With AKTU’s Question Paper, you may embark on an Exciting Cloud Computing Journey. Improve your understanding, test your knowledge, and fly to exam achievement.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Cloud Computing: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 4th Year
Section A: Very Short Question Cloud Computing
a. Define threat Agents ? Explain their role in cloud security.
Ans. Threat agents: A threat agent is an entity that can carry out an attack and thus poses a threat. Internal or external threats to cloud security can come from humans or software programmes.
Role: Threat agent has the power to, exploit vulnerability or conduct other damaging activities.
b. What are security services in the cloud ?
Ans. Security services in the cloud are :
- 1. Identity and access
- 2. Data loss prevention
- 3. Web security
- 4. E-mail security
- 5. Security assessment
c. What is encryption ? Define the types of encryption.
Ans. Encryption: Encryption is a method of scrambling data so that only authorised parties can decipher it. It is the process of converting plaintext that can be read by humans into incomprehensible text, also known as ciphertext.
Types of encryption:
- 1. Asymmetric encryption
- 2. Symmetric encryption
d. What is utility computing ?
Ans. Utility computing is a model in which computing resources are provided to customers on a demand basis. As large volumes of data are distributed across multiple servers or backend systems, utility computing helps to eliminate data redundancy.
e. What is IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS ?
Ans. IaaS: Infrastructure-as-a-Service is a model that allocates virtualized computing resources to the user through the internet.
PaaS: Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is a type of cloud computing service that provides a platform for customers to develop, run, and manage applications without having to build and maintain the infrastructure.
SaaS: SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) is an application hosted on a remote server and accessed through the internet. SaaS is the web-based e-mail service offered by an organization.
f. What is VM network routing ?
Ans. Routers for virtual machines are used to organise traffic between virtual switches, physical switches, and physical network adapters.
g. Give some examples of Web 2.0 applications.
Ans. Examples of Web 2.0 applications include social networking sites or social media sites. For example, Facebook, blogs, wikis, YouTube, image sharing sites.
h. What are IaaS, PaaS and SaaS ?
Ans. IaaS: Infrastructure-as-a-Service is a model that allocates virtualized computing resources to the user through the internet.
PaaS: Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is a category of cloud computing services that provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure.
SaaS: SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) is an application hosted on a remote server and accessed through the internet. SaaS is the web-based e-mail service offered by an organization.
i. What are security services in the cloud ?
Ans. Security services in the cloud are :
- 1. Identity and access
- 2. Data loss prevention
- 3. Web security
- 4. E-mail security
- 5. Security assessment
j. What are modules of Hadoop ?
Ans. Modules of hadoop are :
- 1. HDES
- 2. Yarn
- 3. MapReduce
- 4. Hadoop common
Section B : Most Discussed Questions in Cloud Computing
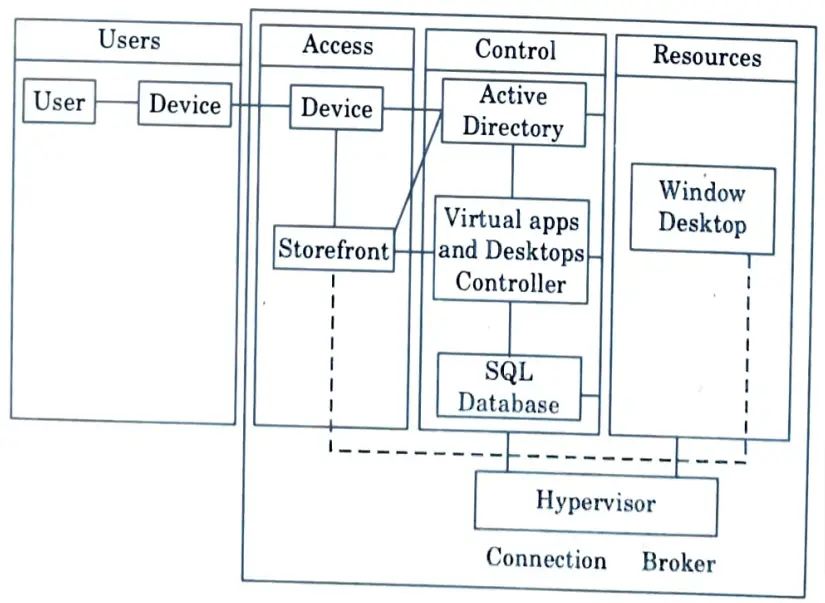
a. What is virtual desktop infrastructure ? Explain with diagram.
Ans. Virtual desktop infrastructure :
- 1. Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) is a technology that enables and manages virtual desktops by utilising virtual machines.
- 2. VDI hosts desktop environments on a centralised server and makes them available to end users on demand.
- 3. VDI is a technology that allows you to create a virtual environment on a remote server.
- 4. It divides the servers into different virtual desktops, which users can access remotely via their devices.
- 5. These virtual desktops are hosted on Virtual Machines (VM), which are managed using management software.
- 6. The functioning of VDI consists of :
- a. Hypervisor :
- i. A hypervisor is software that separates the operating system from the hardware on which it runs.
- ii. It creates a virtual environment in which hardware can be partitioned into multiple Virtual Machines (VMs).
- iii. Each VM hosts virtual desktops, each with its own configuration, operating system, and applications.
- iv. Citrix Hypervisor, Microsoft Hyper-V, and VMware vSphere are three well-known hypervisors on the market.
- b. Connection Broker :
- i. A connection broker is a software programme that connects users to resources such as Windows desktops, Linux applications, and so on.
- ii. It is also in charge of authenticating users and granting them access to their desktop instances.
- iii. The connection broker also keeps track of which desktops are active and which are inactive.
- iv. When a user sends a request to connect to a desktop, it returns an idle desktop instance to the user.
- v. When a user disconnects the desktop, it updates the status of the desktop to inactive.


b. How does an unauthorized access can be detected by the help of virtualization techniques ?
Ans. Following are the techniques used to detect unauthorized access :
- 1. URL filtering :
- a. While most organisations use this technology to restrict inappropriate Web browsing or unauthorised social media services, the tools are capable of detecting a wide range of cloud access.
- b. The Web serves as the primary management interface for all cloud services. Even most API calls use HTTP to reach known URLs and are thus easy to detect.
- c. URL filters, at least for major services, can provide insight into who is accessing management consoles and API interfaces.
- 2. Data loss prevention :
- a. DLP tools support HTTP analysis, including looking inside SSL sessions if the supporting platform and configuration are in place.
- b. DLP rules should be able to detect sensitive data leaving your organisation, whether to the cloud or elsewhere. We can fine-tune these for cloud-specific concerns by taking into account context, such as the destination.
- 3. Database activity monitoring :
- a. Database Activity Monitoring can detect dumps of major production databases, which could indicate a potential move to either an internal or external test environment.
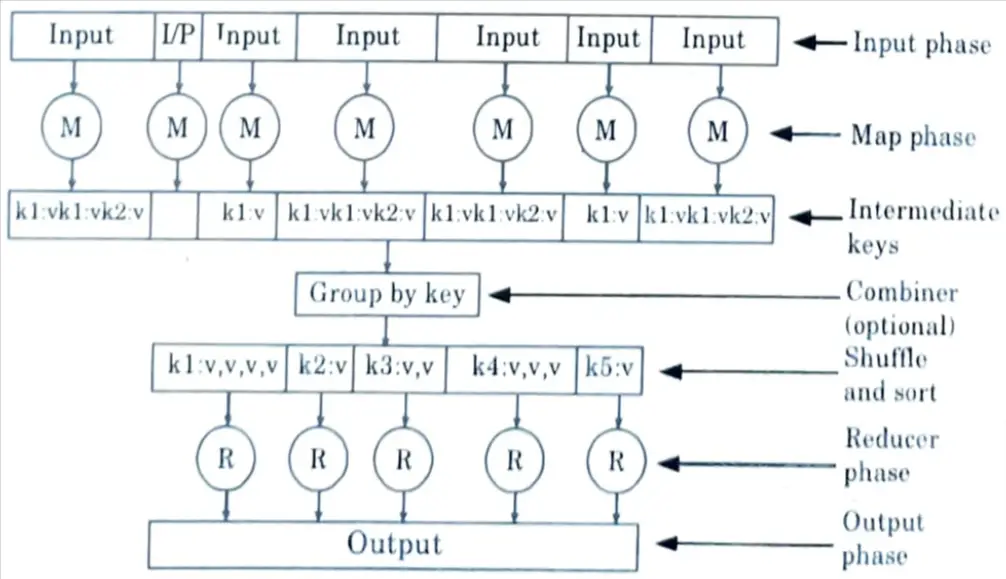
c. Take a suitable example and explain the concept of Map Reduces.
Ans. 1. The MapReduce algorithm contains two important tasks, namely Map and Reduce :
- i. The Map task converts a set of data into another set of data in which individual elements are broken down into tuples (key value pairs).
- ii. The Reduce task takes the Map output as an input and merges the data tuples (key-value pairs) into a smaller set of tuples.
2. The reduce task is always performed after the map task.
Phases of MapReduce :
- 1. Input phase: Here we have a record reader that translates each record in an input file and sends the parsed data to the mapper in the form of key-value pairs.
- 2. Map: Map is a user-defined function, which takes a series of key-value pairs and processes each one of them to generate zero or more key value pairs.
- 3. Intermediate keys: They key-value pairs generated by the mapper are known as intermediate keys.
- 4. Combiner :
- i. A combiner is a type of local reducer that groups together similar data from the map phase into distinct sets.
- ii. It takes the intermediate keys from the mapper as input and uses a user-defined code to aggregate the values in a single mapper’s small scope.
- iii. It is not a part of the main MapReduce algorithm; it is optional.
- 5. Shuffle and sort :
- i. The shuffle and sort step is the first step in the Reducer task.
- ii. It saves the grouped key-value pairs to the machine where the reducer is running.
- iii. The individual key-value pairs are sorted into a larger data set by key.
- iv. The data list organises the equivalent keys so that their values can be easily iterated in the reducer task.
- 6. Reducer :
- i. The reducer takes the grouped key-value paired data and applies a reducer function to each of them.
- ii. In this case, the data can be aggregated, filtered, and combined in a variety of ways, necessitating extensive processing.
- iii. When the execution is complete, it passes zero or more key-value pairs to the next step.
- 7. Output phase :
- i. In the output phase, we have an output formatter that translates the final key-value pairs from the reducer function and writes them onto a file using a record writer.


d. Explain cloud computing reference model with diagram.
Ans. Cloud computing architecture refers to the components and subcomponents required for cloud computing. These components consist of :
- 1. Front end platform :
- i. The cloud computing architecture is made up of front-end platforms known as clients or cloud clients.
- ii. Servers, fat (or thick) clients, thin clients, zero clients, tablets, and mobile devices are examples of these clients.
- iii. These client platforms communicate with cloud data storage via an application (middleware), a web browser, or a virtual session.
- iv. The front end of a cloud computing system refers to the client side of the system. It consists of interfaces and applications used to access cloud computing platforms, such as a web browser.
- 2. Back end platform :
- i. The cloud itself is referred to as the back end. It includes all of the resources needed to provide cloud computing services.
- It includes massive data storage, virtual machines, security mechanisms, services, deployment models, servers, and so on.
- iii. It is an online network storage system that stores data and makes it available to multiple clients.
- 3. Cloud based delivery: These include the following :
- i. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) :
- i. The Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model allows customers to use an application hosted on the cloud infrastructure.
- ii. In this model, the customer has little control over the application configuration settings but no control over the cloud infrastructure.
- iii. Client devices, such as thin clients or web browser interfaces, provide access to the applications.
- ii. Development-as-a-Service (DaaS): Web-based, community-shared development tools are used in development as a service. In the traditional (non-cloud computing) delivery of development tools, this is equivalent to locally installed development tools.
- iii. Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) :
- i. The Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) model allows customers to deploy customer-created applications into cloud infrastructure using the programming language or tools supported by the cloud provider.
- ii. The consumer does not manage the underlying cloud infrastructure such as network, storage, and so on, but he or she does have control over the deployed applications.
- iii. It also offers market-oriented solutions for integrating cloud computing into existing applications, services, and infrastructure.
- iv. Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) :
- i. The Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) model enables customers to provision processing, storage, networking, and other critical software such as operating systems and applications.
- ii. Although the consumer has no control over the underlying infrastructure, he or she does have control over the operating systems, storage, and deployed applications.
- i. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) :
e. What is the difference between cloud computing and distributed computing ?
Ans.
| S. No. | Cloud computing | Distributed computing |
| 1. | Cloud computing is the provision of on-demand IT resources/services such as server, storage, database, networking, analytics, software, and so on via the internet. | Distributed computing is the process of solving a problem using distributed autonomous computers that communicate with one another via a network. |
| 2. | It is a technique that delivers hosted services over the internet to its users/ customers. | It allows to multiple computers to communicate and work to solve a single problem. |
| 3. | It is classified into four different types such as Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Community Cloud and Hybrid Cloud. | There are three types of distributed computing systems: distributed computing systems, distributed information systems, and distributed pervasive systems. |
| 4. | It provides services such as hardware, software, networking resources through internet. | It helps to achieve computational tasks more faster than using a single computer as it takes a lot of time. |
| 5. | Its goal is to provide on demand computing services over internet on pay per use model. | Its goal is to distribute a single task among multiple computers and to solve it quickly by maintaining coordination between them. |
| 6. | It contributes to the provision of a shared pool of configurable computing resources, on-demand service, pay per use, provisioned by Service Providers, and so on. | It is used for distributed computations such as distributing a single task among computers to progress the work at the same time, Remote Procedure calls, and Remote Method Invocation. |
Section 3 : Infrastructure Virtualization in Cloud Computing
a. Explain cloud computing security architecture.
Ans. Cloud security architecture based on the type of cloud model as software-as-a-service (SaaS), infrastructure-as-a-service (laaS), or platform-as-a-service model (PaaS).
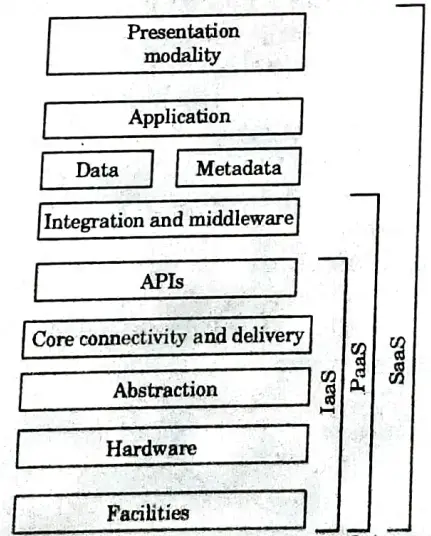


- laaS cloud computing security architecture :
- 1. This infrastructure provides cloud networking with storage and networking components.
- 2. It heavily relies on application programming interfaces (APIs) to allow businesses to manage and interact with the cloud.
- 3. The Cloud Service Provider (CSP) is in charge of the infrastructure and abstraction layers’ security. The rest of the stack, including the applications, is subject to the enterprise’s security obligations.
- 4. laaS cloud computing service models require those additional security features :
- a. Virtual web application firewall placed in front of a website to protect against malware.
- b. Virtual network-based firewall localdate the cloud network edge that guards the perimeter,
- c. Virtual routers
- d. Intrusion Detection Systems and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IDS/PS).
- e. Network segmentation.
- SaaS cloud computing security architecture :
- 1. SaaS centrally hosts software and data that are accessible via a browser.
- 2. Security features for the SaaS cloud environment include :
- a. Logging
- b. IP restrictions
- c. API gateways
- PaaS cloud computing security architecture :
- 1. It is defined as the deployment of applications without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software and provisioning hosting capabilities.
- 2. The CSP secures a majority of a PaaS cloud service model.
- 3. The essential components to secure the PaaS cloud include :
- a. Logging
- b. IP restrictions
- c. Cloud access security brokers.
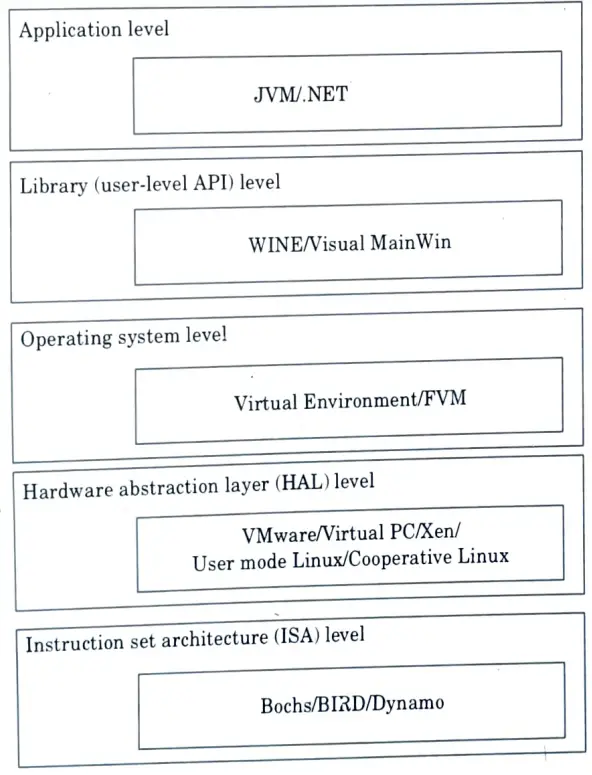
b. Explain infrastructure virtualization and cloud computing solutions with the help of diagram.
Ans. Various implementation level of virtualization :
- 1. Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) level:
- i. At the ISA level, virtualization is performed by emulating a given ISA by the ISA of the host machine.
- ii. The basic emulation method is through code interpretation.
- iii. An interpreter program interprets the source instructions to target instructions one by one.
- iv. One source instruction may require tens or hundreds of native target instructions to perform its function. This process is relatively slow.
- v. For better performance, dynamic binary translation is desired.
- vi. This approach translates basic blocks of dynamic source instructions to target instructions.
- vii. The basic blocks can also be extended to program traces or super blocks to increase translation efficiency.
- viii. A Virtual Instruction Set Architecture (V-ISA) thus requires adding a processor-specific software translation layer to the compiler.
- 2. Hardware abstraction level :
- i. It is performed directly on top of the bare hardware and creates a virtual hardware environment for a virtual machine.
- ii. The concept is to virtualize a computer’s resources, such as its processors, memory, and I/O devices, in order to improve hardware utilisation rate by multiple users concurrently.
- 3. Operating system level :
- i. OS-level virtualization creates isolated containers on a single physical server and the OS instances in data centres to use the hardware and software.
- ii. The containers operate in the same manner as traditional servers. To allocate hardware resources among a large number of mutually distrusting users, OS-level virtualization is commonly used in the creation of virtual hosting environments.
- iii. Library Support Level Virtualization is possible with library interfaces by controlling the communication link between applications and the rest of the system via API hooks.
- 4. Library support level:
- i. Library interface virtualization is possible by controlling the communication link between applications and the rest of the system via API hooks.
- ii. To support Windows applications on top of UNIX hosts, the software tool WINE has implemented this approach.
- 5. User-application level :
- i. Virtualization at the application level virtualizes an application as a VM.
- ii. On a traditional OS, an application often runs as a process.
- iii. Therefore, application-level virtualization is also known as process-level virtualization. The most popular approach is to deploy High Level Language (HLL).


Section 4 : Load Balancing in Cloud Computing
a. What are the different techniques used for of implementation hardware virtualization ? Explain them in detail.
Ans. Binary translation with full virtualization :
- 1. Full virtualization :
- i. With full virtualization, non-critical instructions run directly on the hardware, while critical instructions are discovered and replaced with traps into the VMM, which are then emulated by software.
- ii. Full virtualization is achieved using both the hypervisor and the VMM approaches.
- iii. Because binary translation has a high performance overhead, critical instructions are trapped in the VMM.
- iv. Non-critical instructions do not control hardware or jeopardise system security, whereas critical instructions do.
- v. Therefore, running non-critical instructions on hardware not only can promote efficiency, but also can ensure system security.
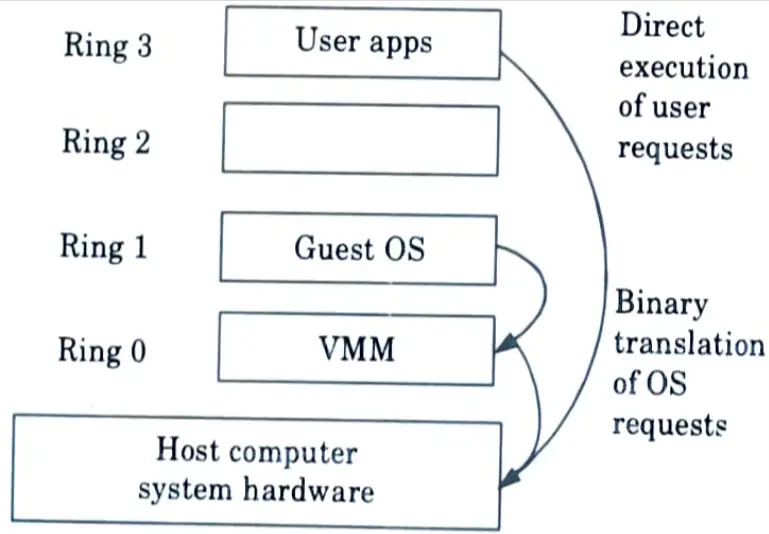
- 2. Binary translation of guest OS requests using a VMM :
- i. VMware puts the VMM at Ring 0 and the guest OS at Ring 1.
- ii. The VMM searches the instruction stream for privileged, control, and behaviour sensitive instructions.
- iii. When these instructions are identified, they are trapped in the VMM, which emulates their behaviour. Binary translation is the method used in this emulation.
- iv. Full virtualization incorporates binary translation as well as direct execution. The guest operating system is completely independent of the underlying hardware. As a result, the guest OS is completely unaware that it is being virtualized.


- 3. Host-based virtualization :
- i. A virtualization layer installed on top of the host OS is an alternative VM architecture. The host OS is still in charge of managing the hardware.
- ii. The guest operating system is installed and runs on top of the virtualization layer.
- iii. The VMs can run dedicated applications. Other applications can, of course, run alongside the host OS.
- iv. Advantages of host- based architecture :
- a. The VM architecture can be installed without modifying the host OS. Device drivers and other low-level services can be provided by the virtualizing software via the host OS. This will simplify the VM design and make it easier to deploy.
- b. The host-based approach is suitable for a wide range of host machine configurations. The performance of the host-based architecture may be inferior to that of the hypervisor/VMM architecture.
b. What is load balancing ? What are the advantages of load balancing?
Ans. Load balancing :
- 1. The process of distributing workloads across multiple computing resources is known as cloud load balancing.
- 2. Cloud load balancing lowers the costs associated with document management systems while increasing resource availability.
- 3. The primary goal of load balancing is to keep any single server from becoming overloaded and possibly failing.
- 4. Load balancing increases service availability and reduces downtime.
Advantages of load balancing :
- 1. It distributes network traffic to prevent failure due to resource overload.
- 2. It improves application, website, database, and other computing resource performance and availability.
- 3. It also aids in the quick and accurate processing of user requests.
Section 5 : Security Challenges in Cloud Computing
a. What are the different security challenges in cloud computing ? Discuss each in brief.
Ans. Some of the security problems which are faced by the cloud computing are as follows :
- 1. Data integrity: When data is stored in the cloud, anyone from any location can access it. Because the cloud does not distinguish between sensitive and common data, anyone can access those sensitive data. As a result, data integrity is lacking in cloud computing.
- 2. Data theft: Instead of purchasing a server, most cloud vendors try to lease one from another service provider because it is more cost effective and flexible in terms of operation.
- 3. Security on vendor level: The vendor should ensure that the server is well protected against all external threats. A cloud is only useful if the vendor provides adequate security to its customers.
- 4. Security on user level: Even if the vendor has provided a good security layer for the customer, the customer should ensure that there is no data loss or tampering for other users who use the same cloud as a result of its own actions.
- 5. Information security: Security concerns the information exchanged between hosts or between hosts and users. This includes issues with secure communication, authentication, single sign on, and delegation.
b. What is Honeypot ? What are the different types of Honeypot ?
Ans. Honeypot :
- 1. A honeypot is a security mechanism that creates a virtual trap in order to attract attackers.
- 2. A maliciously compromised computer system allows attackers to exploit vulnerabilities, allowing us to study them and improve our security policies.
- 3. A honeypot can be used on any computing resource, from software and networks to file servers and routers.
- 4. Honeypots are a type of deception technology that allows us to understand the patterns of attacker behaviour.
- 5. To gather intelligence on how cyber criminals operate, security teams can use honeypots to investigate cybersecurity breaches.
- 6. When compared to traditional cyber security measures, they also reduce the risk of false positives because they are unlikely to attract legitimate activity.
- 7. There are two primary types of honeypot designs :
- a. Production honeypots :
- i. Act as decoy systems within fully operational networks and servers, frequently as part of an Intrusion Detection System (IDS).
- ii. They divert criminal attention away from the real system while analysing malicious activity to aid in vulnerability mitigation.
- b. Research honeypots :
- i. It is used for educational purposes and security enhancement.
- ii. They contain traceable data that we can trace when stolen to analyze the attack.
Section 6 : Third Party Cloud Services in Cloud Computing
a. What do you mean by third party cloud services ? Give suitable examples.
Ans. Third party cloud services :
- a. The third party cloud services is the services in which user want to acquire when he/she is not getting that service with acquired or hired cloud provider.
- b. For example, Amazon Web Services, Google etc.
Advantages :
- 1. Maintenance and support: If something goes wrong it is the duty of the provider to ensure the problem is fixed.
- 2. Skilled company with all the resource :
- a. When we use a third party for cloud computing infrastructure, we benefit from a service in which the staff is highly trained in this field and the company has all of the necessary resources.
- 3. Security benefit: Many businesses feel more secure entrusting their data to an experienced cloud computing provider rather than venturing into the unknown and attempting to manage the security of their critical data themselves.
- 4. Cost advantages: Third party clouds do not require huge outlays. To be able to bring our infrastructure in-house we would need to make a sizeable investment.
Disadvantages :
- 1. Security worries: We are entirely responsible for the security of our data. Time and resources will need to be heavily to get it right.
- 2. Lack of control: We have little control over how quickly we can expand the cloud and the granularity of its management with third-party cloud computing.
- 3. Potential cost drawbacks: If we must use a personal cloud, we will be able to keep our ongoing costs to a minimum, though the initial costs will most likely be high. Furthermore, with third-party computing, we must pay for additional storage space whenever we run out.
b. Explain the major cloud features of Google applications engine.
Ans. Features of Google App Engine :
- i. Persistent storage with queries, sorting and transactions.
- ii. Automatic scaling and load balancing.
- iii. APls for authenticating users and sending email using Google accounts.
- iv. Task queues for performing work outside of the scope of a web request.
- v. Scheduled tasks for triggering events at specified times and regular intervals.
- vi. Dynamic web serving, with full support for common web technologies.
Section 7 : Cloud Federation Stack in Cloud Computing
a. Give a suitable definition of cloud federation stack and explain it in detail.
Ans.
- 1. Cloud federation is the unionization of software, infrastructure, and platform services from disparate networks that a client can access via the internet.
- 2. Cloud resource federation is facilitated by network gateways that connect public or external clouds, private or internal clouds (owned by a single entity), and/or community clouds (owned by several cooperating entities), resulting in a hybrid cloud computing environment.
- 3. The existence of physical datacenters is required for federated cloud computing services.
- 4. Two approaches of cloud federation are :
- a. Centralized federation model: This is the approach taken by several identity federation standards. It distinguishes two operational roles in transaction :
- i. The identity provider
- ii. The service provider
- b. Claim-based model: This approach approaches user authentication from a different angle, requiring users to provide claims about who they are and what they can do in order to access content or complete a transaction.
- a. Centralized federation model: This is the approach taken by several identity federation standards. It distinguishes two operational roles in transaction :
b. Write short notes on any two of the followings :
i. HADOOP
ii. Microsoft Azure
Ans. i. HADOOP :
- 1. Hadoop is an open-source software framework for storing data and running applications on commodity hardware clusters.
- 2. It offers massive data storage, enormous processing power, and the ability to handle virtually infinite concurrent tasks or jobs.
- 3. The Hadoop ecosystem is a collection of complex and evolving tools and components. Some of these elements are very different in terms of architecture; however, what keeps them all together under one roof is that they all derive their functionalities from Hadoop’s scalability and power.
- 4. A Hadoop ecosystem is a comprehensive collection of tools and technologies that can be effectively implemented and deployed to provide cost-effective big data solutions.
- 5. MapReduce and Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) are two key components of the Hadoop ecosystem for managing large amounts of data. They are, however, insufficient to address the big data challenges.
- 6. In addition to these two, the Hadoop ecosystem includes a number of other components that aid in the development and deployment of large data solutions.
ii. Microsoft Azure :
- 1. Microsoft Azure is Microsoft’s public cloud computing platform, formerly known as Windows Azure.
- 2. It offers a variety of cloud services such as compute, analytics, storage, and networking.
- 3. Users can select from these services to develop and scale new applications in the public cloud, or to run existing applications.
- 4. The Azure platform is designed to assist businesses in managing challenges and meeting organisational goals.
- 5. It offers tools that support all industries – including e-commerce, finance.

1 thought on “Cloud Computing: Last year Question Paper Questions with Answer”