With AKTU’s Question Paper, you may embark on an Exciting Project Management and Entrepreneurship Journey. Improve your understanding, test your knowledge, and fly to exam achievement.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Project Management and Entrepreneurship: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 4th Year
Section A: Short Question In Project Management and Entrepreneurship
a. What do you understand by entrepreneurship ?
Ans. An entrepreneur is an individual who starts a new firm, bearing the majority of the risks and reaping the majority of the benefits.
b. Differentiate achievement and motivation.
Ans. Difference between achievement and motivation :
| S. No. | Achievement | Motivation |
| 1. | Achievement refers to competence. | Motivation refers to the energization and direction of behavior. |
c. Differentiate between creativity and innovation.
Ans.
| S. No. | Creativity | Innovation |
| 1. | Creativity is defined as the act of developing new ideas, imaginations, and possibilities. | Innovation is the introduction of something new and effective into the market. |
| 2. | It is related to thinking something new. | It is related to introducing something new. |
d. Restate the term “Value creation”.
Ans. Value creation is the process that creates output which are more valuable than input.
e. List the factors of Project Management.
Ans. Following are the factors of project management :
- 1. Defining Project Goals
- 2. Understanding the Project Scope
- 3. Communicating at Every Stage
- 4. Managing Potential Risks
f. Differentiate between implementation and evaluation.
Ans. Difference between implementation and evaluation :
| S. No. | Implementation | Evaluation |
| 1. | Implementation is putting a strategy into action. | Evaluation assesses how well a strategy has been executed. |
g. Define the term project development.
Ans. The methodical use of resources, knowledge, and processes to plan and implement a given project and accomplish its goals and objectives under certain constraints is known as project development.
h. Discuss about uncertainties in project implementation.
Ans. Following are the uncertainties in project implementation :
- 1. Variability associated with estimates.
- 2. Uncertainty about the basis of estimates.
- 3. Uncertainty about design and logistics.
- 4. Uncertainty about goals and priorities.
- 5. Uncertainty about fundamental relationships between project parties.
i. Reframe the term “management for social venture”.
Ans. Management for social ventures is defined as “managing an organization with the goal of maximizing social impacts while maintaining financial viability.”
j. Discuss about legal framing of ventures.
Ans. Legal structures used in social entrepreneurship sectors are :
1. Non-profits or charitable organizations.
2. The for-profit social enterprise.
3. The hybrid model.
Section B : Long Questions Project Management and Entrepreneurship
a. Explain entrepreneurial motivation theory in detail. And also discuss different theories associated with it.
Ans. Motivation theory :
- 1. The term ‘motivation’ has been derived from the word motive.
- 2. Motivation is described as an inner condition of our mind that activates and leads our thinking to achieve our objectives.
- 3. Motivation is thus defined as the process that causes a person to act and induces him to continue doing in order to achieve goals.
- 4. According to Dalton E. McFarland, motivation is “the process through which urges, drives, desires, striving, aspirations, or needs influence, control, or explain human behaviour.”
- 5. Process of motivation can be understood by the diagram below :
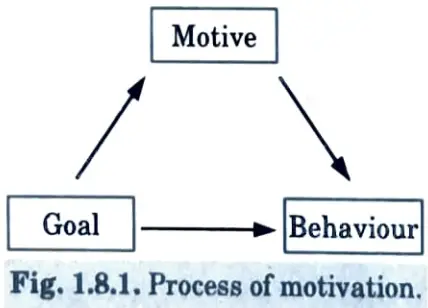


Different theories :
McClelland’s Achievement Motivational Theory :
David McClelland is most noted for describing three types of motivational need, which he identified in his 1961 book, The Achieving Society :
- 1. Achievement motivation (n-ach)
- 2. Authority/power motivation (n-pow)
- 3. Affiliation motivation (n-affil)
All workers have these demands to varied degrees, and this blend of motivational needs determines a person’s style and conduct, both in terms of being motivated and in management and motivating others.
- 1. The Need for Achievement (n-ach) :
- i. Because the n-ach person is ‘achievement oriented,’ he or she pursues achievement, the achievement of reasonable but demanding goals.
- ii. There is a great desire for feedback on completion and growth, as well as a sense of accomplishment.
- 2. The Need for Authority and Power (n-pow) :
- i. The n-pow is “authority motivated.” This creates a desire to be influential, effective, and have an impact.
- ii. There is a significant demand for them to lead and for their ideas to be accepted.
- iii. There is also drive and a need to raise one’s personal position and prominence.
- 3. The Need for Affiliation (n-affil) :
- i. The n-affil person is ‘affiliation motivated,’ with a need for pleasant ties and a desire to interact with others.
- ii. The affiliation driver generates motivation and must be liked and respected.
- iii. These people are team players.
b. Differentiate between entrepreneur and intrapreneur, enlist the different types of entrepreneurs.
Ans. Difference between entrepreneur and intrapreneur :
| Basis of distinction | Entrepreneur | Intrapreneur |
| Status | An independent businessman. | Works as a senior executive in company. |
| Ownership | Have complete ownership of the business. | Have partial ownership or may be an employee. |
| Financing | Controls the finance of the business. | Not responsible for the business finance. |
| Risk bearing | Bear full risk of the business. | Does not bear the risk of business. |
| Reward | There may be uncertain profits or loss. | Salary is fixed with Some incentives. |
| Origin | It starts as a separate enterprise. | It pursues the idea within an existing organisation. |
| Security | Need of security is low. | High need of security is required. |
| Decision making | They guide their venture by their own judgment. | They have to persuade their bosses for their new ideas. |
Different types of entrepreneurs :
- 1. On the Basis of Economic Development :
- i. Innovating Entrepreneurs: Entrepreneurs in this category are generally aggressive in terms of experimentation and putting appealing possibilities into action.
- ii. Adoptive or Imitative Entrepreneur: Imitative entrepreneurs replicate or implement applicable inventions created by inventive entrepreneurs.
- iii. Fabian Entrepreneur: They love to remain in the existing business with the age-old technique of production.
- iv. Drone Entrepreneur: Drone entrepreneurs are those who refuse to accept and utilise opportunities for production adjustments.
- 2. On the Basis of Type of Business :
- i. Business Entrepreneurs: These are the entrepreneurs that have a concept for a new product or service and then start a business to make it a reality.
- ii. Trading Entrepreneur: These entrepreneurs undertake trading activities and are not concerned with the manufacturing work.
- iii. Industrial Entrepreneur: These entrepreneurs are essentially manufacturers who identify client requirements and build products or services to meet those demands.
- iv. Corporate Entrepreneur: These entrepreneurs used their innovative skill in organizing and managing a corporate undertaking.
- v. Agricultural Entrepreneur: Agricultural entrepreneurs are persons who engage in agricultural activities such as automation, irrigation, and crop production using technology.
- 3. According to the Use of Technology :
- i. Technical Entrepreneurs: These entrepreneurs may enter business to commercially exploit their inventions and discoveries.
- ii. Non-technical Entrepreneur: They are concerned only with developing alternative marketing and promotional strategies for their product or service.
- iii. Professional Entrepreneur: Entrepreneur who is interested in establishing a business but does not have interest in managing it after establishment.
- 4. According to Motivation :
- i. Pure Entrepreneur: A pure entrepreneur is the one who is motivated by psychological economical, ethical considerations.
- ii. Induced Entrepreneur: This type of entrepreneur is one who is induced to take up an entrepreneurial task due to the policy reforms of the government.
- iii. Motivated Entrepreneur : They come into being because of the possibility of making and marketing some new products for the use of consumers.
c. Illustrate the different types of skill set required to run an enterprise. Emphasize on entrepreneurship skill set.
Ans. The managerial skills required to become a successful entrepreneur are :
- 1. Time Management: It is vital to get more work done in less amount of time by eliminating interruptions, prioritizing tasks and increasing effectiveness as well as productivity.
- 2. Business Planning:Every entrepreneur must create a business plan to help them fit their business into the industry, define their target market, and prepare to capture them.
- 3. Employee Management: Successful entrepreneurs should know how to motivate the employees in order to work effectively.
- 4. Customer Management: An entrepreneur must understand how to manage his relationship with existing clients in order to build loyalty to his company.
- 5. Sales Management: Understanding the sale activities helps the entrepreneurs to tackle the challenges that they may face in their sale management journey.
- 6. Financial Management: Even if your company’s finances are handled by an accountant, you must understand the processes of planning, organising, directing, and regulating financial activities.
- 7. Business Management: A solid understanding of general management, finance, marketing, operations management, purchasing, supply chain, human resources, and public relations is essential to be a successful entrepreneur.
d. Explain the different stages of project report preparation, methods for evaluation.
Ans. Following are the different stages/steps of project report preparation :
- 1. General Information: These are the details of the products, such as size, types or classifications, colours, market demand and supply, and the product’s potential state, among other things. Furthermore, this basic information includes the entrepreneur’s personal information.
- 2. Description of Project: This description covers information about the project’s location, structure, cost, power sources, raw materials, manufacturing process, machinery and equipment specifics, technical elements, and so on.
- 3. Sources of Finance: It includes separate information regarding the financial sources, such as term loan, personal capital of the entrepreneur, seed money, etc.
- 4. Cost of Capital and Working Capital: It contains information about land, buildings, technical infrastructure, furniture, startup expenses or fees, and so forth. The necessary working capital for the business operation is also provided.
- 5. Market Possibilities: Here, information regarding the product’s demand and supply, as well as anticipated probability, marketing methods, level of competition, and so on, is presented.
- 6. Financial Results/Profit: Here, the projected results and anticipated profit are explained.
- 7. Project Implementation Programme: Here, the period of implementation in its various stages and time limitation are detailed.
- 8. Summary: It includes the entire detail of project application and its main points.
Methods for evaluation: Following are the various methods for evaluation :
- A. Management Evaluation :
- 1. Memorandum and Articles of Association : object, authorized and paid-up share capital, promoter’s contribution.
- 2. Constitution and management of the industrial concern.
- 3. Present and proposed composition of the board of directors, details of Chief Executive and functional executives.
- B. Technical Feasibility :
- 1. Technology and manufacturing process.
- 2. Location of the project.
- 3. Plant and Machinery.
- 4. Raw material, Utilities and Manpower.
- 5. Project monitoring and implementations.
- C. Environmental Aspects :
- 1. Air, Water & Soil Pollution, list of pollutants/hazardous substances, their safety, handling & effluent disposal arrangements.
- 2. Compliance with national and International Standards.
- D. Commercial Viability :
- 1. Proposed products existing and potential market demand and supply.
- 2. Proposed products share forecasted and analysed with respect to the market.
- 3. Manufacturing cost analysis.
- 4. Sale price of the proposed product.
- 5. Export potential analysis.
- E. Financial Feasibility :
- 1. Project Cost Analysis.
- 2. Operating cost and profits.
- 3. Operational performance and financial evaluation.
- 4. Financing modes.
- 5. Working Capital requirements.
- 6. Projections of Profitability.
e. Enlist all social entrepreneurship opportunities and successful models, discuss about the term risk management in social enterprises.
Ans. Social entrepreneurship opportunities :
Different opportunities for social entrepreneurship are :
- 1. Waste Management: Entrepreneurship in solid waste management can help protect the environment, restructure the economy, and create jobs. Entrepreneurship prospects in solid waste planning include in trash collection, waste management, waste sorting, waste storage, waste transport, waste transformation, and waste energy recovery.
- 2. Cleaning Services: To keep the earth clean and green, we must all contribute to it. And for ambitious social entrepreneurs, this is an excellent industry to enter. The cleaning industry is still underutilized, and it need new blood to enter and transform the face of the industry through innovative skills and practises.
- 3. Green Infrastructure: Green infrastructure is critical for delivering and connecting urban life support services. Parks and reserves, streams and wetlands, transportation corridors, greenways, roof gardens and living walls are all part of it. This field offers numerous potential for entrepreneurs to meet the world’s green infrastructure.
- 4. Water Management: Access to potable water is a difficult issue for any household living in remote places nowadays. A social entrepreneur can investigate this issue and choose the best method to tackle it using his or her entrepreneurial talents.
- 5. Recycling Space: Recycling is the most effective method of converting waste into wealth by changing unwanted products into usable ones. With people’s increasing concern for a greener planet and eco-consciousness, the recycling company has emerged as one of the most innovative and profitable.
Successful models :
Successful models of social entrepreneurship are :
- 1. Study Hall Education Foundation (SHEF): It is an organisation dedicated to providing education to India’s most vulnerable females. With the programme, SHEF has worked with over 900 schools and transformed the lives of 150,000 girls.
- 2. Selco: It is a company rendering sustainable energy source to rural regions of the country. This project was the first rural solar financing program in India.
- 3. Childline: It aims to provide help in form of healthcare and police assistance, especially to street children.
- 4. Goonj:It is a social enterprise that gathers used clothes from the urban population, sorts it, repairs it, and then distributes it to the poor and needy. Goonj’s humanitarian efforts during natural disasters in Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala have been widely recognised.
- 5. Pipal Tree: It was successful in creating job chances for unemployed kids in rural India. Pipal Tree was founded as a firm with the goal of providing formal training to adolescents and placing them in respected professions in companies around the country.
- 6. Rangasutra: It aspires to resurrect the untapped skill and talent in rural India and to give them the attention they deserve.
- 7. Frontier Markets: It seeks to give the greatest technical solutions to India’s distant communities at the lowest possible cost. It provides solar energY powered products to rural India at a very low cost.
- 8. Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR): It all started with a PIL against politicians, which led to the formation of the Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR), an organisation that scrutinises Indian election procedures.
Risk management in social enterprises :
Steps to manage risks in social enterprise :
- 1. Risk Identification: The crucial first stage is for the social enterprise to identify risk occurrences that could potentially inhibit the achievement of its goals through environmental scanning. These risks can arise from
- i. Government legislation,
- ii. Policies and regulations,
- iii. Inadequate funding,
- iv. Technological challenges,
- v. Security and safety,
- vi. Withdrawal of grants and donations,
- vii. Legal restrictions,
- viii. Norms and culture,
- ix. Climatic hazards, and
- x. Managerial incompetence.
- These and many other risk factors are identified for impact assessment.
- 2. RiskImpact Assessment :
- i. The social enterprise evaluates the frequency and severity of each indicated danger.
- ii. Assessment criteria are utilised to assess the impact of these risks on enterprise goals. It can think about how risk occurrences effect cost, schedule, quality, programme scope, or performance.
- 3. Developing the Approach and Plan :
- i. For a specific project, the risk management approach sets the processes, strategies, tools, and team roles and responsibilities.
- ii. The risk management plan specifies how risk management will be organised and carried out on the project.
- 4. Selecting the Risk Management Tools :
- i. Risk management tools help with programme risk management implementation and execution in systems engineering programmes.
- ii. When deciding on the right tools, the project team takes into account issues such as programme complexity and available resources.
- 5. Risk Prioritization Analysis :
- i. The detected risk events, their impact evaluation, probability of occurrence, and consequences are compiled to generate a risk rank order from most critical to least critical.
- ii. The major reason for prioritising these risks is to establish a foundation for allocating finite resources and determining the importance of attention.
- 6. Risk Mitigation Planning, Implementation, and Progress Monitoring :
- i. At this stage, the social company plans and executes measures to improve opportunities and remove or lessen dangers to an acceptable level.
- ii. Following the implementation of a strategy, the outcome is frequently monitored with the goal of changing any course of action as needed.
- iii. The risk mitigation approach or choice (accept, avoid, transfer, enhance, or minimise) will be determined by evaluating the probability of occurrence and severity of the consequence for an identified risk. The iterative process is still ongoing.
Section 3 : Key Concepts of Entrepreneurship
a. Describe the Me Clellend’s achievement theory of motivation. Discuss brief about EDP.
Ans. Mc Clellend’s achievement theory :
David McClelland is most noted for describing three types of motivational need, which he identified in his 1961 book, The Achieving Society :
- 1. Achievement motivation (n-ach)
- 2. Authority/power motivation (n-pow)
- 3. Affiliation motivation (n-affil)
All workers have these demands to varied degrees, and this blend of motivational needs determines a person’s style and conduct, both in terms of being motivated and in management and motivating others.
- 1. The Need for Achievement (n-ach) :
- i. The n-ach person is ‘achievement motivated’ and therefore seeks achievement, attainment of realistic but challenging goals.
- ii. There is a strong need for feedback as to achievement and progress and a need for a sense of accomplishment.
- 2. The Need for Authority and Power (n-pow) :
- i. The n-pow is “authority motivated.” This creates a desire to be influential, effective, and have an impact.
- ii. There is a significant demand for them to lead and for their ideas to be accepted.
- iii. There is also drive and a need to raise one’s personal position and prominence.
- 3. The Need for Affiliation (n-affil) :
- i. The n-affil person is ‘affiliation motivated,’ with a need for pleasant ties and a desire to communicate with others.
- ii. The affiliation driver produces motivation and needs to be liked and held in popular regard.
- iii. These people are team players.
Entrepreneurial Development Programmes (EDPs) :
- 1. The Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP) is a programme that assists individuals in acquiring entrepreneurial skills.
- 2. In other words, it refers to the development and refinement of entrepreneurial skills in a person required to start a business.
- 3. EDP is an excellent method of developing entrepreneurs, which can aid in the acceleration of socioeconomic development, balanced regional expansion, and the utilisation of locally accessible resources.
- 4. In recent years, EDP has evolved into a professional responsibility that heavily fosters the establishment of both financed and private firms.
b. What are influencing factors of corporate entrepreneurship also talk about the key concepts of entrepreneurship? Discuss.
Ans. Influencing factors of corporate entrepreneurship :
The Factors Affecting Entrepreneurial Development are :
- 1. Economic factors
- 2. Non-economic factors
- 3. Psychological factors
- 4. Governmental actions
- 1. Economic Factors :
- i. Capital: The availability of capital enables the entrepreneur to bring together diverse resources such as land, machinery, and raw materials in order to combine them and manufacture things. As a result, capital is referred to as a lubricant in the production process.
- ii. Labour: The quality and skilled labour is another factor which affects entrepreneurial development.
- iii. Raw Materials: The availability of raw materials is the most important requirement before starting any industrial operation. As a result, it has an impact on entrepreneurial development.
- iv. Market: It’s necessary to find the ideal target market for your idea, service or product if you have hope of opening an enterprise.
- 2. Non-economic Factors :
- i. Social Mobility: It refers to the degree of movement in both social and geographic terms. And the type of the mobility channel within the enterprise system.
- ii. Marginality: Individuals or groups on the perimeters of given social system provide the ideas to assume the entrepreneurial roles.
- iii. Security: When an entrepreneur is afraid of losing assets or facing different unfavourable punishments, his or her behaviours become less entrepreneurial.
- 3. Psychological Factors :
- i. Need Achievement: Characteristics which indicates high need of achievement is the major determinant of entrepreneurship development.
- ii. Withdrawal of Status Respect: There may be some kind of events that lead an entrepreneur to the loss of status.
- 4. Governmental Actions: Government actions, and the failure of government actions, have an impact on both economic and non-economic elements influencing entrepreneurship.
Section 4 : Business Opportunities in India
a. Summarize the different tools/techniques available for generating ideas. Identify the different business opportunities in India.
Ans. Different tools for generating ideas :
- 1. Mind Mapping: A mind map involves writing down a central theme and thinking of new and related ideas which radiate out from the centre.
- 2. Reverse Thinking: This technique asks us to think oppositely. Instead of working on the problem in front of us, we work on the exact opposite of it.
- 3. Brainstorming: Brainstorming is a group creativity technique by which efforts are made to find a conclusion for a specific problem by gathering a list of ideas.
- 4. SCAMPER: The word SCAMPER is an acronym. S -Substitute, C-Combine, A -Adapt, M -Modify, P – Put to another use, E- Eliminate, R- Reverse.
- 5. Role-Playing: In this technique, the participants take up roles to play. These roles are different from the ones they usually play. It adds an element of fun and helps get innovative ideas.
- 6. The 5 W’s: Who, What, Where, When, and Why are the five W’s. Answering these five W’s helps us achieve a view of the topic under discussion. And it is an efficient way to come up with solutions and ideas.
- 7. Synectics: In this technique, we take apart a thing and then put it back together. This helps us get a better understanding of how things work.
Different business opportunities in India: This is a very broad question. There are numerous business opportunities in India. Following are some of the business opportunities available in India :
- 1. Alcoholic and Non-Alcoholic Beverages, Drinks
- 2. Bamboo and Bamboo Products
- 3. Battery Operated Electric Rickshaw
- 4. Bicycle Industry
- 5. Biofuel
- 6. Cold Storage for Fruits & Vegetables
- 7. Computer Products and Information Technology (IT) Based
- 8. Dairy/Milk Processing
- 9. Electric Vehicles
- 10. Food Industry Ingredients
- 11. Food Processing and Agriculture Based Projects
- 12. Herbal Based Projects
- 13. Hygiene Products, Essential Personal Hygiene Products
- 14. Industrial & Engineering Products
- 15. Organic Farming, Neem Products
b. Explain in brief the functions of an entrepreneur especially to the Economic Development of the Country. Explain briefly Skill Development Program.
Ans. Following are the functions of entrepreneur in the economic development of a country :
- 1. Improvement in Per Capita Income: Entrepreneurs identify and capitalise on opportunities. They generate national income and wealth by converting latent and idle resources such as land, labour, and capital into commodities and services. They contribute to the country’s increased Net National Product and Per Capita Income.
- 2. Generation of Employment: Entrepreneurs create jobs both directly and indirectly. By beginning their own firm, they provide an opportunity for others to work by offering positions.
- 3. Balanced Regional Development: Entrepreneurs contribute to the elimination of regional differences in economic growth. They establish industries in backward areas to provide numerous substitutes and to accelerate the development of that region.
- 4. Improvement in Living Standards: Entrepreneurs establish industries that introduce new products on a large scale. They are less expensive, which helps to raise the average person’s standard of living.
- 5. Economic Independence: Entrepreneurship is critical for national self-sufficiency. Industrialists contribute to the production of replacements for imported goods, reducing reliance on foreign countries. These businessmen also export goods, earning foreign currency for the country.
- 6. Skill Development Program: The National Skill Development Mission launched by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship on July 15, 2015, aims to create convergence across sectors and States in terms of skill training activities.
Section 5 : Project Development Life Cycle
a. Demonstrate various stages of a project development life cycle.
Ans. Project Life Cycle :
- 1. The project life cycle is the succession of phases through which the project will evolve.
- 2. In layman’s terms, a project life cycle is defined by the phases that a project goes through before reaching the handover stage.
- 3. The phases in project life cycle are as :
A. Phase 1: Start up / Conceptualization of Project :
It contains the following keywords :
- i. Purpose,
- ii. Strategic fit,
- iii. Objective,
- iv. Scope,
- v. Terms of reference,
- vi. Draft schedule.
B. Phase 2 : Planning of Project Activities and Resources :
It contains following keywords :
- i. Scope,
- ii. Select team members,
- iii. Plan delivery,
- iv. Quality plan,
- v. Baseline schedule,
- vi. Baseline budget,
- vii. Risk analysis,
- viii. Issue register,
- ix. Approvals, and
- x. Communication plan.
C. Phase 3 : Execution of Project :
It contains following keywords :
- i. Production of key deliverables,
- ii. Monitor/ control,
- iii. Quality management,
- iv. Cost management,
- v. Risk management,
- vi. Issue resolution, and
- vii. Change control reporting.
D. Phase 4: Termination of Project :
It contains following keywords :
- i. Contract close out,
- ii. Team feedback,
- iii. Recommendation for further action, and
- iv. Post implementation review.
4. The level of activity required during project life cycle will vary with time.
5. This can be illustrated by project life cycle curve as shown in Fig.1
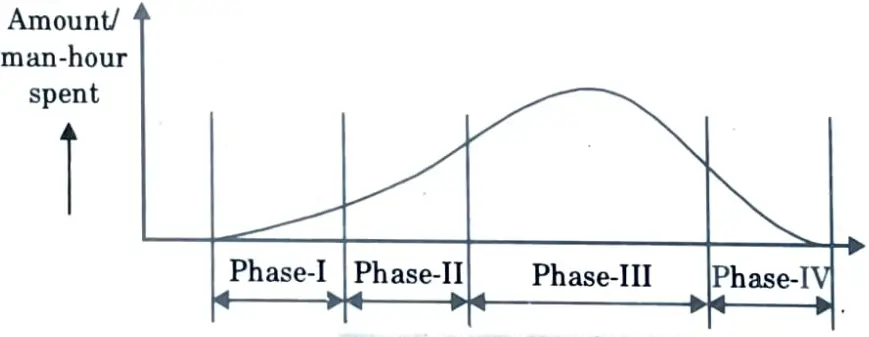


6. The level of activity is relatively low during the early phases, increases through the implementation stage where the major volume of work is done.
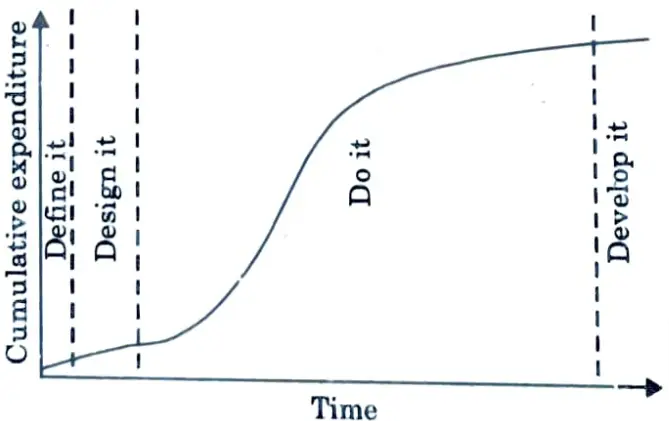
7. This pattern is shown as a group of cumulative expenditure against time in Fig.2


b. Demonstrate project appraisal. Illustrate its different types.
Ans.
- 1. Project assessment is the process of thoroughly examining various components of a given project before proposing the same.
- 2. Project evaluation is a scientific tool that follows a set pattern.
- 3. The organisation that has promoted the initiative must be completely satisfied before proceeding with the project’s launch.
- 4. The group or institution must ensure that the proposed project will create a suitable return on investment and that the loan amount disbursed for project implementation will be recovered along with interest within an acceptable time frame.
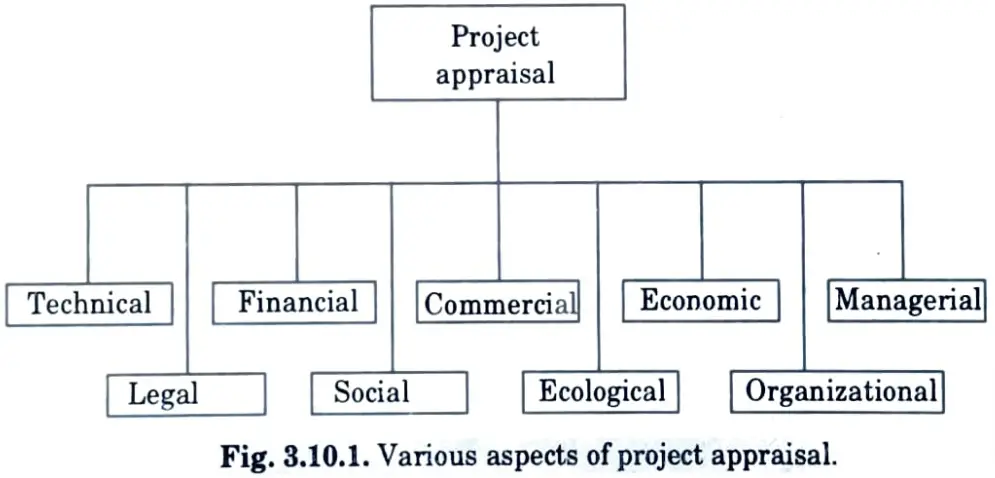
- 5. The various factors considered for project appraisal are shown in Fig. 3.10.1 and include technical, financial, commercial, economic, ecological, social and managerial aspects.


6. The main stages of the system of project appraisal are given in Table.
| Steps | Aspects | Process of Security |
| 1. | Process of Security | Indicates priority use. |
| 2. | Technical | Involves scale of the project and the process adopted. |
| 3. | Organizational | Suitability is examined. |
| 4. | Managerial | Adequacy and competence are critically scrutinized. |
| 5. | Operational | Capacity of the project. |
| 6. | Financial | Determines the financial viability for sound implementation and efficient operation. |
- 7. Different factors are not independent but are highly interrelated.
- 8. The methods of analysis may vary from project to project.
- 9. Certain common aspects of study from the point of view of engineering and technology are given below :
- i. Selection of technical process and appropriate technology.
ii. Technical know-how and collaboration made, if any. - iii. Size and scale of operation.
- iv. Location advantages and availability of infrastructure facilities.
- v. Selection of plant and machinery along with qualifications and capabilities of the supplies.
- vi. Details of plant layout and factory buildings.
- vii. Technical engineering services including power, water, etc.
- viii. Project design and network analysis for project implementation schedule.
- ix. Design of effluent disposal system and utilization of byproducts.
- x. Project cost and comparison with similar projects regarding technology, product mix, time spread and machinery.
- i. Selection of technical process and appropriate technology.
Section 6 : Project Financing
a. Explain the term Project financing. Elaborate different sources of finance in detail.
Ans. Project financing :
- 1. Project finance is the use of a non-recourse or limited recourse financial structure to fund (finance) long-term infrastructure, industrial projects, and public services.
- 2. The debt and equity used to finance the project are repaid from the project’s cash flow.
- 3. Project financing is a loan arrangement that is repaid largely through the project’s cash flow, with the project’s assets, rights, and interests serving as secondary collateral.
- 4. Project finance is particularly appealing to the private sector since it allows corporations to fund large projects off-balance-sheet (OBS).
Different sources of finance: Following are the different sources of finance :
- 1. Commercial Banks: Commercial banks are critical in terms of funding. Banks lend to businesses in a variety of methods, including cash credits, overdrafts, term loans, bill discounting, and the issuance of letters of credit.
- 2. Financial Institutions: The government has formed a number of financial institutions to give financing to businesses. They supply both owned and loan capital for long- and medium-term needs.
- 3. Public Deposits: Public deposits are funds that are directly raised from the general population. It can be used to increase a company’s medium and short-term requirements.
- 4. Lease Financing: A contractual agreement in which one party grants the other party the right to utilise any asset in exchange for a recurring payment. It is also known as renting an asset for a set amount of time. Fixed assets are typically leased.
- 5. Trade Credit: Trade credit is a type of short-term financing in which one merchant extends credit to another for the purchase of products and services. It makes it easier to buy items or services that do not require immediate payment.
- 6. Commercial Paper: Commercial Paper is a short-term unsecured promissory note issued by a company to raise finance. It can be granted by any business to another business.
- 7. International Financing: Organizations can raise cash on a global scale. Commercial banks, international agencies and development banks, the international capital market, and other international sources of funding are examples.
b. Discuss about project cost estimation process along with all its required components.
Ans. The process of developing cost estimation includes :
- 1. Define Estimate’s Purpose: Determine the purpose of the estimate, the level of detail which is required, who receives the estimate and the overall scope of the estimate.
- 2. Develop Estimating Plan: Form a cost-estimating team and define their strategy. Create a timeline and decide who will perform the independent cost estimate. Finally, make a schedule for the team.
- 3. Define Characteristics: Create a baseline description of the purpose, system, and performance parameters. This includes any technological ramifications, system configurations, timelines, tactics, and links to current systems.
- 4. Determine Estimating Approach: Create a work breakdown structure (WBS) and select the optimal estimating method for each element in the WBS. Check for cost and scheduling drivers, and then make a checklist.
- 5. Identify Rule and Assumptions: Clearly define what is included and excluded from the estimate, and identify specific assumptions.
- 6. Obtain Data: Create a data collection plan, and analyze data to find cost drivers.
- 7. Develop Point Estimate: Develop a cost model by estimating each WBS element.
- 8. Conduct Sensitivity Analysis: Test sensitivity of costs to changes in estimating input values and key assumptions, and determine key cost drivers.
- 9. Conduct Risk and Uncertainty Analysis: Identify the cost, scheduling, and technical risks associated with each WBS item and how to manage them.
- 10. Document the Estimate: Document each stage of the process to ensure that everyone is on the same page with the cost estimate.
- 11. Present Estimate to Management: Brief stakeholders on cost estimates to get approval.
- 12. Update Estimate: Any changes must be updated and reported on the estimate accordingly.
Section 7 : Risk Involved in Social Enterprise
a. Identify the different types of risk involved in social enterprise. How can social entrepreneurs attract talent when there aren’t high salaries and options ?
Ans. Types of risk involved in social enterprise :
The risks involved in a social enterprise are as follows :
- 1. Obtaining Finance :
- i. While beginning their business ventures, most entrepreneurs require some form of capital.
- ii. The issue with social entrepreneurship is that the company models rarely generate large profits.
- iii. Because of this, as well as the fact that social entrepreneurship is largely misunderstood, lenders are hesitant to offer financial support to social entrepreneurs.
- 2. Backlash :
- i. If you are fighting for a cause, there will almost always be others fighting against you.
- ii. The more divisive your cause, the more opposition you can expect.
- iii. Despite the fact that social entrepreneurs are known for their selflessness and desire to help individuals and communities in need, they frequently face backlash and criticism.
- 3. Not Focusing on Profit :
i. Many social entrepreneurs are so focused on their cause that they neglect to make a profit. - ii. Yet, profit is critical when it comes to satisfying your investors and running a profitable firm.
- 4. Burnout :
- i. When social entrepreneurs work long hours, burnout is a real risk.
- ii. Because there are no established working hours for entrepreneurs, their personal and professional lives become intertwined.
- 5. Lack of Public Knowledge :
- i. Despite the fact that social entrepreneurship is growing and increasing, the majority of the general population does not understand what it is. This makes gaining support for your cause harder.
- 6. Not Having a Substantial Support Structure :
- i. Having a support system and entities to whom you can turn for assistance and advice is critical for every firm.
- ii. Because social entrepreneurship is still in its early stages, there aren’t many support mechanisms that fall under the social entrepreneurship umbrella.
- 7. Marketing :
- i. Marketing a social business is undoubtedly difficult.
- ii. Many social entrepreneurs may not place enough attention on good marketing and may lack the resources, time, or cash to do so, which can pose a significant risk and obstacle.
Social entrepreneurs attracting talent when there aren’t high salaries and options :
- 1. By providing people with job possibilities that match their skills, interests, and values.
- 2. By instilling in them the desire to change the world and be a part of something bigger than themselves.
- 3. By giving them hard and deeply important work with colleagues they respect and care about.
b. What are the roles of social responsibilities and benefits in the growth of an entrepreneur ? Why many prominent businesses people move into social entrepreneurship?
Ans. Roles of social responsibility and benefits in the growth of an entrepreneur :
- 1. Employees are empowered to use the company resources at their disposal to achieve good through social responsibility.
- 2. Being a socially responsible business can improve a company’s image and help it establish its brand.
- 3. Social responsibility programmes can raise employee morale in the workplace and lead to increased productivity, which has an impact on the company’s profitability.
- 4. Social responsibility measures implemented by businesses can boost consumer retention and loyalty.
- 5. Socially responsible companies have the opportunity to stand out from the competition because they cultivate superior and positive brand recognition.
Prominent business people moving into social entrepreneurship :
- 1. Business people are becoming more involved in social entrepreneurship because they perceive fresh potential to solve problems in novel ways.
- 2. They have significantly more power as individuals to understand and address problems.
- 3. They see great needs to solve problems that established institutions, whether businesses, governments, or organizations, are not addressing.
- 4. They have witnessed the “failure of success” – the phenomenal increase of riches and possessions over the last fifty years that has left them dissatisfied and frequently empty.

2 thoughts on “Project Management and Entrepreneurship: Last year Question Paper Questions with Answer”