Find out more about Concrete Technology Short Question Notes from the B.Tech. AKTU Quantum Book. Discover the design, construction, and durability principles of concrete mixes for the building of robust and sustainable infrastructure.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Concrete Technology: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Unit-I: Cement Production and Aggregates (Short Question)
Q1. What do you understand by cement ?
Ans. The highly fine-grained substance cement has cohesive and adhesive qualities that act as a binder for the separate elements.
Q2. Give the chemical composition of ordinary portland cement.
Ans.



Q3. Enlist the Bogue’s composition of cement.
Ans. The composition of portland cement is basically consist of four main compounds :
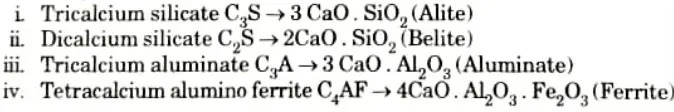
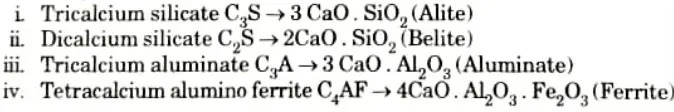
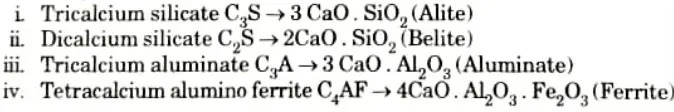
Q4. What do you mean by hydration of cement ?
Ans. Hydration of cement refers to the chemical processes that occur when cement and water are combined.
Q5. Define heat of hydration.
Ans. When cement and water react, a significant amount of heat is released in the process. The term “heat of hydration” refers to this heat release.
Q6. Give the various types of cement.
Ans. Following are the various types of cement :
i. Ordinary Portland cement. ii. Rapid hardening cement.
iii. Sulphate resisting cement. iv. Quick setting cement.
v. Low heat cement. vi. High alumina cement.
vii. Air entraining cement.
Q7. Where are rapid hardening cement used ?
Ans. Rapid hardening cement is recommended in the following situation:
- i. In pre-fabricated concrete construction.
- ii. Road repair works.
- iii. In cold weather concrete construction.
Q8. Under what situations, we use sulphate resisting cement.
Ans. Following are the conditions in which sulphate resisting cement used:
- i. Concrete to be used in marine condition.
- ii. Concrete to be used in foundation and basement, where soil is infested with sulphates.
- iii. Concrete to be used in the construction of sewage treatment works.
Q9. What are the advantages of Portland slag cement ?
Ans. Following are the advantages of Portland slag cement:
- i. It lowers hydration heat.
- ii. The porous structure is improved.
- It reduces permeability, in part.
- iv. It strengthens defences against chemical assault.
Q10. Give the use of Portland pozzolana cement.
Ans. Following are the uses of Portland pozzolana cement:
- i. For hydraulic structure.
- ii. For mass concrete structure like dam, bridge pier and raft foundations.
- iii. For marine structure.
- iv. For sewers and sewage disposal work, etc.
Q11. What are the pozzolanic materials ?
Ans. Pozzolanic materials are siliceous or siliceous and aluminous materials that, by themselves, do not have much cementitious value but, when finely divided and exposed to moisture, chemically react with calcium hydroxide released upon hydration at room temperature to produce compounds with cementitious properties.
Q12. Enlist the various types of pozzolanic materials.
Ans. Following are the various types of pozzolanic materials:
1. Natural Pozzolanas:
i. Clay and shales. ii. Diatomaceous earth.
iii. Volcanic tuffs and Pumicites.
2. Artificial Pozzolanas:
i. Fly ash. ii. Blast furnace slag. iii. Silica fume.
iv. Rice husk ash. v. Metakaolin. vi. Surkhi.
Q13. Define fly ash.
Ans. It is a finely separated byproduct of powdered coal burning that is carried by flue gases and collected by an electrostatic precipitator.
Q14. Discuss silica fume.
Ans. Silica fume is a very thin pozzolanic substance created when silica or ferrosilicon is produced in an electric arc boiler at a temperature of more than 2000 °C. It is made up of ultrafine, amorphous glassy spheres of silicon dioxide.
Q15. What do you understand by surkhi ?
Ans. Bricks or burned clay balls are ground into a powder to create surkhi, an artificial pozzolana.
Q16. What are the properties of aggregate that affects the concrete properties?
Ans. Following are the important properties of aggregate which affect the properties of concrete:
i. Particle shape. ii. Surface texture.
iii. Specific gravity. iv. Bulk density.
v. Bulking of sand. vi. Soundness of aggregate.
vii. Alkali aggregate reaction etc.
Q17. What are the deleterious substances in aggregates ?
Ans. Following are the deleterious substances in aggregates:
- i. Organic impurities, which intertere the hydration ot concrete.
- ii. Salt when aggregate is obtained from sea-shore.
- iii. Weak or unsound particles.
Q18. Discuss alkali-aggregate reaction between aggregate and cement.
Ans. Alkali-silicate gel is created when the active silica components of the aggregate react with the alkalies in the cement. Alkali-aggregate reaction is the name given to this reaction.
Q19. What are the effects of alkali-aggregate reaction on concrete?
Ans. Alkali-silicate gel is created as a result of this reaction, and when it grows and exerts internal pressure on cement paste, it causes it to expand, crack, and break.
Q20. Enumerate the controlling measure of alkali-aggregate reaction.
Ans. Following are the controlling measures of alkali-aggregate reaction:
- i. Selection of non-reactive aggregate.
- ii. By the use of low alkali cement.
- iii. By controlling moisture, void space and temperature of concrete.
- iv. By the addition of reactive silica in finely powdered form.
Q21. What do you understand by term ‘all in aggregate’?
Ans. Sometimes, all-in-aggregates combined aggregates made up of various proportions of fine and coarse aggregates are found in nature.
Q22. What do you mean by single size aggregates ?
Ans. The term “single-size aggregates” refers to aggregates that mainly consist of particles falling within a small range of size fractions.
Q23. Describe the soundness of aggregate.
Ans. The soundness reflects the aggregate’s capacity to withstand drastic volume fluctuations brought on by alterations in the external environment. For instance, heat fluctuations, freezing and thawing, and alternating wetting and drying.
Q24. Enlist the thermal properties of aggregates.
Ans. Following are the thermal properties of aggregate :
- i. Coefficient of thermal expansion.
- ii. Specific heat.
- iii. Thermal conductivity.
Q25. Explain the gap grading of aggregates.
Ans. Grading that lacks one or more intermediate size fractions is known as gap grading.
Q26. Give the features of gap graded aggregates.
Ans. Following are the features of gap graded aggregates:
- i. The compressive or tensile strength of a gap-graded aggregate is unaffected.
- ii. Less cement and a lower water cement ratio are needed for gap-graded aggregate.
- iii. Gap-graded aggregate is used in concrete to lessen drying shrinkage.
- iv. Gap graded aggregate has a lower specific surface area due to a higher percentage of coarse aggregate.
Q27. Enlist the various tests which are performed on the aggregate.
Ans. Following are the various test performed on the aggregates:
- i. Aggregate crushing value test.
- ii. Aggregate impact value test.
- iii. Aggregate abrasion value test.
- iv. Bulk density test, etc.
Q28. What are the effects of impurities in water on properties of concrete?
Ans. Following are the effects of impurities in water on properties of concrete.
- 1. The presence of contaminants in the mixing water reduces the strength and durability of concrete.
- 2. Water that contains a lot of chlorides tends to create surface efflorescence, prolonged wetness, and increased corrosion of the reinforcing steel.
Unit-II: Chemical and Mineral Admixtures (Short Question)
Q1. Classify the admixtures used in concrete production.
Ans. Following are the different types of admixtures:
- i. Plasticizers.
- ii. Superplasticizers.
- iii. Retarders.
- iv. Accelerators.
- v. Air entraining admixtures.
- vi. Pozzolanic or mineral admixtures.
- vii. Water proofing admixtures, etc.
Q2. What are accelerators ?
Ans. These are materials that, when added to concrete, mortar, or grout, speed up the hydraulic cement’s hydration, reduce the time it takes to set, or quicken the process of hardening or developing strength.
Q3. Give the examples of accelerating admixtures.
Ans. Calcium chloride, soluble carbonates, silicates, fluosilicates, etc.
Q4. Describe the application of accelerator in concrete.
Ans. Accelerators are utilized for underwater construction particularly in cold climates.
Q5. Discuss retarders.
Ans. These are the compounds that slow down the rate at which concrete sets.
Q6. Enlist the some retarding admixtures.
Ans. Sugar, carbohydrates derivatives, soluble zinc salt, etc., are used as retarders.
Q7. Where are retarding admixtures used ?
Ans. They are especially useful in warm climates or for ready-mixed concrete where it is necessary to postpone cement setting.
Q8. Define plasticizers.
Ans. These are the substances that, when added to concrete, make it more workable without adding more water; as a result, the concrete formed with these admixtures flows.
Q9. In what situation, plasticizers are used in concrete.
Ans. Following are the situation where plasticize used:
- i. It is especially helpful for very strongly reinforced portions or when quick concrete placement is preferred.
- ii. It is used to lower the water-to-cement ratio in concrete that has an extraordinarily high strength.
Q10. Enumerate the new generation superplasticizers.
Ans. Following are the new generation superplasticizers:
- i. Acrylic polymer based.
- ii. Copolymer of carboxylic acrylic ester.
- iii. Cross linked acrylic polymer.
- iv. Polycarboxylate ester.
- v. Multicarboxylate ethers, etc.
Q11. Write down the advantages of accelerators.
Ans. Following are the advantages of accelerators:
- i. Enable the formwork to be removed earlier.
- ii. Shorten the time needed for curing.
- iii. Increase the window of opportunity for setting a structure in concrete.
- iv. During the urgent repairs.
Q12. What do you understand by air-entraining agents ?
Ans. These are the admixtures that, while mixing, introduce air into concrete in the form of tiny bubbles to improve workability, resistance to freezing and thawing, and resistance to the disruptive effects of de-icing salts.
Q13. Enlist the air entrainment agents used in concrete production.
Ans. The materials to be employed as air entraining agents include natural wood resin, vinsol resin, animal/vegetable fats, etc.
Q14. Write down the effect of air entrainment on the properties of concrete.
Ans. Following are the effect of air entrainment on properties of concrete:
- 1. Enhanced resilience to freezing and thawing.
- 2. An increase in workability.
- 3. A loss of strength.
- 4. lessens the reactivity of alkali aggregates.
- 5. Allows for a decrease in water content.
Q15. Write down the application of pozzolans.
Ans. i. Pozzolana used for reduction in the heat of hydration.
ii. It is used for improvement in the workability.
Q16. Give the advantages and disadvantages of air-entraining admixtures.
Ans. Advantages:
- i. Strengthen concrete’s ability to withstand freezing and thawing.
- ii. Improve the concrete’s usability.
- iii. Minimize concrete mix bleeding and segregation.
Disadvantages :
- i. Strength reduction in concretes with a high cement percentage.
Q17. What are the advantages and disadvantages of water reducing admixtures?
Ans. Advantages:
- i. Make concrete more workable.
- ii. The same cement content can produce high strength.
- iii. Save up to 10% on cement.
Disadvantages:
- i. Aggravate the rate of slump loss with time.
Q18. Describe the merits and demerits of plasticizers.
Ans. Merits:
- i. Increase the early strength of concrete.
- ii. Create flowing concrete to be used in large, densely reinforced structures with difficult-to-reach places.
Demerits:
- i. A quick slump loss that results in a lack of workability.
- ii. The incompatibility of plasticizers with cement.
Q19. Enumerate the advantages and disadvantages of accelerating admixtures.
Ans. Advantages:
- i. Cement’s setting time should be sped up.
- ii. Improve density and compressive strength while reducing segregation.
- iii. Decrease the amount of water necessary.
Disadvantages:
- i. May result in discolouration.
- ii. The potential for reinforcement corrosion.
- iii. A rise in shrinkage during drying.
Unit-III: Mix Design and Rheology of Concrete (Short Question)
Q1. What do you understand by the term ‘proportioning of mix’ ?
Ans. The skill of attaining a suitable ratio of the different components of concrete with the desired qualities at the lowest cost is hence proportioning a concrete mix for a certain purpose.
Q2. Discuss the principles of mix proportioning.
Ans. Following are the data required for proportioning a concrete mix:
- i. The environmental exposure conditions.
- ii. Grades of concrete.
- iii. Types of cement.
- iv. Types and size of aggregates.
- v. Maximum and minimum cement content.
- vi. The maximum free water-cement ratio.
- vii. Degree of workability.
- viii. Type of admixture used.
- ix. Density of concrete.
- x. Type of mixing and curing.
Q3. Write down the environment exposer conditions for concrete.
Ans. Following are the environment exposers conditions:
- i. Mild.
- ii. Modulate.
- iii. Sever.
- iv. Very sever.
- v. Extreme.
Q4. What are the properties of concrete related to mix design?
Ans. Following are the properties of concrete related to mix design:
- i. Durability.
- ii. Workability.
- iii. Strength.
Q5. Define harshness of mix.
Ans. The inability of concrete to produce a smooth finish even after trowelling is what is meant by this term. This occurs when there are too many huge or uniformly sized particles and when there is not enough cement mortar to fill all the gaps.
Q6. What the various methods of proportioning concrete mixes.
Ans. Following are the various methods of proportioning concrete mixes :
- i. Trial mixes.
- ii.. Normal mixes.
- iii. America concrete institute method.
- iv. BIS method.
- v. Minimum voids method.
- vi. Maximum density method.
Q7. Write down the factors that affects the workability.
Ans. Following are the factors affecting the workability of concrete:
- i. Types of aggregate rounded, angular, flaky, etc.
- ii. Poor and well-graded grading of fine and coarse aggregates.
- iii. The amount of cement paste used in the mixture.
- iv. The paste’s consistency.
Q8. Write down the compressive strength formula according to Abram’s law.
Ans. Compressive strength is expressed as:
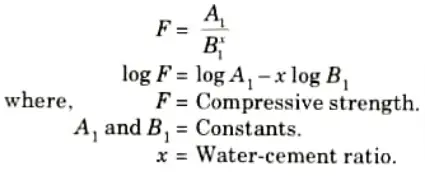
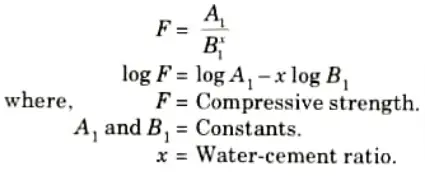
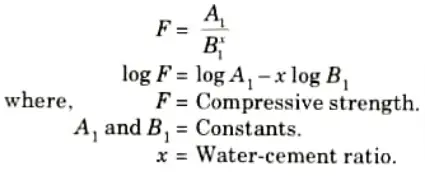
Q9. Define variance.
Ans. This is a measurement of how much any individual observed data can vary from the mean strength.
Q10. Define characteristic strength of concrete.
Ans. It is described as the threshold number below which not more than 5% of test findings are anticipated to be negative.
Q11. Give the statement of Abram’s law.
Ans. According to Abram’s law, “the strength of fully compacted hardened concrete is approximately inversely proportional to the water content per cubic metre of cement i.e., water-cement ratio”.
Q12. What is rheology and rheological models of concrete?
Ans. Rheology is the study of material flow. Fresh concrete’s ability to flow under its own weight and completely fill moulds is described by rheological models of often-fresh concrete.
Q13. Write down the rheological characteristics of fresh concrete.
Ans. Following are the characteristic of fresh concrete:
- i. Workability.
- ii. Compactability.
- iii. Flowability.
- iv. Pumpability.
- v. Flow under its own weight.
- vi. Fillability.
- vii. Stability.
- viii. Finishability.
Q14. Classify the flow of fresh concrete.
Ans. i. Confined Flow: Concrete flows through an aperture under its own weight.
ii. Free Flow: Concrete can be poked and inserted by a rod or plunger using just gravitational power, or it can flow freely under its own weight.
iii. Vibration Flow: Concrete moves as a result of vibrations.
Q15. What are the factors which affects the rheological properties of concrete?
Ans. Following are the factors affecting the rheological properties of concrete:
- i. Mixing of concrete.
- ii. Effect of cohesion.
- iii. Effect of water and super plasticizers
- iv. Heat of hydration and air entrained.
Unit-IV: Concrete Production, Properties and Testing (Short Question)
Q1. What are the step in concreting process?
Ans. The concreting process involves the following five steps :
- i. Batching or measurement of materials.
- ii. Mixing of concrete.
- iii. Transportation.
- iv. Placing, compacting and finishing of concrete.
- v. Curing.
Q2. Write down the factors affecting the batching process.
Ans. Following are the affecting factor of batching process :
- i. Size of job.
- ii. Required production rate, and
- iii. Required standard of batching performance.
Q3. Classify the breathing process of concrete.
Ans. Following are the batching process of concrete:
- i. Manual batching.
- ii. Semi automated batching.
- iii. Automated batching.
Q4. Classify the mixers, which are used in mixing of concrete.
Ans. Following are the various types of mixer commonly employed:
- 1. Horizontal or inclined (B drum) mixer
- i. Tilting drum.
- ii. Non-tilting drum.
- iii. Reversing drum.
- 2. Vertical (Pan) mixer
Q5. Enumerate the various equipments which are used for transporting of concrete.
Ans. Following equipments are used for transporting concrete:
- i. Barrows.
- ii. Dumpers and trucks.
- iii. Elevating tower and hoists.
- iv. Cranes and cableways.
- v. Belt conveyor.
Q6. Define curing of concrete.
Ans. In order to give freshly laid concrete the desired strength and hardness, curing involves maintaining an appropriate moisture content and temperature.
Q7. What are the advantages of curing in concrete ?
Ans. Following are the advantages of curing in concrete:
- i. Concrete that has been favourably cured is stronger.
- ii. Drying reduces shrinkage and cracking.
- iii. Better-durable concrete.
Q8. What are the different methods of curing ?
Ans. Following are the various methods of curing:
- i. Covering concrete surface with hessian or gunny bags.
- ii. Sprinkling of water.
- iii. Ponding method.
- iv. Membrane curing.
- v. Steam curing.
- vi. Electrical curing.
Q9. What are the limitations of slump cone test of concrete ?
Ans. In cases of more rigid, severe concrete, the slump cone test does not produce favourable findings.
Q10. Define compacting factor.
Ans. The weight of partially compacted concrete divided by the weight of fully compacted concrete is known as the compacting factor.
Q11. In which conditions compacting factor test is not suitable.
Ans. It is not suitable for concrete of very low workability of 0.7 or below.
Q12. Discuss Abram’s law.
Ans. “For plastic mixtures using neat and clean aggregate the strength of concrete under specified conditions is governed by the net quantity of water mixed per bag of cement”.
Q13. What is gel space ratio ?
Ans. The volume of hydrated cement paste divided by the total volume of hydrated cement and capillary holes is known as the gel-space ratio.
S = 240 x3
Q14. Write the factor affecting the strength of concrete ?
Ans. Following are the factors affecting the strength of concrete:
- i. Size of test specimen.
- ii. Size of specimen relative to maximum size of aggregate.
- iii. Moisture condition of specimen.
- iv. Air voids
- v. Rate of loading.
- vi. Age and types of cement, etc.
Q15. What is maturity of concrete and how it is calculated ?
Ans. It is defined as the summation of product of time and temperature.
Maturity = 𝚺(Time x Temperature)
Q16. What is creep ?
Ans. It can be described as a sustained load that causes concrete to become more strained over time. This is sometimes referred to as a temporal field or plastic flow.
Q17. What do you mean by shrinkage ? How is it determine ?
Ans. Contraction of concrete in the absence of load is known as shrinkage.
Shrinkage can be estimated by,
Es = 0.00125(0.90-h)
where, h = Relative humidity.
Q18. Define plastic shrinkage.
Ans. Concrete shrinkage brought on by aggregate absorption of water, water evaporating quickly, and bleeding.
Q19. Describe drying shrinkage.
Ans. Shrinkage caused by capillary water, absorbed water, or interlayer water after the concrete has set and hardened.
Q20. Give the remedial measures to overcome the effect of creep.
Ans. The effect of creep can be reduced by,
- i. Using high strength concrete.
- ii. Delaying the application of finishes, partition wall, etc
- iii. Adding reinforcement.
- iv. Steam curing under pressure.
Q21. Write down the various types of test performed for determining the compressive and flexural strength.
Ans. Following are the various test performed for determining the compressive and flexural strength of concrete :
- A. Destructive Test:
- i. Cube test.
- ii. Tensile strength test
- a. Split tensile test.
- b. Flexure test.
- iii. Concrete core test.
- B. Non-Destructive Test:
- i. Rebound hammer test.
- ii. Ultrasonic pulse velocity test.
- iii. Pull out test.
- iv. Penetration resistance test.
Q22. What is creep coefficient ?
Ans. It is the ratio of the ultimate creep strain to the elastic strain at the age of loading.
| Age of Loading | Creep Coefficient |
| 7 days | 2.2 |
| 28 days | 1.6 |
| 1 year | 1.1 |
Q23. Define initial tangent modulus of concrete.
Ans. It is a slope of the curve from origin.
Q24. What are the advantages of ultrasonic pulse velocity test ?
Ans. Advantages:
- i. High penetrating power.
- ii. High sensitivity.
- iii. Greater accuracy
- iv. Some capability in estimating the size, shape, nature of the flows.
- v. Portability.
Q25. Give the disadvantages of ultrasonic pulse velocity test.
Ans. Disadvantages:
- i. Skilled person are required.
- ii. Difficulty in inspecting the parts which are irregular.
- iii. Requirement of the couplants.
- iv. Test objects should be water resistant.
Q26. What is the relation between cohesiveness and segregation ?
Ans. 1. Cohesive implies bonding force and segregation indicates separation; when boding between concrete elements increases, segregation decreases.
2. Cohesiveness and segregation are thus inversely connected.
Unit-V: Specifie Concretes (Short Question)
Q1. What is the self compacting concrete ?
Ans. Self-compacting concrete is a type of concrete that can be compacted into every corner of a formwork using only its own weight and no external vibrators.
Q2. Discuss the material required for self compacting concrete.
Ans. Following are the material required for self compacting concrete:
i. Cement. ii. Fine aggregate.
iii. Coarse aggregate. iv. Water.
v. Chemical admixture such as superplasticizers, viscosity modifying agents, air-entraining agents.
vi. Mineral admixtures such as fly ash, GBFS, silica fume.
Q3. What are the advantages of self compacting concrete ?
Ans. Following are the advantages of self compacting concrete:
- i. Better compaction and uniformity of concrete improves the quality, durability, and reliability of concrete constructions.
- ii. Reduced permeability.
- iii. Ease of placement result in cost savings.
Q4. What do you understand by fiber reinforced concrete ?
Ans. Fiber Reinforced Concrete: Fiber reinforced concrete is made up of cement, water, aggregate, and discontinuous, evenly scattered, or discrete fibres.
Q5. What are the affecting factors of properties of fiber reinforced concrete ?
Ans. Following are the factors affecting properties of fiber reinforced concrete:
- i. Mixing.
- ii. Workability and compaction of concrete.
- iii. Size of coarse aggregate.
- iv. Orientation of fibres.
- v. Aspect ratio of fibres.
- vi. Volume of fibres.
Q6. Give the advantages of fiber reinforced concrete.
Ans. Advantages of Fiber Reinforced Concrete:
- i. Concrete has a lower permeability
- ii. Higher toughness.
- iii. Improved fatigue strength and endurance limit.
- iv. Increased bond strength.
- v. Lower shrinkage and cracking.
Q7. Discuss the application of fiber reinforced concrete.
Ans. Application of Fiber Reinforced Concrete:
- i. Repairs and rehabilitation works.
- ii. Wearing surface to exiting bridges/ culverts.
- iii. Precast products.
- iv. Blast resistance structures.
- v. Water retaining structures.
- vi. Pavements and floors.
Q8. Write down the comparison of FRC and NRC.
Ans.
| S. No. | FRC (Fiber Reinforced Concrete) | NRC (Normal Reinforced Concrete) |
| 1. | High durability. | Lower durability. |
| 2. | Protect steel from corrosion. | Steel potential to corrosion. |
| 3. | Lighter materials. | Heavier material. |
| 4. | More expensive. | Economical. |
| 5. | With the same volume, the strength is greater. | With the same volume, the strength is less. |
| 6. | Less workability. | High workability as compared to FRC. |
Q9. What is ferro-cement ?
Ans. It is a type of thin wall reinforced cement made of hydraulic cement mortar with closely spaced layers of continuous and relatively tiny size wire mesh.
Q10. What are the constituents of ferro-cement ?
Ans. Following are the constituents of ferro-cement:
- i. Cement mortar mix.
- ii. Skeleton steel.
- iii. Steel mesh reinforcement or fibre reinforcement polymeric meshes.
Q11. Enumerate the manufacturing techniques of ferro-cement.
Ans. Following are the manufacturing techniques of ferro-cement:
- i. Hand plastering.
- ii. Semi-mechanized process.
- iii. Centrifuging and guniting.
Q12. Describe properties of ferro-cement.
Ans. Following are the properties of ferro-cement :
- i. It is very durable, cheap and versatile material.
- ii. High tensile strength and stiffness
- iii. Better impact and punching shear resistance.
Q13. Enumerate the mechanical properties of ferro-cement.
Ans. Mechanical Properties of Ferro-cement:
- i. Compressive strength- 27.5 to 60 N/mm2.
- ii. Allowable tensile strength -10.0 N/mm2
- iii. Ultimate tensile strength-34.5 N/mm2
- iv. Steel cover – 1.5 mm to 5 mm.
- v. Steel percentage – 5 to 8 %.
- vi. Thickness – 10 mm to 60 mm.
Q14. Describe the various application of ferro-cement.
Ans. 1. Marine Application: It is used for constructing boats, fishing vessels, barrages, docks, floating buoys. etc.
2. Rural Energy Application: Biogas digester, biogas holder, incinerator etc.
Q15. Compare recycled aggregate and natural aggregate.
Ans.
| S. No. | Recycled Aggregate | Natural Aggregate |
| 1. | It has rough textured angular elongated particles. | It has smooth and rounded compacted particles. |
| 2. | It is well graded. | It is not well graded. |
| 3. | It has more water absorption. | It has less water absorption. |
| 4. | It has lower dry density. | It has more dry density. |
Q16. Write down the applications of recycled aggregate.
Ans. Following are the applications of recycled aggregate:
- i. Embankment Fill Materials: The embankment is located on moist subgrade sections. Recycled aggregate can help to stabilize the base and improve the working surface.
- ii. Backfill Materials: After laboratory testing, recycled aggregate can be used as backfill materials in the pipe zone along trenches.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Concrete Technology Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Concrete Technology Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |

4 thoughts on “Aktu Concrete Technology KCE-051 Btech Short Question, Quantum Pdf”