Table Of Contents
In B.Tech AKTU Quantum Book, learn about the practical Application of Soft Computing. Learn about significant applications, frequently asked questions, and important tips for learning this cutting-edge technology. Unit-1 Neural Networks-I (Introduction and Architecture)
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Application of Soft Computing: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year * Aktu Solved Question Paper
Q1. Explain the structure of a biological neuron with the help of diagram.
Ans. A neuron is a tiny cell that receives electrochemical signals from many sources and sends them to other neurons.
Nerve structure:
- 1. A neuron is made up of a nucleus (a cell body) called the soma. Dendrites are irregularly formed filaments that connect to the soma.
- 2. Dendrites function as input channels, with all input from other neurons passing through them.
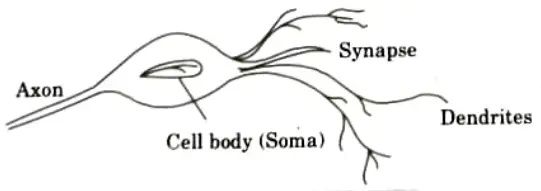


- 3. The axon is electrically active and serves as a conduit of output.
- 4. Axons are non-linear threshold devices that emit a millisecond voltage pulse known as an action potential or spike.
- 5. If the soma’s cumulative inputs boost the cell’s internal electric potential, known as membrane potential, the neuron fires by propagating the action potential down the axon to activate other neurons.
Synapse:
- 1. Synapses (nerve endings) are elementary structural and functional units that mediate the interactions between neurons.
- 2. The axon ends in a specialised contact known as a synapse or synaptic junction, which connects the axon to the dendritic connections of another neuron.
- 3. A neuro-transmitter fluid is present at the synaptic junction, which is a very small gap at the end of the dendritic connection.
- 4. Each dendritic link might have a large number of synapses activating on it, resulting in tremendous interconnectedness.
- 5. It is thought that the size of the synapse is connected to learning. Consequently, larger synapses are assumed to be excitatory, while smaller ones are thought to be inhibitory. Likewise, it is considered that increased neural activity is responsible for learning and memory.
Q2. What are the three technologies involved in artificial intelligence ?
Ans. Artificial Intelligence:
- 1. Artificial intelligence (AI) is the branch of computer science concerned with the research and development of computer systems that exhibit intelligence.
- 2. Artificial intelligence is an area of computer science that works with ways of encoding knowledge using symbols rather than numbers, as well as heuristic methods for information processing.
Technologies in artificial intelligence:
- 1. Robotics: This entails creating mechanical or computer equipment that accomplish activities that require a high degree of precision.
- 2. Natural language processing: It assists computers with understanding and responding to natural language statements and commands such as English.
- 3. Neural networks: It is a branch of artificial intelligence in which the development of a neural network model results in a computer programme that can think and learn.
Q3. Write the expression for bipolar continuous and bipolar binary activation function.
Ans.
- 1. The neuron as a processing node performs the operation of summation of its weighted inputs, or the scalar product computation to obtain a net.
- 2. Subsequently, it performs the non-linear operation f(net) through its activation function.
- 3. Typical activation functions used are:



- 3. Activation functions (a) and (b) are known as bipolar continuous and bipolar binary function respectively.
- 4. By shifting and scaling the bipolar activation function defined in a and b, both positive and negative responses of neurons are produced for the above formulation of the activation function.
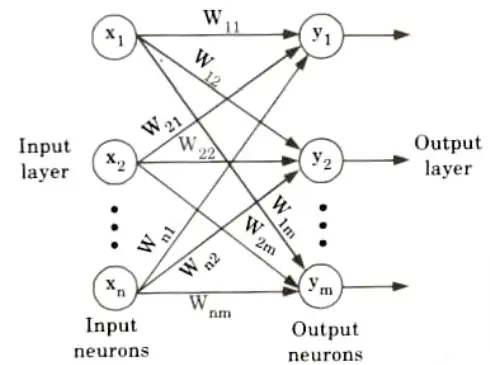
Q4. Draw a single layer feed forward network and explain its working functions.
Ans. Working function:
- 1. A single layer feed forward network has two layers: an input layer and an output layer.
- 2. Input signals are received by the neurons in the input layer, and output signals are received by the neurons in the output layer.
- 3. The synaptic linkages that carry the weights connect every input neuron to the output neuron but not the other way around.
- 4. Such a network is said to be feed forward in type or acyclic in nature.
- 5. Output layer performs computation.
- 6. The sum of the product of weights and the inputs is calculated in each node.
- 7. The input layer transmits the signals to the output layer.


Q5. Briefly discuss classification of learning algorithms.
Ans. Classification of learning algorithm:
1. Supervised learning:
- i. Learning is performed with the help of a trainer.
- ii. In ANN, each input vector requires a corresponding target vector, which represents the desired output.
- iii. The input vector along with target vector is called training pair.
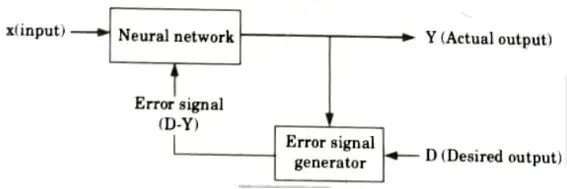


- iv. The input vector results in output vector.
- v. The actual output vector is compared with desired output vector.
- vi. If there is a difference means an error signal is generated by the network. It is used for adjustment of weights until actual output matches desired output.
2. Unsupervised learning:
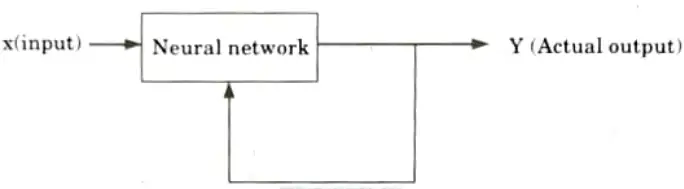


- i. Learning is performed without the help of a trainer.
- ii. In ANN, during training process, network receives input patterns and organizes it to form clusters. It is observed that no feedback is applied from environment to inform what output should be or whether they are correct.
- iii. The network itself discovers patterns, regularities, features/ categories from the input data and relations for the input data over the output.
- iv. Exact clusters are formed by discovering similarities and dissimilarities so called as self-organizing.
3. Reinforcement learning:
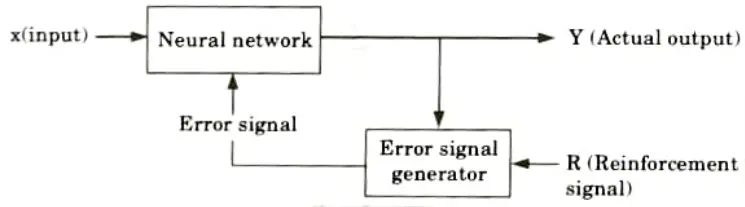


- i. It is similar to supervised learning.
- ii. Reinforcement learning is learning based on critic information, and the feedback delivered is known as a reinforcement signal.
- iii. The network receives some environmental feedback.
- iv. Every feedback is purely evaluative.
- v. The external reinforcement signals are evaluated in the critic signal generator, and the resulting critic signals are given to the ANN for suitable weight modification in order to get critic feedback in the future.
Q6. Explain Hebbian learning.
Ans. Hebbian learning:
- 1. The Hebbian learning rule describes how much the weight of the connection between two units should be increased or decreased in proportion to their activation product.
- 2. According to this rule, if two neurons fire at the same time, their connections may be reinforced.
- 3. Three major points were stated as a part of Hebbian learning mechanism:
- i. Information is stored in the connections between neurons in neural networks, in the form of weights. In this the input-output pattern pairs (xi, yi) are associated by the weight matrix W
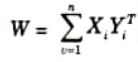
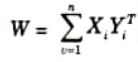
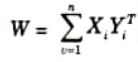
- ii. Weight change between neurons is proportional to the product of activation values for neurons.
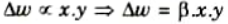
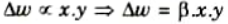
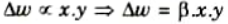
- iii. Simultaneous or repetitive stimulation of weakly linked neurons affects the strength and pattern of weights, resulting in stronger connections as learning occurs.
- 4. The Hebbian rule works well as long as all the input patterns are orthogonal or uncorrelated.



Important Question with solutions | AKTU Quantums | Syllabus | Short Questions
Application of Soft Computing Btech Quantum PDF, Syllabus, Important Questions
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| Subject Syllabus | Syllabus |
| Short Questions | Short-question |
| Question paper – 2021-22 | 2021-22 |
Application of Soft Computing Quantum PDF | AKTU Quantum PDF:
| Quantum Series | Links |
| Quantum -2022-23 | 2022-23 |
AKTU Important Links | Btech Syllabus
| Link Name | Links |
|---|---|
| Btech AKTU Circulars | Links |
| Btech AKTU Syllabus | Links |
| Btech AKTU Student Dashboard | Student Dashboard |
| AKTU RESULT (One VIew) | Student Result |
