Examine the notes on E-Commerce from BCA solved question papers. Learn the fundamentals of internet commerce, e-payment methods, and obtain insightful knowledge of the world of digital trade.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For E-Commerce: * Important Short Questions * Solved Question Paper * Syllabus
Section A: E-Commerce Very Short Question Answers
Q1. Define server.
Ans. A client is a computing device that contacts a server in order to access a shared resource. A server, on the other hand, accepts client computer requests and shares its resources, applications, and/or data with one or more client computers on the network. Thus, a client-server system specifies how a server makes resources and services available to one or more clients. Web servers, mail servers, and file servers are examples of servers. Client devices such as desktop PCs, laptops, tablets, and smartphones can access resources from any of these servers.
Q2. What is e-commerce?
Ans. E-commerce (Electronic Commerce or EC) refers to the purchasing and selling of goods and services, as well as the transmission of payments or data, over an electronic network, most notably the internet. Business-to-business, business-to-consumer, consumer-to-consumer, and consumer-to-business transactions are all possible.
Q3. What is supply chain?
Ans. The supply chain is the network of all the people, organisations, resources, activities, and technology involved in creating a product from raw materials and delivering it to the ultimate customer.
Q4. Discuss internet.
Ans. The Internet is a worldwide network of interconnected computer networks that use the standard internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to connect over a billion people.
It is a network made up of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks.
The TCP/IP protocol is also used by two newer internet technology modifications, the intranet and the extranet.
Q5. Explain e-marketing.
Ans. E-marketing refers to the strategies and techniques employed in the promotion of products and online services. It ensures that the products are exposed to the appropriate audience and that a desire to purchase is created. Web design, search engine optimisation, e-mail marketing, online promotion, and blogs are examples of tactics.
Section B: E-Commerce Short Question Answers
Q6. Discuss intellectual property system.
Ans. Intellectual Property System : Inventions, literary and artistic works; designs; and symbols, names, and pictures used in trade are examples of intellectual property (IP).
Patents, copyright, and trademarks, for example, are legal mechanisms that allow people to get recognition or financial advantage from what they innovate or create. By finding the correct balance between the interests of innovators and the larger public interest, the IP system attempts to create a more conducive environment for creativity and innovation.
Q7. Explain the role of administrator in client technology.
Ans. Administrator Role in Client/Server Technology: In client/server technology, an administrator is responsible for configuring and managing the system or server. He could be a member of the IT department in charge of installing, supporting, and maintaining servers or other computer systems, as well as planning for and responding to other issues. He plays an important role in client/ server technology and is responsible for the following things:
- 1. He carries out user administration, i.e. setting up and maintaining accounts.
- 2. He verifies that peripherals are working properly.
- 3. He quickly arranges repair for hardware in occasion of hardware failure.
- 4. He monitors system performance and creates file systems.
- 5. He creates a backup and recover policy and monitors network communication.
- 6. He updates system as soon as new version of OS and application software comes out.
- 7. He implements the policies for the use of the computer system and network.
- 8. He sets up security policies for users.
- 9. He provides documentation in the form of internal wiki.
- 10. He carries out password and identity management.
Hence, in client/server technology an administrator performs many tasks. Whenever, work station or server goes down, he is called to solve the problem. So, he must be able to quickly and correctly diagnose the problem. He must figure out what is wrong and how best it can be fixed in small amount of time.
Q8. Explain the importance of internet commerce.
Ans. The internet is extremely significant in e-commerce since it allows firms to reach a worldwide audience and make transactions online. E-commerce would not be possible without the internet.
Here are some ways in which the internet is important for e-commerce:
- (a) It allows customers to browse and compare products and prices from different retailers and make purchases from the comfort of their own homes.
- (b) It allows people from all over the world to get connected inexpensively and reliably.
- (c) It helps in business to grow.
- (d) It enables safe payment processing and money transfers, making it simple for clients to pay for their online transactions.
- (e) It speeds up communication while saving money. Businesses employ web technologies such as Skype web, email, video calls, and so on to provide near-instant communication.
- (f) It makes no distinction between users. It enables communication to take place all over the world without regard for a specific person, institution, or country.
Section C: E-Commerce Detailed Question Answers
Q9. What is the difference between e-commerce and e-marketing?
Ans. Difference between E-commerce and E-marketing
| S. No. | Basis of difference | E-commerce | E-marketing |
| 1. | Concept | It is the online purchase and sale of goods and services via devices such as mobile phones, telephones, fax machines, ATMs, and so on. | It refers to the methods and techniques utilised for online marketing of products and services. |
| 2. | Strategies | E-commerce uses strategies such as public relations, referrals, banner ads, etc. | Web design, search engine optimisation, e-mail marketing, online promotion, and blogs are all examples of e-marketing tactics. |
| 3. | Objective | It aims to enable the customers to have their products even without going to the stores. | It assures that the products are displayed to the right audience and a desire to purchase born. |
| 4. | Scope | It has a wider scope as it carries business transactions through electronic mediums like internet, ATMs, credit cards, etc. | It has less scope and it deals with business transactions carried through iternet, e-mails, search engines, etc. |
Q10. What is extranet products and services? Explain business models of extranet applications.
Ans. An extranet is a private network that leverages interconnection technology and the public telecommunications system to securely share a portion of a company’s information or activities with suppliers, vendors, partners, customers, or other companies. An extranet is a subset of a corporation’s intranet that is accessible to users outside the firm.
Business Models of the Extranet Applications
There are some business models of extranet applications:
- 1. Extranet/partner network architecture.
- 2. Acquisition integration data center consolidation, network integration.
- 3. Service catalogue and provisioning.
- 4. B2B collaboration solutions and network architecture.
- 5. Service provisioning and Cisco intelligent automation for cloud.
- 6. Data center consolidation/private cloud, Cisco UCS, Nexus.
- 7. Collaboration applications for sales enablement.
- 8. Integrated service routers, wide area application services and security for partner network enablement.
Q11. Explain electronic payments and protocols. Discuss security schemes in electronic payment systems.
Ans. The possibility of prosecution is the most effective deterrent to double spending. Cryptography techniques can aid in the creation of e-cash that can be tracked back to its source. To create anonymous e-cash, a bank must issue e-cash with integrated serial numbers, allowing the bank to sign the coins and then eliminate any association of the coins with any specific consumer. Every protocol consists of at least three types of transactions:
- (a) Withdrawal; transfers coins to the customer.
- (b) Payment; transfers coins to the merchant.
- (c) Deposit; transfers coins to real currency.
Some procedures include an additional phase called the opening procedure, which is analogous to creating a bank account. This technique often allows the bank to provide the user with a password that he can use to identify himself to the bank. There are two types of electronic cash schemes: Online and offline.
Security Schemes in Electronic Payment Systems: Following are the security schemes in electronic payment systems:
1. Authenticity: The electronic cheque may include a document signed using the consumer’s private key. The receiver (the merchant or the merchant’s bank) decrypts the digital signature using the payer’s public key. This ensures the receiver that the cheque was truly signed by the sender. It also includes non-repudiation, which means that the payer cannot dispute issuing the cheque because it is signed with the payer’s private key (which only the payer is intended to have).
Furthermore, the electronic cheque may necessitate the digital signatures of the originator’s bank. This step ensures that the cheque is written on a genuine bank account. The receiver (or receiver’s bank) can authenticate the validity of the originator’s bank by utilising the originator’s bank’s public key. Additional security requirements may be imposed for big quantities of money.
2. Delivering Public Keys: Both the originator and the originator’s bank must supply the receiver with their public keys. The public keys can be obtained by attaching their X.509 certificates to electronic cheques. These certificates may include the signatures of the root certifying authority in their certificate chains. To avoid fraud, the root certification authority’s public key should be widely distributed.
3. Storage of Private Keys: To avoid fraud, the private key of the customer must be securely held and made available to the consumer. This can be accomplished by offering a smart card that the consumer can carry.
4. Cashier’s Cheques: A bank issues a cashier’s cheque, which is signed by the bank’s private key. The originating bank’s certificate is included with the electronic cheque. The receiving bank decrypts the digital signature using the originating bank’s public key. The receiving bank is so convinced that the cashier cheque was truly generated by the bank specified on the cheque. It also provides non-repudiation to the receiving bank, as the originating bank cannot dispute issuing this cheque because it is signed by the originating bank’s private key (which only the originating bank is assumed to have).
Q12. Discuss ethical and other public policy issues. Explain protecting intellectual property.
Ans. Public policy is largely concerned with governmental action and inaction. Of course, this includes both empirical and normative issues. At the empirical level, there are concerns about what governments actually do and how this varies over time and among countries. Key issues at the normative level include what governments should and should not do, as well as what principles should drive decision-making.
According to this viewpoint, ethics is at the heart of public policy and is crucial to all elements of the policy-making cycle, including the duties of defining the problem, identifying and assessing potential options, decision-making, implementation, evaluation, and, when appropriate, termination.
Strategies to Protect the Intellectual Property: There are various methods for protecting and managing our intellectual property (IP). Creating an IP strategy is critical to maximising our investment. An IP strategy should highlight our competitive advantages. Our brand, inventions, and designs are unique to our company. What kind of IP we use and how we handle it could have serious effects. Some of the strategies to protect intellectual property are:
1. Integrate IP Strategy with our Business Plan and Seek Advice: Whatever strategy we adopt to protect and exploit our IP, it should be integrated into our business plan. We must explore all the options available and seek professional advice.
2. Combining Registered and Unregistered Rights: To maximise IP protection for our company, we can mix registered and unregistered rights. These may include the use of commercial secrets and confidentiality agreements, as well as registered rights like trademarks and designs.
Not all of the intellectual property we own is worth the money and time it takes to properly register it. For example, we can decide that getting our product to market as soon as possible is a preferable strategy than patent protection. Other intellectual property, on the other hand, may be vital to our company’s growth and necessitate registration. It is our intellectual property, our business strategy, and, ultimately, our decision.
3. Importance of Secrecy: Unless an invention or design is completely new, it cannot be registered. This means they couldn’t have been made public or displayed beforehand.
If we want to get a patent or design, we must protect and keep our ideas secret until we file our application. We may decide that keeping our creation a secret is preferable to applying for a patent and having to disclose its contents. This type of safeguard is known as a trade secret.
4. Implement Security Measures: AIl businesses are conducted today using technology or the internet. There is a need to implement security measures within the IT framework. These include the following:
- (a) Setting up password protection for all computer networks.
- (b) Encypting data as files are shared within the IT system.
- (c) Using virtual private network access.
- (d) Establishing Wi-Fi protected access
Q13. Explain internet protocols, web-based server and internet security.
Ans. Internet Protocol (IP): As the fundamental protocol in the internet layer of the internet protocol suite, internet protocol is responsible for delivering packets from the source host to the destination host purely based on the IP addresses in the packet headers. IP defines packet structures that encapsulate the data to be conveyed for this purpose. It also specifies addressing methods for labelling datagrams with source and destination information.
Web-based System: A server owned and controlled by the EMR provider is present in a web-based system. We utilise a web browser to connect to the server (Internet Explorer, Firefox Chrome, etc.). Because the web browser is unaware of the application, the web server is in charge of accepting the browser’s request, constructing the resulting web page, and sending it all back to the browser to be displayed. As a result, a large amount of data is sent between the browser and the web server.
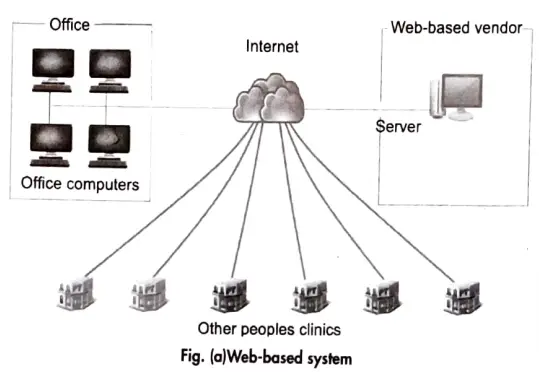


Internet Security: It is a subset of computer security that is especially relevant to the internet, frequently involving browser security but also network security on a broader level because it pertains to other programmes or operating systems as a whole.
