Explore the realm of Optical Communication with the B.Tech AKTU Quantum Book. Access important notes, frequently asked questions, and valuable insights for learning this cutting-edge technology. Unit-2 Signal Loss in Optical Fiber
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Optical Communication: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Q1. Write a short note on attenuation.
Ans. 1. As light pulses travel the length of the fiber, attenuation also known as signal decay or loss of light power occurs.
2. The logarithmic unit of decibel is typically used to indicate signal attenuation within optical cables (dB).
3. dB is used to compare two power levels, may be defined for a particular optical wavelength in the ratio of the input power pi into a fiber to the output optical power p0 from the fiber as
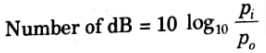
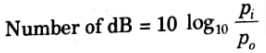
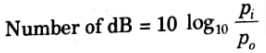
4. In optical fiber communication the attenuation usually expressed in dB per km.
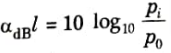
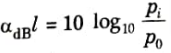
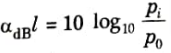
where 𝛼dB is signal attenuation per unit length in dB and l is the length of the fiber.
Q2. Explain absorption loss mechanisms with their causes in the silica glass fibers in detail.
Ans. Absorption loss is related to the material composition and fabrication process of fiber. The absorption of the light may be intrinsic or extrinsic.
i. Intrinsic absorption:
- 1. This kind of absorption happens when a substance is completely pure, with no inhomogeneities or variations in density. This is a characteristic that glass by nature has.
- 2. Due to its fundamental material structure in the near infrared range, a perfectly pure silicate glass has low intrinsic absorption.
- 3. Atomic vibration bands in the near infrared range and electronic absorption bands in the UV regions are the sources of intrinsic absorption.
- 4. The band gaps of the amorphous glass materials are connected to the electrical absorption bands.
- 5. When an electron in the valence band meets with a photon and is excited to a higher energy level, absorption takes place.
- 6. In a large area where fiber systems can operate, intrinsic losses are largely negligible, but they prevent the extension of fiber systems towards longer and ultraviolet wavelengths.
ii. Extrinsic absorption:
- 1. Charge shifts from one ion to another and electronic transitions between energy levels cause extrinsic absorption to take place.
- 2. The transition of metal impurity ions, such as those from iron, chromium, cobalt, and copper, is a significant cause of attenuation.
- 3. The main cause of loss in useful fibers is the existence of contaminants in the fiber material.
- 4. Absorption because of water that has been dissolved in the glass is another significant extrinsic loss mechanism.
- 5. These hydroxyl groups are bonded into the glass structure and have fundamental stretching vibrations which occur at wavelengths between 2.7 and 4.2 𝛍m depending on group position in the glass network.
Q3. What is self phase modulation ? Explain Kerr effect.
Ans. 1. The refractive index n of many optical materials has a weak dependence on optical intensityI (equal to the optical power per effective area in the fiber) given by
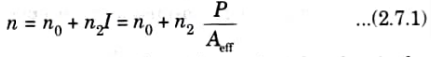
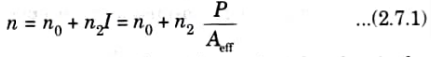
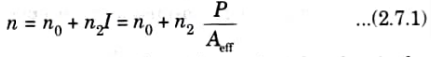
where n0 is the ordinary refractive index of the material and n2 is the non-linear index coefficient. In silica, the factor n2 is about 2.6 x 10-8 𝛍m² W.
2. The refractive index’s nonlinearity is referred to as the Kerr non linearity. The Kerr effect, which is caused by this non-linearity, is a carrier-induced phase modulation of the propagating signal.
3. This results in self phase modulation (SPM) in single wavelength links, which transforms optical power fluctuations in a propagating light wave into spurious phase fluctuations in the same wave.
4. The main parameter 𝛶 which indicates the magnitude of the non-linear effect for SPM is given by,



where 𝜆 is the free space wavelength and Aeff is the effective core area.
5. The value of 𝛶 ranges from 1 to 5 W-1 km-1 depending on the fiber type and the wavelength. For example, 𝛶 = 1.3 W-1 km-1 at 1550 nm for a standard single mode fiber that has an effective area equal to 72 𝛍m².
6. The frequency shift 𝚫𝛗 arising from SPM is given by
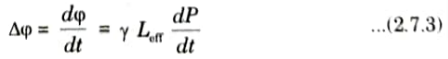
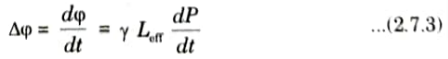
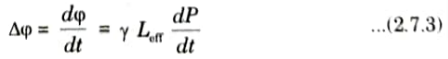
Here Leff is the effective length given by eq. (2.7.3) and dP/dt is the derivative of the optical pulse power, that is, it shows that the frequency shift occurs when the optical pulse power is changing in time.
Q4. Describe the mechanism of intermodal dispersion in multimode graded index fiber.
Ans. 1. Intermodal dispersion in multimode fibers is minimized with the use of graded index fibers.
2. Comparing multimode graded index fiber to multimode step index fiber, bandwidth is enhanced. A ray diagram can be used to determine the cause of the fibers’ better performance.
3. The index profile is given as
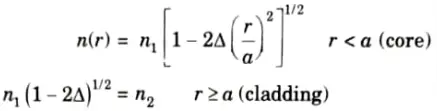
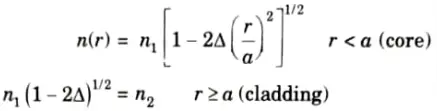
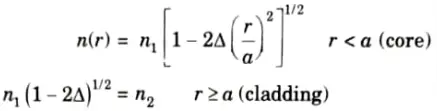
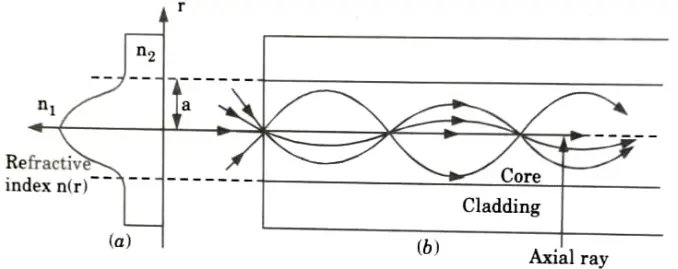


4. It is demonstrated in Fig. that meridional rays from the axial ray follow sinusoidal trajectories with various journey lengths as a result of index grading.
5. The greater speeds in the lower index medium away from the axis make up for the longer sinusoidal routes since group velocity is inversely proportional to the local refractive index.
6. Multimode fiber bandwidth is improved by using a parabolic refractive index profile. This can be explained by considering reduced delay difference between the fastest and slowest modes for this graded index fiber 𝛿Tg.
7. Ray theory gives an expression for delay difference as:
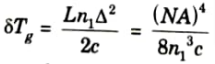
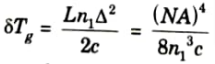
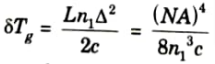
8. The electromagnetic mode theory gives an expression as:
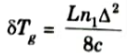
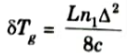
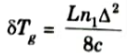
9. The rms pulse broadening of a near parabolic index profile graded index fiber is related to the rms pulse broadening of step index fiber by the expression as
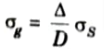
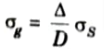
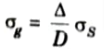
where D is the constant between 4 and 10 depending on the precise evaluation.
10. The best theoretical intermodal rms pulse broadening for a graded index fiber is given as
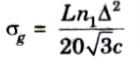
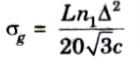
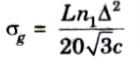
Q5. Describe the scheme for realizing the dispersion shifted fiber.
Ans. 1. Single mode fiber refractive index profiles are capable of modification in order to tune the zero dispersion wavelength point 𝜆0 to a specific wavelength within a region adjacent to the zero material dispersion (ZMD) point.
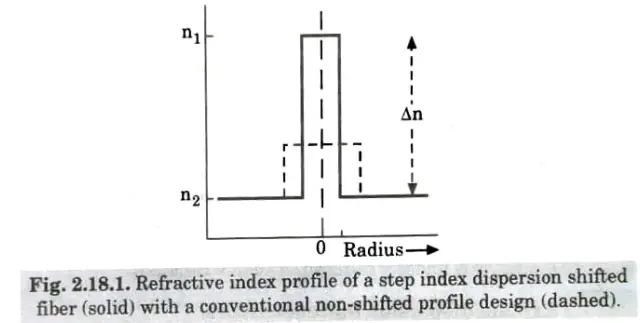


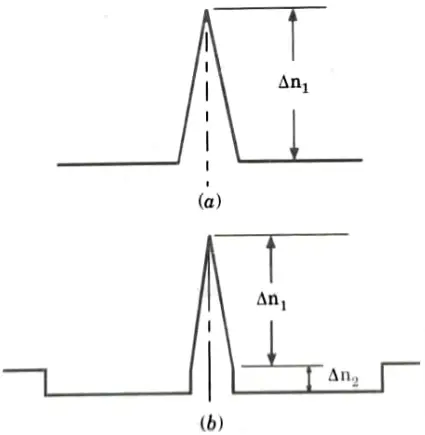


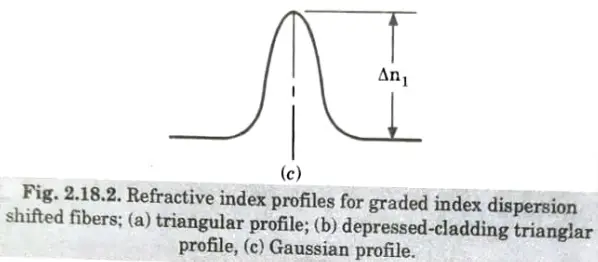


- 2. The step index profile gives a shift to longer wavelength by reducing the core diameter and increasing the fractional index difference. Typical values for the two parameters are 4.4 𝛍m and 0.012 𝛍m respectively.
- 3. 𝜆0 could be shifted to longer wavelength by altering the material composition of the single mode fiber.
- 4. For suitable power confinement of the fundamental mode, the normalized frequency V should be maintained in the range 1.5 to 2.4 𝛍m and the fractional index difference must be increased as a square function while the core diameter is linearly reduced to keep V constant.
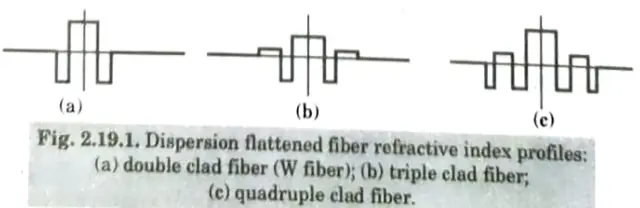
Q6. Explain dispersion flattened fibers.
Ans.
- 1. To alter single mode fibers’ dispersion properties so that they produce two wavelengths with zero dispersion. Fig. displays a typical double-clad W fiber index profile (a).
- 2. Dispersion flattening using the W structure was first demonstrated in practice in 1981, according to a report.
- 3. However, the demand for a high level of dimensional control in order to produce repeatable DF fibers was a downside of the W structural design.
- 4. By adding another region of higher index to the structure, light that enters the outside cladding area can be confined, reducing the sensitivity to bend losses associated with the W fiber structure.





Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Optical Communication Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Optical Communication Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |
