We’re here to look at the most essential Air and Noise Pollution Control repeated questions and notes that may appear in your upcoming exams, such as Btech and others. Unit-4 Control of Gaseous Contaminants
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well.
Important Questions For Air and Noise Pollution Control:
*Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus
*Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT
* Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Q1. Enumerate the various engineering devices that are used to control the emission of gaseous air pollution from industries. Describe any one.
Ans. Following are the devices used to control the emission of gaseous air pollution from industries:
- 1. Absorption units.
- 2. Adsorption units.
- 3. Combustion or incineration equipments.
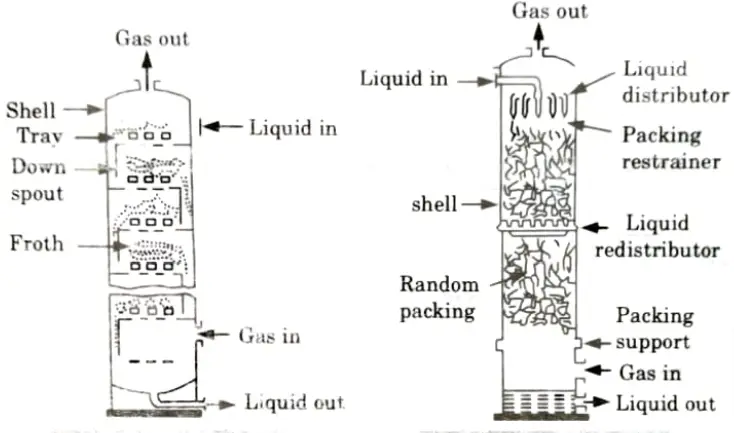
Absorption Units: Absorption units includes spray towers, plate towers, packed towers, and venturi scrubbers.
- 1. Spray towers and venturi-scrubbers can both be utilised to remove particle contaminants at the same time.
- 2. Scrubbers are less successful than towers in eliminating gaseous pollutants, although towers are commonly clogged by particle matter.
- 3. Plate towers and packed towers, two other successful systems for eliminating gaseous pollutants, are depicted in Figs. 1 and 2, respectively.
- 4. These absorption units work on the principle of pollutant transfer from the gas phase to the liquid phase.
- 5. In other words, the pollutants from the unclean gas are absorbed in the liquid that allows the gas to pass through these units.
- 6. Diffusion and dissolution are both methods of absorption.
- 7. The effectiveness of these devices, naturally, depends upon the solvent (liquid), through which the gas is made to pass.
- 8. When water is used as the solute, the removal is restricted only to a few inorganic gases, such as NH3, Cl2, and SO2.
- 9. Before adopting one of these absorbent devices, all of them must be adequately developed for the specified conditions.
- 10. It is also important to guarantee that contaminants transmitted from air to water do not produce severe and unmanageable water contamination.


Q2. Write a short note on catal/tie convertor, which is used to control the air pollution from automobiles.
Ans. Catalytic Convertor:
- 1. The catalytic convertors are usually made of noble metals, like platinum. palladium, etc., and help in oxidising CO and HC into their final end product of CO2, and also to reduce NO into nitrogen.
- 2. These noble metal catalysts are extremely active and can withstand sulphur poisoning.
- 3. They can be manufactured in the form of pellets or as a monolithic one-piece metal.
- 4. A catalytic converter is often installed inside the tailpipe of a vehicle to pass partially oxidised emissions through it before they are released into the atmosphere.
- 5. Formerly, two distinct catalytic metal beds were employed for oxidising CO and HC and reducing NO; however, current catalysts have been engineered to catalyse both sets of processes.
- 6. These catalysts, popularly called three way catalysts, (Pt, Pd and Rh), have simplified the dual bed to a single bed catalytic converter.
- 7. At the moment, the installation of such three-way catalytic converters is required for all automobiles on the roads of the United States and Japan.
- 8. However, automakers in India have avoided incorporating catalytic converters into their automobiles, owing to the high cost of noble metals.
- 9. Because these converters impair engine efficiency, certain adjustments in the basic design of the engines will be required.
- 10. Indian Institute of Petroleum-Dehradun, Regional Research Laboratory Bhubaneswar, and Projects and Development India Ltd. Sindri are also working to develop an efficient catalytic system using less expensive metals such as Mn, Cu, Cr-Cu, and composite oxides.
- 11. Regardless, Indian car manufacturers have now begun installing catalytic converters in new cars being released in our metro cities, and the lead-free gasoline required to power such vehicles has been available in all of India’s metropolitan cities since around the year 1996.
- 12. While the designs of petrol-powered vehicles have improved, automakers are increasingly turning to diesel-powered vehicles due to the lower unit cost of diesel as compared to petrol.
- 13. However, diesel fumes have been found to be more harmful than gasoline fumes, notably in terms of hazardous carcinogenic particulate matter emitted by diesel automobiles.
- 14. The ban on diesel cars has also been recommended by the environmental Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority (EPCA).
Q3. Explain in detail about condensation and combustion equipments which are used as pollution control device.
Ans. Combustion or Incineration Equipments:
- 1. When the pollutants in the gas streams are oxidizable to an inert gas, it can be employed to filter dirty gases.
- 2. Pollutants such as hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide (CO) can be easily burned, oxidised, and eliminated in such machines.
- 3. Direct flame combustion by burners (Fig.1) and catalytic combustion (Fig.2) have both been employed commercially.
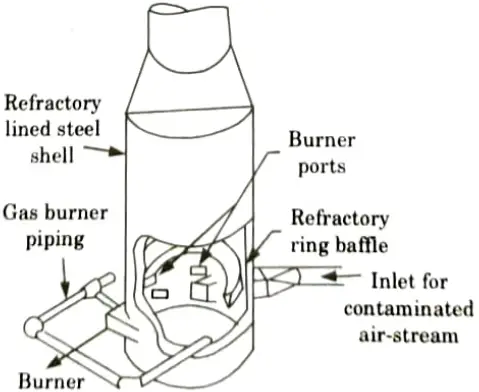


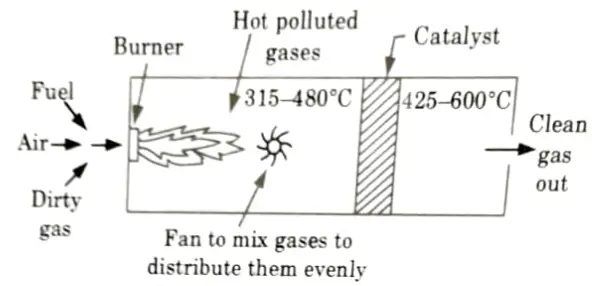


- 4. Catalytic incineration can be used when combustible materials in the waste polluted gas, are too low to make direct-flame incineration feasible.
- 5. This generally happens when the energy of the polluted gas is lesser than 3.7 MJ/m3.
- 6. For all such energy concentrations, the petrol burning becomes self-sustaining after first ignition, allowing direct flame incinerators to be used. Secondary supporting fuel may also be employed to make such a strategy possible in some cases.
- 7. It must also be ensured that the incinerator’s ultimate combustion product is easily disposable and less harmful than the original gas pollutants being eliminated.
- 8. Direct flame incineration has been used successfully in the Varnish cooking, Meat smoke houses, and Paint bake oven industries to purify industrial gases.
- 9. When the combustible fuel value of dirty gases is low, various catalytic materials have been discovered to accelerate the rate of oxidation without undergoing a chemical change, lowering incineration time or making incineration viable even with low energy contaminated gases.
- 10. Expensive platinum (Pt) or palladium (Pd) compounds are frequently used as catalysts. Typically, such a catalytic substance is deposited on a bed similar to absorption beds, with a ceramic supporting lattice.
- 11. Because the earlier catalytic systems were only efficient when hot gases were pushed through them, heater pre-heating (as indicated in Fig.2) was a must. However, in current times, cold catalytic systems that operate at room temperature have been developed, eliminating the need for pre-heating.
- 12. Catalytic incinerators have often been NOx, CO, successfully used to control SO2, hydrocarbons, etc. Besides being costly, their major drawback is their susceptibility to poisoning by sulphur and lead compound, even in trace amounts.
- 13. Catalytic combustion has been utilised successfully to clean pollutants from varnish boiling, bitumen oxidation, printing presses, and other processes.
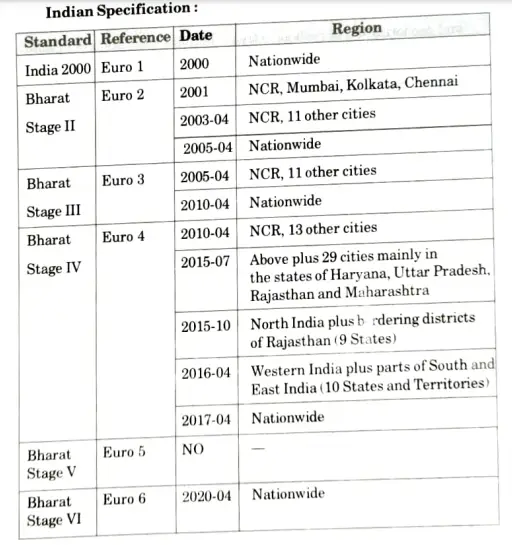
Q4. What are the Indian specifications of pollution control from automobiles?
Ans. Indian Specifications of Pollution Control from Automobiles:
- 1. The initial Indian emission standards, which went into effect in 1989, were idle emission limitations.
- 2. Idle emission regulations were quickly superseded by mass emission limits for both gasoline (1991) and diesel (1992) cars, which were gradually tightened throughout the 1990s.
- 3. Beginning in the year 2000, India began to adopt European pollution and fuel requirements for four-wheeler light-duty and heavy-duty vehicles.
- 4. Two- and three-wheeled vehicles continue to be subject to India’s own emission laws.
- 5. During the early 2000s, two papers from the Indian Planning Commission have served as the framework for car emission limits in India.
- 6. The National Car Fuel Policy, unveiled on October 6, 2003, called for a phased approach to implementing Euro 2-4 emission and fuel rules by 2010.
- 7. To set restrictions beyond Bharat Stage IV, the Indian Planning Commission formed an Expert Group in 2013 to prepare a new Car Fuel Policy, Auto Fuel Vision and Policy 2025, which was published in May 2014.


Q5. What are the application of adsorption for control of gaseous and odour emission at source?
Ans. Application of Adsorption: Following are the application of adsorption for control of gaseous and odour emission at source:
- 1. Vapor Recovery in Process Industries:
- i. The recovery of solvents from air streams that are devoid of particle matter and have vapour concentrations above 700 ppm is a major application.
- ii. Activated carbon has been found to be extremely effective in the adsorption of a variety of organic compounds.
- 2. Deodorization of Odours Emissions: Many odorants are perceptible and disagreeable at low concentrations, such as 100 ppb or less, and deodorization of such gas streams by solid adsorption is often an effective and cost-effective process.
- 3. Adsorption of H2S and Carbon disulphide from Waste Gases of Viscose Production Plants: Hydrogen sulphide and carbon disulphide are common pollutants in waste gases from the Viscose rayon industry, and these gases can be separated from the waste gas stream using activated carbon in a single adsorption plant.
- 4. Adsorption of Sulphur Containing Gases:
- i. Adsorptive separation of various sulphur compounds like H2S, SO2 can be achieved by physical adsorption catalysis.
- ii. Activated carbon serves as a contact catalyst for various reactions of sulphur compounds including air oxidation of H2S to sulphur of SO2, to SO3 or to sulphuric acid and reduction of SO2, or sulphuric acid by H2S to produce sulphur.
- 5. Adsorption of NOx: The methods applied for removal of NOx from waste gases are trusted on physical and catalized adsorption.
- 6. Adsorption of Mercury Vapours: Adsorbents such as activated carbon and ion-exchange resin can be used to extract mercury vapours.
- 7. Control of Caseous Radio Active Emission: Activated carbon adsorption can be used to prevent radioactive gas emissions from nuclear reactors and other sources. Adsorbable radioactive gases include radon and radio-iodine.
- 8. Gas Masks: Activated carbon or charcoal is generally universally utilised in gas because it is the finest all-around adsorbent for dangerous gases.
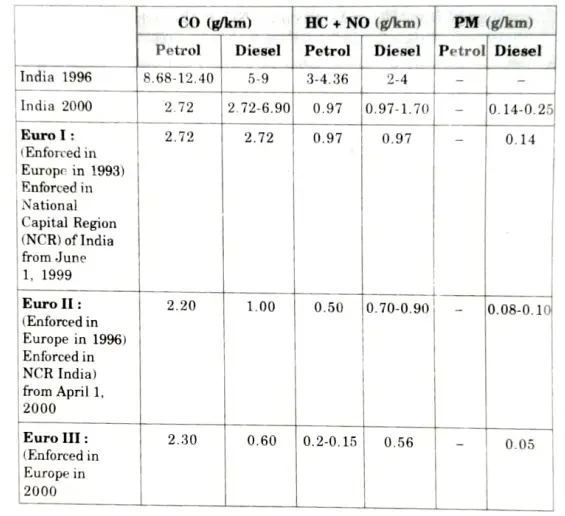
Q6. Write down the specifications of Euro-l, Euro-II and Euro-III.
Ans. Table. Existing as well as notified Euro-1, Euro-lI and Euro-II Emission Norms





Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Air and Noise Pollution Control Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Air and Noise Pollution Control Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One View) | Student Result |
