following are the loT applications :
- A. Smart metering :
- 1. A smart metre is an electronic device that monitors electric energy consumption and transmits the data to the power supplier for monitoring and billing.
- 2. Smart metres collect and report energy data hourly or more frequently.
- 3. Two-way communication between the metre and the central system is enabled by smart metres.
- B. E-health :
- 1. The Internet of Things (IoT) has a wide range of applications, including healthcare.
- 2. IoT in e-health enables medical centres to operate more efficiently and patients to receive better care.
- 3. There are unrivalled benefits to using this technology-based healthcare strategy, which could increase the quality and efficiency of treatments, and thus the health of patients.
- 4. The Internet of Things is extremely important in the context of e-health since connected data on patients would allow for more efficient and complete therapy.
- C. Smart city :
- 1. A smart city is one that uses information technology and the Internet of Things to govern and regulate its operations.
- 2. This encompasses both administration and facility management, such as libraries, hospitals, and utilities, as well as the public transit system.
- 3. The primary goal of smart cities is to improve infrastructure and services through the use of technology, information, and data.
- 4. This includes access to water, electricity, affordable housing, education, health care, and information technology communication.
- 5. Smart cities can increase the efficiency of city services by reducing redundancies and streamlining staff roles.
b. Explain the main components of the IoT architecture.
Ans. Following are the components of IoT architecture :
- 1. Applications and analytics component :
- a. This is the component that analyses and displays data collected via loT.
- b. It has analytics tools, AI and machine learning capabilities, and visualisation capabilities.
- 2. Integration component :
- a. This is the component that ensures the apps, tools, security, and infrastructure successfully connect with the company’s existing ERP and other management systems.
- b. Suppliers include software and cloud players, as well as open source and middleware providers such as Oracle Fusion Middleware, LinkSmart, Apache Kafka, and others.
- 3. Security and management component :
- a. LoT security entails safeguarding the system’s physical components using firmware and embedded security providers such as Azure Sphere, LynxOS, Mocana, and Spartan.
- b. Conventional security providers, such as Forescout, Symantec, and Trend Micro, also provide IoT security solutions.
- 4. Infrastructure component :
- a. Physical devices are included. IoT sensors that collect data and actuators that control the environment.
- b. It also includes the network that the sensors or actuators are connected to. This is usually, but not necessarily, a wireless network, such as Wi-Fi, 4G, or 5G.
c. Explain an embedded system on an IoT device.
Ans.
- 1. Embedding is the process of incorporating function software into computing hardware in order to enable a system function for specific targeted applications.
- 2. A device embeds software into processing and communication hardware, and the device performs application-specific functions.
- 3. Embedded system consists of the following components :
- a. Embedded software :
- i. Software consists of instructions, commands and data.
- ii. A computing and communicating device needs software.
- b. Bootloader :
- 1. A bootloader is a software that runs at the beginning of a computing device, such as a microcontroller unit (MCU).
- 2. When the system power is turned on, a bootloader begins the loading of system software (OS), and the power-on-self test is completed.
- 3. A bootloader may also make system hardware and networking capabilities more accessible.
- c. Operating system :
- 1. An operating system makes system hardware and networking capabilities more accessible.
- 2. After the OS has been loaded into RAM, the MCU enters the typical operational runtime environment.
- 3. The operating system provides memory allocation to distinct processes, and process prioritisation enables the utilisation of network hardware and device hardware operations, as well as the execution of software components and processes.
- d. Real-time operating system :
- 1. A real-time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system that facilitates the execution of operations on computer and communication devices in real time.
- 2. To enable real-time process execution, RTOS employs the idea of prioritisation and priority allocation.
- e. Integrated development environment :
- i. An integrated development environment (IDE) is a collection of software components and modules that provides a software and hardware environment for development and prototyping.
- ii. An IDE allows for code development on a computer as well as code execution on a hardware platform.
- iii. IDE allows software to communicate with a web server or cloud server on the internet.
- f. Simulator: It is software that enables development on the computer without any hardware, and then prototyping hardware can be connected for embedding the software and further tests.
- g. APIs: Software consists of device Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and device interfaces for network communication, as well as communication circuit/port(s) and middleware.
- h. Device interfaces: A connectivity interface consists of communication APls, device interfaces and processing units.
d. What are the primary hardware components that make up an embedded system ?
Ans. Following are the hardware components of an embedded system :
- 1. Power supply :
- a. It is an electrical device mainly used to power up the electrical load.
- b. Normally, a 5V power supply is required for the system; however, it can also range from 1.8 to 3.3 V.
- 2. Microcontroller :
- a. An embedded system is one that is either microcontroller-based or microprocessor-based. They are known as integrated circuits and provide computational power to a system.
- b. The performance of embedded hardware is mostly determined by the processor, which is commonly referred to as the brain of the embedded system.
- 3. Timers / Counters :
- a. Timers are used to create a delay before a specific function.
- 4. Output and Input :
- a. In order to engage with the embedded system, input is necessary. To supply input to the system, a sensor can be employed.
- b. The system’s microcontroller can be configured as an input or output port.
- 5. ROM/RAM :
- a. Memory is essential to store important information in the embedded computer system.
- b. Memory is integrated into a microcontroller or microprocessor.
- 6. Communication Ports :
- a. Communication ports allow embedded systems to communicate with other embedded systems.
- b. A variety of communication ports are available, including USB, UART, USB, I2C, SPI, and RS-485.
e. What are some of the main differences between arduino and raspberry Pi ?
Ans.
| S. No. | Arduino | Raspberry Pi |
| 1. | Control unit of Arduino is from Atmega family. | Control unit of Raspberry Pi is from ARM family. |
| 2. | Arduino is based on a microcontroller. | Raspberry Pi is based on a microprocessor. |
| 3. | It is designed to control the electrical components connected to the circuit board in a system. | Raspberry Pi computes data and produces valuable outputs, and controls components in a system based on the outcome of its computation. |
| 4. | Arduino boards have a simple hardware and software structure. | Raspberry Pi boards have a complex architecture of hardware and software. |
| 5. | CPU architecture: 8 bit. | CPU architecture: 64 bit. |
| 6. | It uses very less RAM, 2 kB. | Raspberry Pi requires more RAM, 1 GB. |
| 7. | It clocks a processing speed of 16 MHz. | Raspberry Pi clocks a processing speed of 1.4 GHz. |
Section 3 : MAC Protocol Survey in Internet of Things
a. Explain MAC protocol survey.
Ans. Schemes of MAC protocol are :
1. Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) :
- a. DMA divides the entire channel bandwidth into equal subchannels that are sufficiently separated (via guard bands) to prevent co channel interference, as shown in Fig.
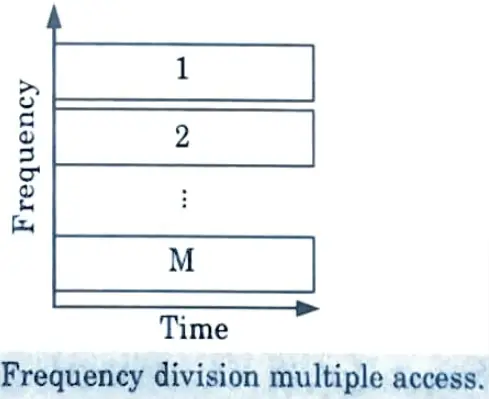


- b. The capacity of each subchannel is the capacity associated with the entire channel bandwidth.
- c. Each source node can then be assigned one (or more) of these subchannels for its own exclusive use.
- d. To receive packets from a particular source node, a destination node must be listening on the proper subchannel.
2. Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) :
- a. TDMA divides the entire channel bandwidth into equal time slots that are then organized into a synchronous frame, as shown in Fig.
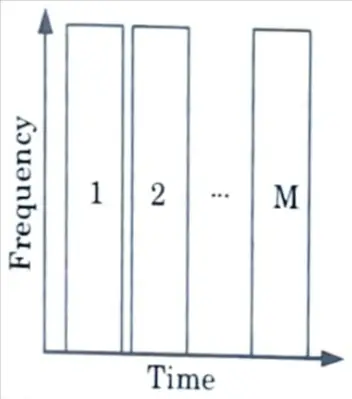


- b. Each slot represents one channel with a capacity equal to the total channel bandwidth.
- c. Each node is subsequently given one (or more) time slots to use exclusively.
- d. As a result, packet transmission in a TDMA system proceeds serially, with each node accessing the channel in turn.
3. Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) :
- a. CDMA allows many transmissions to use the same channel without interfering.
- b. Collisions are prevented by employing unique coding techniques that enable information to be extracted from the combined signal.
- c. CDMA operates by effectively spreading information bits across a channel that has been artificially expanded.
- d. This enhances the frequency variety of each transmission, making it less vulnerable to fading and lowering the level of interference that other systems running in the same spectrum may experience.
- e. It also simplifies system design and deployment because all nodes operate in the same frequency spectrum.
b. Explain IOT application layer protocols : HTTP, CoAP and MQTT.
Ans. HTTP :
The protocol that is used to transfer hypertext between two computers is known as HyperText Transfer Protocol.
HTTP provides a communication standard between a web browser and a web server. It is a set of rules that govern the transfer of data from one computer to another. In the World Wide Web, data such as text, photos, and other multimedia files are shared. When a web user opens their browser, they are indirectly using HTTP. It is a distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information system application protocol.
Constrained Application Protocol (COAP) :
A client-server protocol, the restricted application protocol. The COAP packet can be exchanged between different client nodes that are commanded by the COAP server using this protocol. The server is responsible for sharing information based on its logic but is not required to acknowledge. This is utilised in apps that implement the state transfer concept.
Message Query Telemetry Transport (MQTT) :
The message query telemetry transport protocol is a communication mechanism for loT devices. This protocol is built on the publish-subscribe paradigm, in which clients receive information solely from the subscribed subject via a broker. Before messages are transmitted, a broker categorises them into labels.
Section 4 : Survey Routing Protocols in Internet of Things
a. Outline the four aspects in your business to master IoT.
Ans. Following are the four aspects in your business to master loT :
- 1. Data collection :
- a. Data collection for manufactured products is a popular way for businesses to employ smart technology.
- b. Understanding how your target consumer uses a specific item of merchandise can lead to a wide range of analytics for future product enhancements.
- 2. Information Sharing with Customers :
- a. About three out of every four customers feel that customer service is the most important component in doing business with any company.
- b. Because smart technology can collect a wide range of information and provide it in an easy-to-read style, the data is extremely valuable to target consumers.
- 3. Clarity within the Organization :
- a. When smart technology is used in conjunction with regular product and service updates, there is more clarity inside the business.
- b. It is simpler to maintain track of items such as tools, inventories, and even office supplies.
- 4. Device Management Mobility :
- a. Handling mobile devices entails more than just company cellphones and tablets.
- b. Security cameras, televisions, and other components can be included in this type of device management.
b. Explain survey routing protocols.
Ans. The routing protocols define how nodes communicate with one another and how information is distributed throughout the network.
Types of routing protocols are :
- 1. Node centric :
- a. The destination node in node centric protocols is supplied with certain numeric IDs, which is not an expected sort of communication in wireless sensor networks.
- b. For example, Low Energy Adaptive Clustering Hierarchy (LEACH), a routing technique that structures the cluster so that energy is distributed evenly among all sensor nodes in the network.
- 2. Data centric :
- a. In the majority of wireless sensor networks, the detected data or information is significantly more valuable than the node itself.
- b. Data-centric routing strategies prioritise the transmission of information indicated by specific attributes over the collection of data from specific nodes.
- c. For example, Sensor Protocol for Information through Negotiation (SPIN), a protocol used to eliminate deficiencies such as flooding and gossiping that arise in other protocols.
- 3. Source initiated routing protocol :
- a. Dynamic Source Routing Protocols (DSR) are reactive routing protocols that are efficient and intended primarily for use in multi-hop wireless ad hoc networks of mobile nodes.
- b. It employs source routing, which means that the source must be aware of the entire hope sequence to the destination.
- c. Ad-hoc On-demand Distance Vector (AODV), for example, is reactive on request protocol. AODV is designed for networks with minimal mobile infrastructure.
- 4. Destination initiated routing protocol :
- a. Protocols are called destination initiated protocols when the path setup generation originates from the destination node.
- b. For examples, Directed Diffusion (DD) and LEACH.
Section 5 : Btech Solved Questions of Internet of Things
a. Explain programming the ardunio for IoT.
Ans. 1. Program coded in Arduino IDE is called a sketch.
2. The basic syntax of the sketch language is simple and runs in at least two parts i.e., setup() and loop()
Syntax :



- a. setup() :
- i. The setup() function is called once when our program starts.
- ii. We use it to initialize pin modes, or begin serial. It must be included in a program even if there are no statements to run.
- iii. The setup function follows the declaration of any variables at the beginning of the program.
- iv. It is the first function to run in the program which runs only once, and is used to set pinMode or initialize serial communication.
- b. loop():
- i. After calling the setup() function, the loop() function allows the program to change, respond, and control the Arduino board.
- ii. The loop function follows next and includes the code to be executed continuously i.e., reading inputs, triggering outputs, etc.
- iii. This function is the core of all Arduino programs.
b. Outline the loT layers with their responsibilities in SMARTIE project.
Ans. Following are the loT layers with their responsibilities in SMARTIE project :
- 1. Perception layer: The physical layer, which has sensors for perceiving and receiving information about the surroundings, is the perception layer. It detects some physical factors or recognises other intelligent items in the environment.
- 2. Network layer: The network layer is in charge of connecting smart things, network devices, and servers. Its capabilities are also employed to transmit and process sensor data.
- 3. Application layer: The application layer is in charge of providing the user with application-specific services. It defines many applications for the Internet of Things, such as smart homes, smart cities, and smart health.
- 4. Transport layer: The transport layer transports sensor data from the perception layer to the processing layer using networks such as WiFi, 3G, LAN, Bluetooth, RFID, and NFC.
- 5. Processing layer: The middleware layer is another name for the processing layer. It receives, stores, analyses, and processes massive amounts of data from the transport layer. It is capable of managing and providing a wide range of services to the lower layers. It makes use of a variety of technologies, including databases, cloud computing, and big data processing modules.
- 6. Business layer: The business layer manages the whole loT system, including applications, business and profit models and users privacy.
Section 6 : Interoperability in Internet of Things
a. Explain designing of smart street lights in smart city.
Ans. Block diagram of street light system :
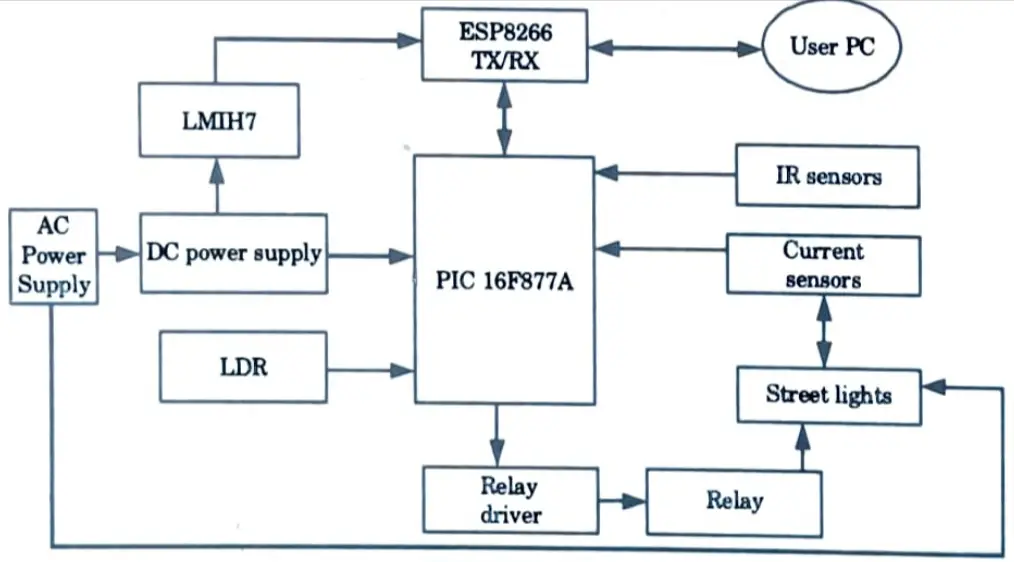


The working principle of “Design of a street light system in a smart city” is divided into six units :
- 1. Sensor circuit :
- a. It senses ambient light to determine whether it is day or night (or evening).
- b. This device has two sensors. The first sensor detects sunlight, while the second detects whether or not the LED panel is functional.
- 2. 8-bit microcontroller :
- a. It is in charge of monitoring the state of the first Light Dependent Resistors (LDR), which determines whether or not the environment receives adequate sunlight.
- b. If there is enough sunshine, it does nothing; if there is insufficient sunlight, the microcontroller activates the following unit.
- 3. Relay driver :
- a. The relay which is controlled by designated I/O pin of the microcontroller.
- b. If there is no sunlight, it activates the relay driver circuit designed with NPN transistor 2N2222. This transistor collector is connected to 1st terminal of relay and the other terminal of the relay is connected to +12V.
- c. When the relay is energized, the mechanical switch in the relay allows to pass current to the LED unit.
- 4. LED panel mode :
- a. It has a 6×8 matrix. By adding more LEDs, the panel’s size can be enhanced.
- b. A solid-state relay can be used to control the panel.
- c. When the microcontroller activates the LED panel, the second LDR detects the light from the panel; if the second LDR detects enough light, the system concludes the panel is working properly; if the second LDR detects insufficient light, the system assumes the panel is not working (2nd LDR is not getting enough light).
- d. The microcontroller sends data to the web server via the ESP8266 unit.
- 5. ESP8266: This is a Wi-Fi modem based on ESP8266, microcontroller is communicating ESP8266 through the serial communication.
- 6. Web server :
- a. The transmitted data is handled by web server.
- b. ESP8266 itself is utilising web server, ESP8266 is used here as client, so it can transfer data to web server and we do not need to number any ESP8266 IP address.
- c. Every device will talk with the same web server.
- d. The web server unit has a collection of web pages that allow us to monitor and configure the street light.
b. Explain interoperability in detail. Why it is essential in IOT?
Ans.
- 1. IoT interoperability refers to the ability of many components inside an IoT deployment to efficiently communicate, share data, and collaborate to achieve a common goal.
- 2. Businesses must be able to send and receive data across all connections from devices to the cloud.
- 3. In an IoT setting, interoperability refers to the capacity to convey relevant, actionable information between systems.
- 4. Effective data transport to different user’s application systems and servers is required for IoT interoperability at the application layer.
- 5. Open-source communications protocols like as MQTT or CoAP, as well as RESTful-based Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), are significant drivers of cross-application interoperability.
Section 7 : H/W Units in Internet of Things
a. Explain smart metering and E-health.
Ans. Smart metering :
- 1. A smart metre is an electronic device that monitors electric energy consumption and transmits the data to the power supplier for monitoring and billing.
- 2. Smart metres collect and report energy data hourly or more frequently.
- 3. Two-way communication between the metre and the central system is enabled by smart metres.
E-health :
- 1. The Internet of Things (IoT) has a wide range of applications, including healthcare.
- 2. IoT in e-health enables medical centres to operate more efficiently and patients to receive better care.
- 3. There are unrivalled benefits to using this technology-based healthcare strategy, which could increase the quality and efficiency of treatments, and thus the health of patients.
- 4. The Internet of Things is extremely important in the context of e-health since connected data on patients would allow for more efficient and complete therapy.
- 5. The first step towards reciprocal knowledge sharing would be to virtualize patient data and make it available to relevant healthcare staff.
- 6. Another critical part of utilising this linked data is the development of an intelligent clinical decision support system that would aid doctors in whatever manner feasible during the therapy phase.
b. Describe communicating data with H/W units.
Ans. Connectivity or communication between various hardware unit in IoT is achieved by using following wireless communication protocols :
- 1. Satellite :
- a. Satellite communications enable cell phone communication from a phone to the next antenna of about 10 to 15 miles.
- b. They are called GSM, GPRS, CDMA, GPRS, 2G / GSM, 3G, 4G/LTE, EDGE and others based on connectivity speed.
- c. This type of communication is commonly referred to as “M2M” (Machine-to-Machine) in Internet of Things terminology since it allows devices such as phones to transmit and receive data via the cell network.
- 2. Wi-Fi :
- a. Wi-Fi isa Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) that utilizes the IEEE 802.11 standard through 2.4 GHz UHF and 5 GHz ISM frequencies.
- b. Wi-Fi provides Internet access to devices that are within the range (about 66 feet from access point).
- 3. Radio Frequency (RF) :
- a. Radio frequency communications are probably the easiest form of communications between devices.
- b. Protocols like ZigBee or ZWave use a low-power RF radio embedded into electronic devices and systems.
- 4. RFID :
- a. RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification.
- b. RFID refers to small electronic devices that consist of a small chip and an antenna.
- c. The chip typically is capable of carrying 2,000 bytes of data or less.
- d. The RFID device serves the same purpose as a bar code or a magnetic strip on the back of a credit card or ATM card.
- 5. Bluetooth :
- a. Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard that allows data to be exchanged over short distances.
- b. Bluetooth is found in a wide range of products, including phones, tablets, media players, and robotics systems.
- c. In low-bandwidth settings, the technique is highly useful for sending information between two or more devices that are close to one other.

1 thought on “Internet of Things: Previous Year’s Question Paper Questions and Answers”