With our AKTU question paper and solution, you can learn about the wonders of Heat and Mass Transfer. Engaging notes make learning about these complex subjects enjoyable and approachable for young brains.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Heat and Mass Transfer: *Quantum *B.tech-Syllabus *Circulars *B.tech AKTU RESULT * Btech 3rd Year
Section A: Heat and Mass Transfer Short Questions
a. What is the difference between thermodynamics and heat transfer ?
Ans.
| S. No. | Thermodynamics | Heat Transfer |
| 1. | It is a branch of study that examines the connections between heat, work, and a system’s balancing features. | It is described as the transfer of energy caused by a temperature gradient from one area to another. |
b. How the thermal conductivity of material is defined? What are its units ?
Ans. The amount of heat transferred through a body of a given area and thickness during a given period of time when the temperature difference between the faces is equal to one. W/mK or W/m °C is the unit for thermal conductivity.
c. What is meant by transient heat conduction ?
Ans. Heat flow and temperature distribution at every point in the system change continuously over time under conditions known as unsteady state heat conduction.
d. Explain effectiveness and efficiency of fin.
Ans. Efficiency of Fin: Assuming the entire fin area were at base temperature, it is defined as the ratio of the actual heat transferred by the fin to the maximum heat transferable by fin.
Effectiveness of Fin: It is the difference between the heat transfer rate with fins and the heat transfer rate without fins.
e. What is turbulent flow ? Define it.
Ans. Turbulent flow is a type of fluid flow in which the fluid fluctuates irregularly. The irregular velocity changes in a turbulent flow are primarily responsible for heat and momentum transmission.
f. Define Reynolds’s number. Also write the significance of Reynolds’s number.
Ans. Reynolds’s Number: It is defined as the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces within a fluid that is moving relative to itself.
Significance of Reynolds’s Number: The Nusselt number is an easy way to calculate the convective heat transfer coefficient. The convective heat transfer coefficient is directly related to the thermal conductivity of the fluid and inversely proportional to the relevant length parameter for a given Nusselt number.
g. Define Stefan-Boltzmann’s law.
Ans. Planck developed the rules regulating the distribution of radiant energy across wavelength for a black body at a constant temperature.
h. Explain black body, opaque body, white body and grey body also.
Ans. Black Body: A dark body absorbs all incident radiation rather than reflecting or transmitting any of it.
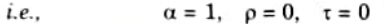
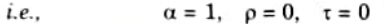
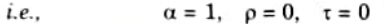
White Body: A white body is one that reflects all incident radiation that strikes it.
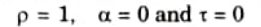
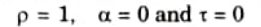
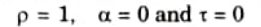
Gray Body: It is described as a body whose surface absorptivity does not vary with temperature or wavelength of incident radiation.
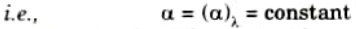
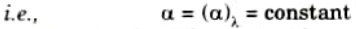
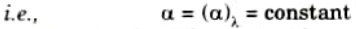
Opaque Body: An opaque body is one that does not transmit incident radiation through it.
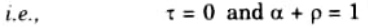
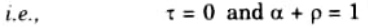
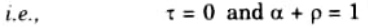
i. How heat exchangers are classified ?
Ans. Heat exchangers are classified as follows:
- a. Classification According to Nature of Heat Exchanger:
- 1. Direct contact heat exchanger.
- 2. Indirect contact heat exchanger.
- b. Classification According to Relative Direction of Fluid:
- 1. Parallel flow.
- 2. Counter flow.
- 3. Cross flow.
- c. Classification According to Design and Constructional Features:
- 1. Concentric tubes.
- 2. Shell and tube.
- 3. Multiple shell and tube passes.
- d. Classification According to Physical State of Fluids:
- 1. Evaporator.
- 2. Condenser.
j. What are the various modes of mass transfer ?
Ans. Various modes of mass transfer are as follows:
- 1. Mass transfer by diffusion,
- 2. Mass transfer by convection, and
- 3. Mass transfer by change of phase.
Section B: Heat and Mass Transfer Important Questions Aktu
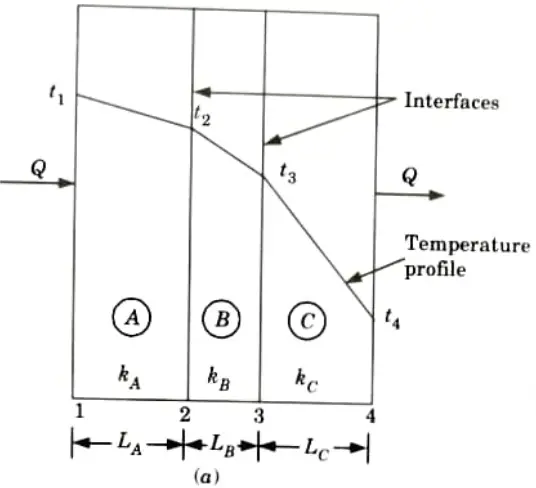
a. Drive an expression for heat conduction through a composite wall.
Ans. 1. Consider the transmission of heat through a composite wall consisting of a number of slabs as shown in Fig.



3. Since the quantity of heat transmitted per unit time through each slab/ layer is same, so we have
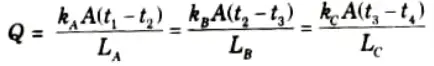
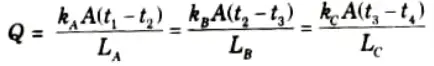
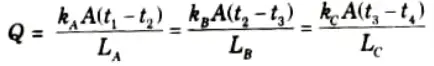
(Assuming complete contact between the layers and no temperature loss across the interface between the materials).
4. Rearranging the above expression, we get





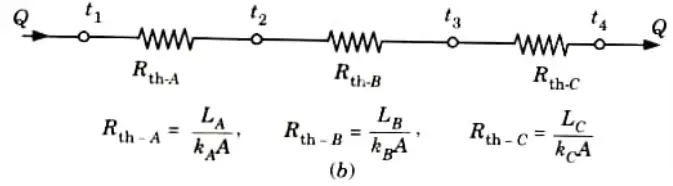


5. Adding eq. (1.11.1), eq. (1.11.2) and eq. (1.11.3), we have
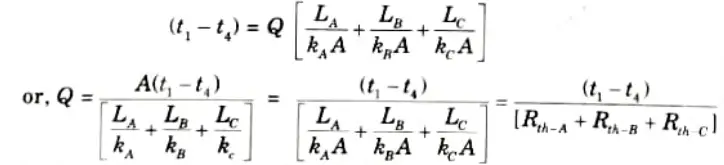
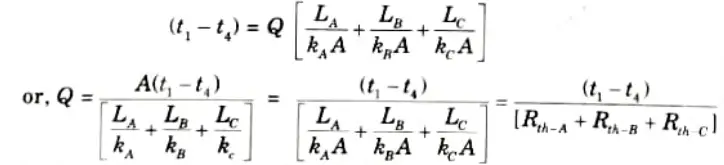
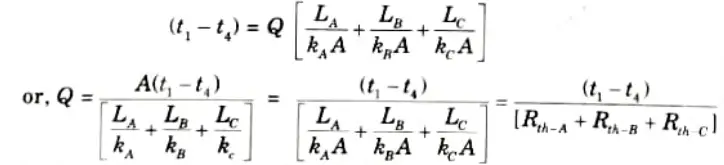
6. If the composite wall consists of n slab/layers, then
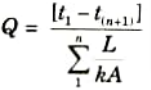
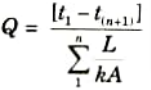
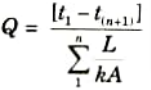
b. It is required to heat oil to about 300 °C for frying purpose. A ladle is used in the frying. The section of the handle is 5 mm x 18 mm the surroundings are at 30 °C. The conductivity of the material is 205 W/m °C. If the temperature at a distance of 380 mm from the oil should not reach 40 °C. Determine the convective heat transfer coefficient.
Ans. Given: to = 300 C, b18 mm = 0.018 m, y = 5 mm = 0.005 m, 380 mm 0.38 m, k = 205 Wm °C, ta = 30 °C.
To Find: The convective heat transfer coefficient, h.
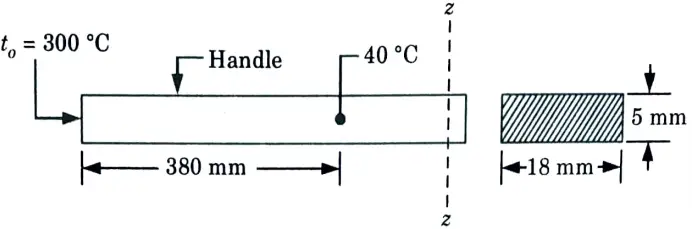


1. Assuming the fin to be long one, we have
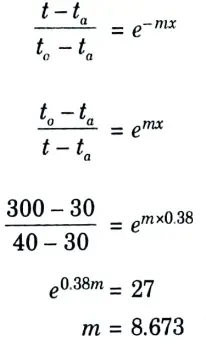
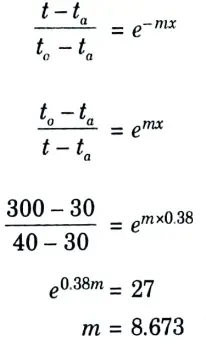
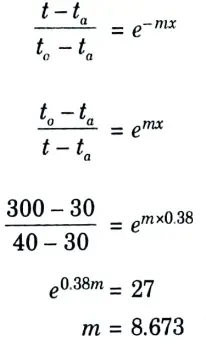
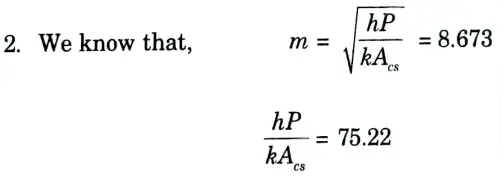
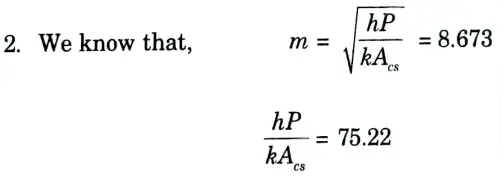
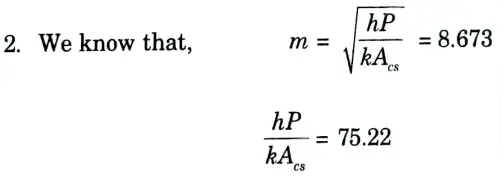
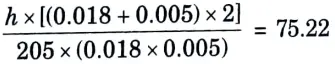
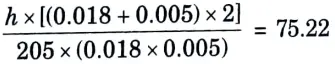
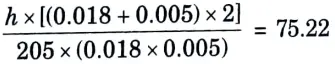
3. Convective heat transfer coefficient,
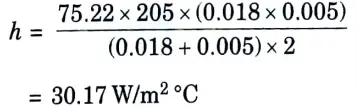
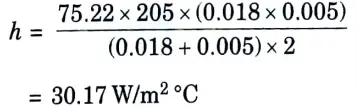
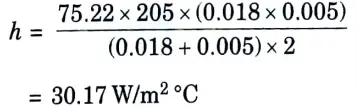
c. Differentiate between:
i. Natural and forced convection.
ii. Hydrodynamic and thermal boundary layer thickness.
Ans. i.
| S. No. | Natural Convection | Forced Convection |
| 1. | Free convection is the movement of a fluid induced by density fluctuations. | Forced convection refers to fluid motion produced by an external source. |
| 2. | It is dominated by the buoyancy force. | It is dominated by inertial force. |
| 3. | Nusselt number is a function of Greshoff number and Prandtl number in this case. | Nusselt number is a function of Reynolds number and Prandtl number in this case. |
| 4. | No external factors affect the heat transfer. | Only external factors can cause heat transfer. |
| 5. | Examples: Cooling down of a boiled eggs when kept in normal air, etc. | Example: Air conditioning, steam turbines, etc. |
ii.
| S. No. | Hydrodynamic Boundary Layer Thickness | Thermal Boundary Layer Thickness |
| 1. | It refers to the region near the wall where viscosity influences fluid velocity. | It refers to the area where the temperature of the fluid is affected by the temperature of the wall. |
| 2. | It depends mainly on the fluid viscosity. | It is determined by the fluid’s viscosity, velocity of flow, specific heat, and thermal conductivity. |
| 3. | Caused due to the velocity gradient. | Caused due to temperature gradient. |
d. A 70 mm long circular surface of a circular hole of 35 mm diameter maintained at uniform temperature of 250 °C. Find the loss of energy to the surroundings at 27 °C, assuming the two ends of the hole to be as parallel discs and the metallic surfaces and surroundings have a black body characteristics.
Ans.
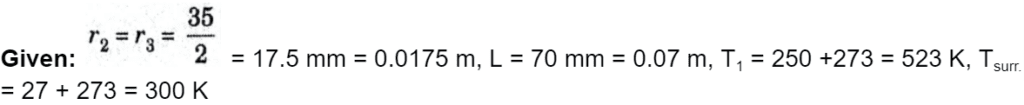
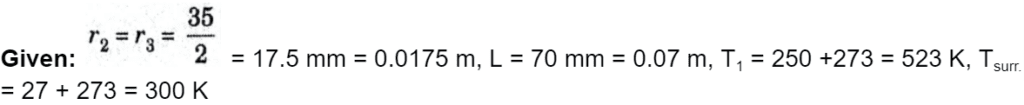
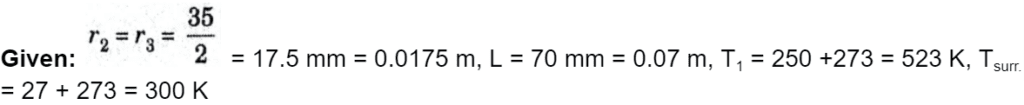
To Find: The total loss of energy.
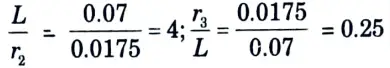
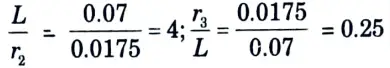
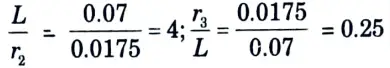
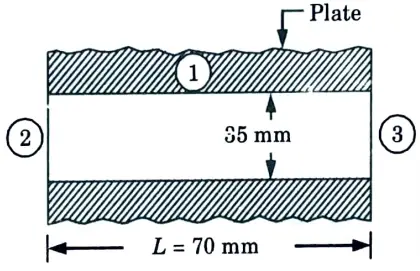


2. From shape factor graph, the configuration factor, F2-3 is 0.065.
3. By summation rule,



F2-1 = 1 – F2-3
= 1 – 0.065 = 0.935
4. By reciprocating theorem, A1F1-2 = A2F2-1
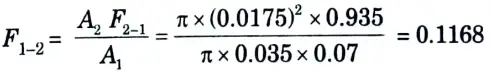
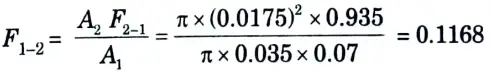
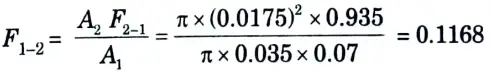
5. By symmetry, F1-3 = F1-2 = 0.1168
6. The total loss of energy = Loss of heat by both ends
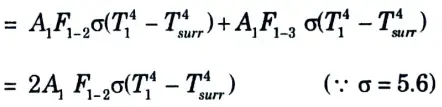
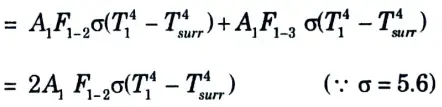
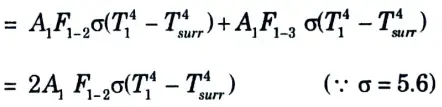



= 6.8 W
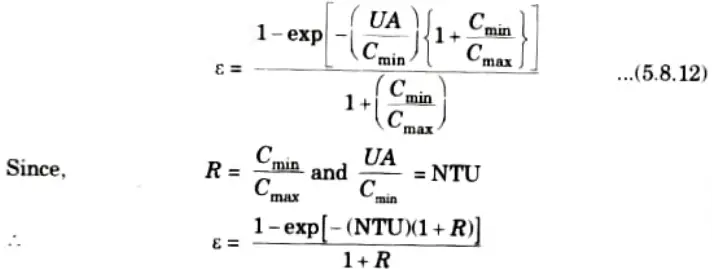
e. Derive an expression for effectiveness by NTU method for parallel flow.
Ans. 1. The heat exchange dQ through an area dA is given by,
dQ = UdA (th – tc) ………(5.8.1)
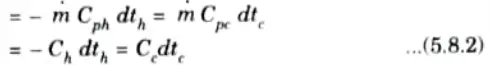
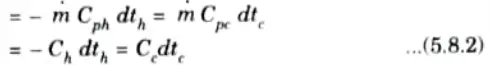
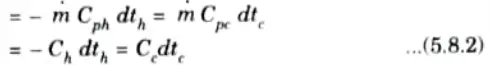
2. From eq. (5.8.2), we get
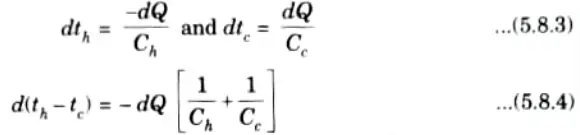
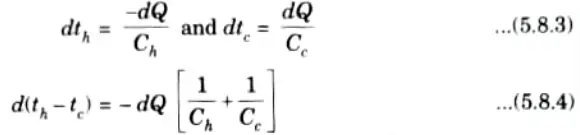
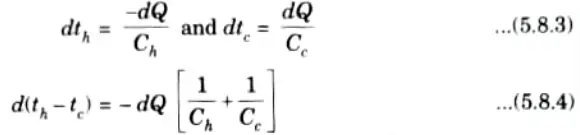
3. Putting the value of dQ from eq. (5.8.1) in eq. (5.8.4), we have
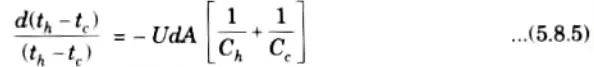
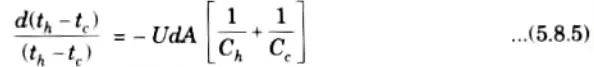
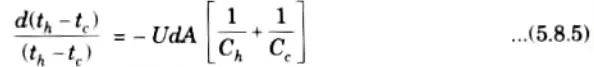
4. On integrating the eq. (5.8.5), we get
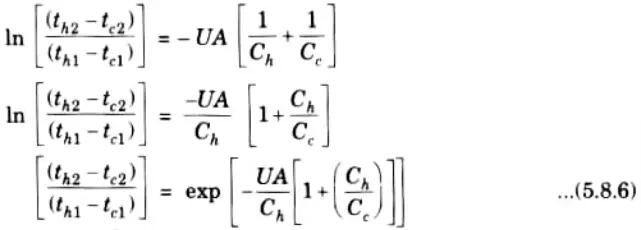
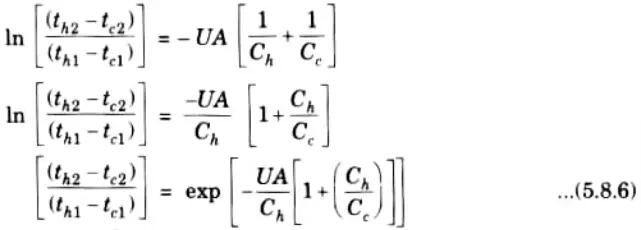
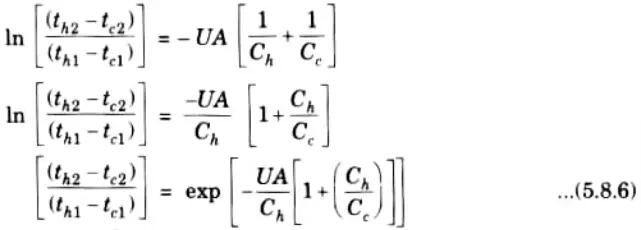
5. The expression of effectiveness is:
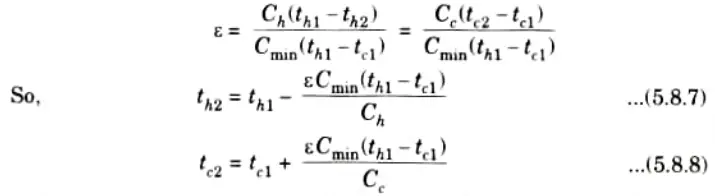
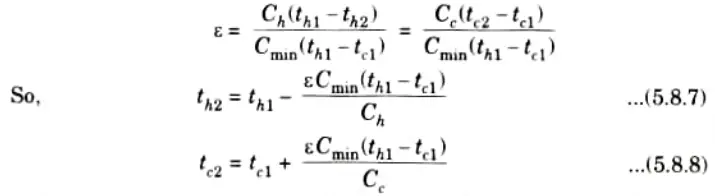
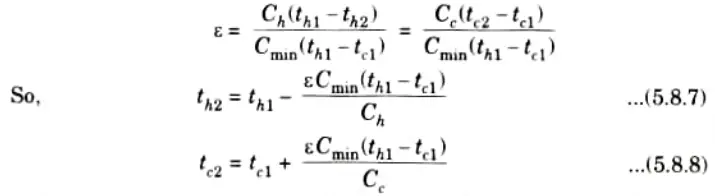
6. On putting value of th2 and tC2 from eq. (5.8.7) and (5.8.8) in eq. (5.8.6), we get
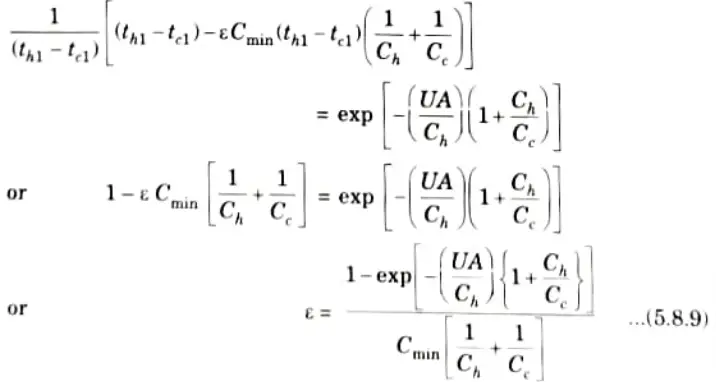
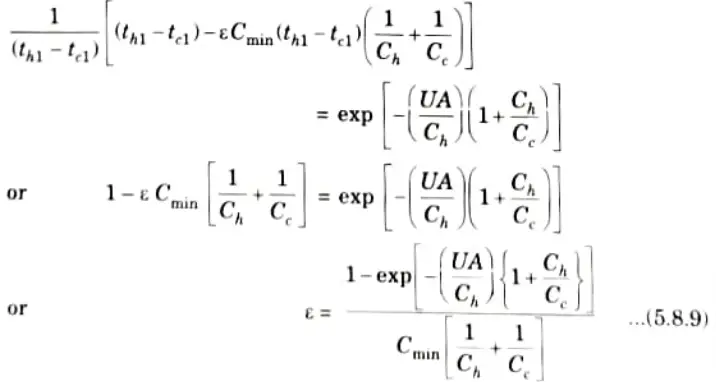
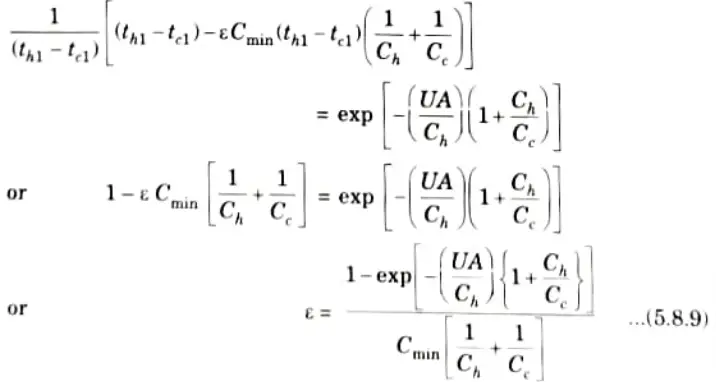
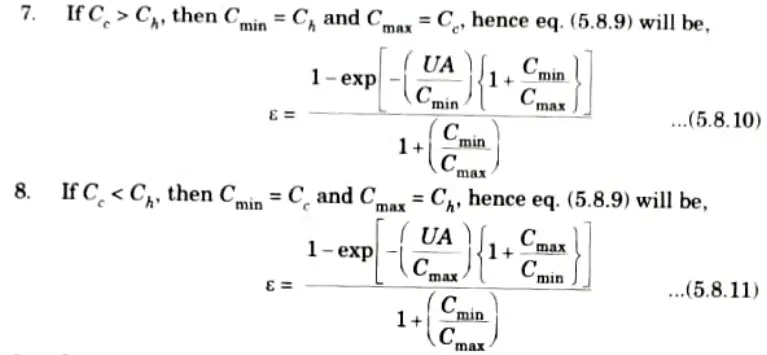


9. On rearranging eq. (5.8.10) and eq. (5.8.11), we have


Section 3: General Heat Conduction Equation
a. Derive a general heat conduction equation for cartesian co-ordinate.
Ans. A. General Heat Conduction Equation for Cartesian Co-ordinate:
1. Consider an infinitesimal rectangular parallelopiped (volume element) of sides dx, dy, and dz parallel, respectively, to the three axes CX, Y, Z) in a medium in which temperature is varying with location and time as shown in Fig.
2. Let, t = Temperature at the left face ABCD; this temperature may be assumed uniform over the entire surface, since the area of this face can be made arbitrarily small, and



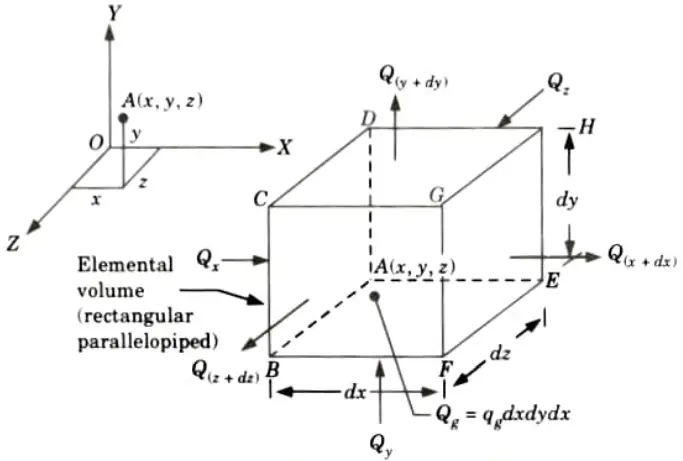


3. Quantity of heat flowing into element from the left face ABCD during the time interval dt in X-direction is given by
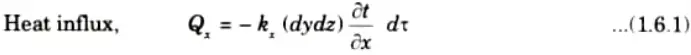
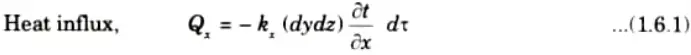
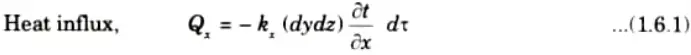
4. During the seme time interval d𝜏 the heat flowing out of the right face of control volume (EFGH) will be
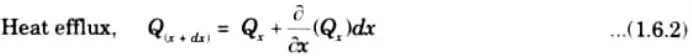
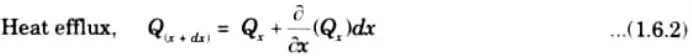
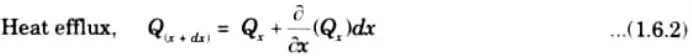
5. Heat accumulation in the element due to heat flow in X-direction, subtracting eq. (1.6.2) from eq. (1.6.1), we get
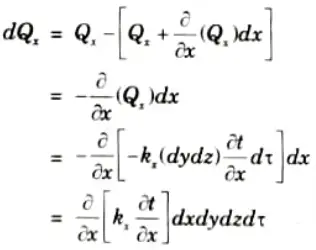
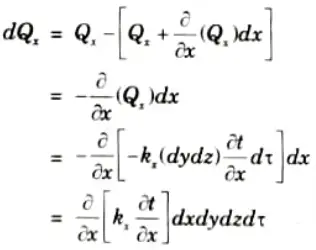
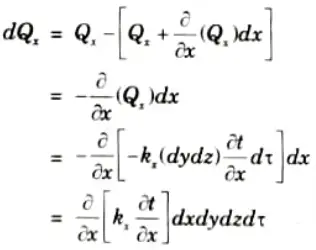
6. Similarly the heat accumulated due to heat flow by conduction along Y and Z-directions in time d𝜏 will be :
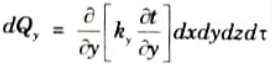
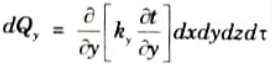
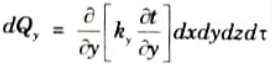
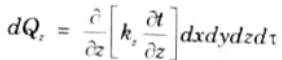
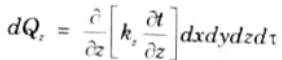
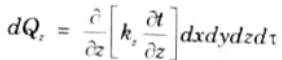
7. So, net heat accumulated in the element due to conduction of heat from all the coordinate directions is given as,
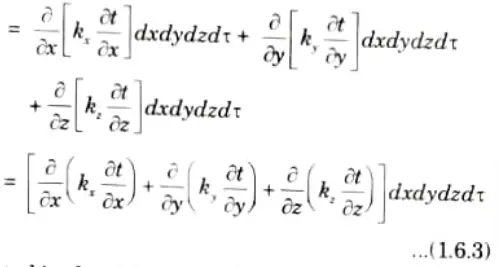
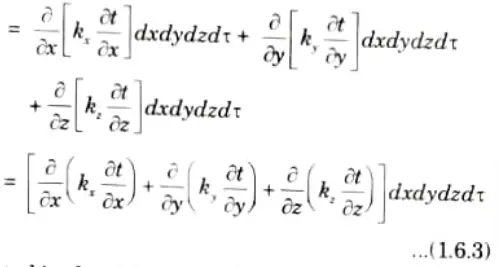
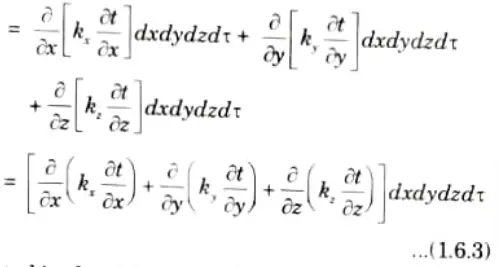
8. The total heat generated in the element is given by



10. Now using energy balance for the element, we have
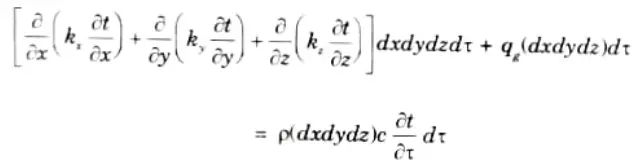
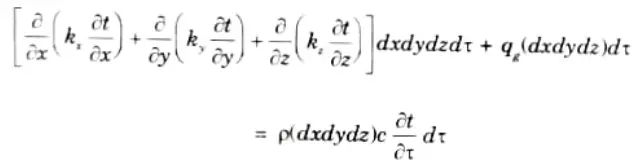
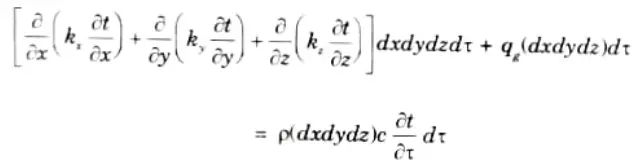
11. Dividing both side by dxdydzdt, we have
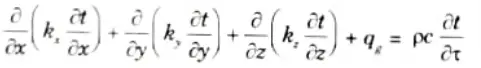
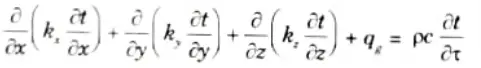
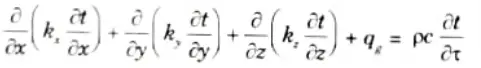
This is known as the general heat conduction equation for ‘nonhomogeneous material’, self heat generating and ‘unsteady three dimensional heat flow’,
12. In case of homogeneous and isotropic material (kx = ky = kz = k),
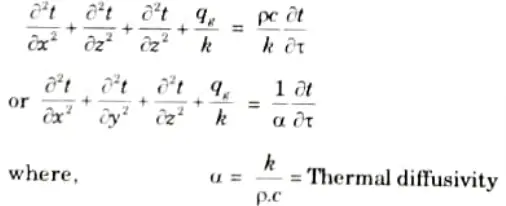
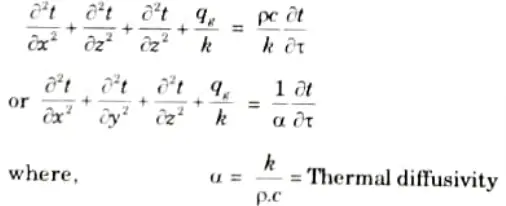
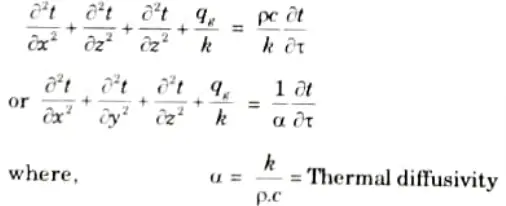
b. A mild steel tank of thickness 12 mm contains water at 95 °C. The thermal conductivity of mild steel is 50 W/m °C, and the heat transfer coefficients for the inside and outside the tank are 2850 and 10 W/m2 °C, respectively. If the atmospheric temperature is 15 °C, calculate:
i. The rate of heat loss per square meter of the tank surface area
ii. The temperature of the outside surface of the tank.
Ans. i. Rate of heat loss = 9.94 W/m2 °C
ii. Temperature of outside surface of tank =94.52 °C
Section 4: Heat and Mass Transfer Numerical
a. An aluminium alloy plate of 400 mm x 400 mm x 4 mm size at 200 °C is suddenly quenched into liquid oxygen at 183 °C. Starting from fundamentals or deriving the necessary expression to determine the time required for the plate to reach a temperature of – 70°C. Assume h =20000 kJ/m2h °C, Cp =0.8 kJ/Kg °C and density = 3000 kg/m3,
Ans. Given: ti = 200 °C.- 183 °C, ta = -70 °C, h = 20000 kJ/m2h °C, 𝜌 = 3000 kg/m3, Cp = 0.8 kJ/Kg °C.
To Find: Time required for the plate to reach a temperature of 70°C.
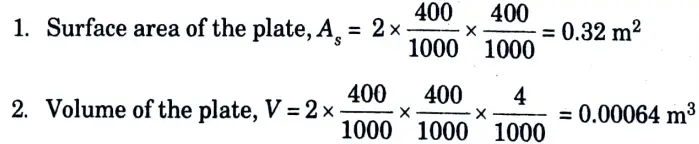
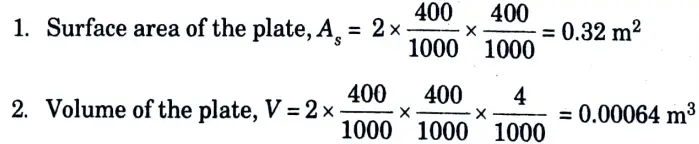
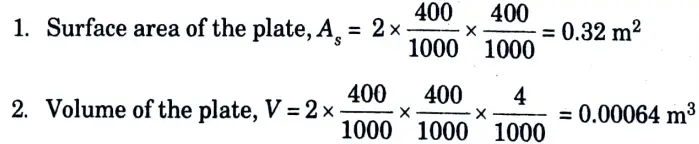



Since Bi is less than 0.1, hence Lump capacitance method may be applied for the solution of the problem.
5. The temperature distribution is given by



b. Prove that for a body whose thermal resistance is zero, the temperature required for cooling or heating can be obtained from the relation
(t – ta)/(ti – ta) =exp [- B, Fa]
Where the symbols have their usual meanings.
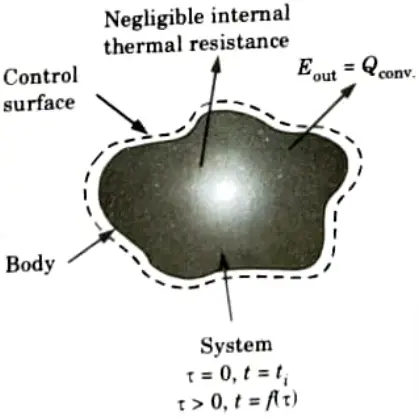
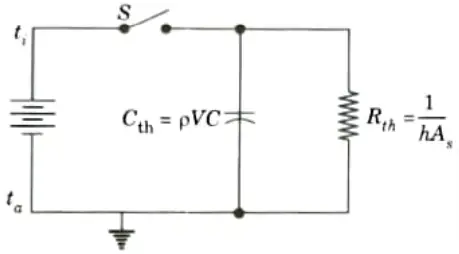
Ans. A. Lump System Analysis:
1. The Newtonian heating or cooling process refers to the assumption that interior resistance is insignificant in compared to surface resistance. At any one time, the temperature in this process is thought to be uniform. The whole solid, whose energy at any time is a function of its temperature and total heat capacity, is treated as a single lump in such an analysis.
B. Expression:
1. Let us consider a body whose initial temperature is ti throughout and which is placed suddenly in ambient air or any liquid at a constant temperature ta.
2. The transient response of the body can be determined by relating its rate of change of internal energy with convective exchange at the surface i.e.,







3. On rearranging the eq. (2.11.1), we get
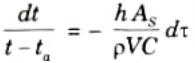
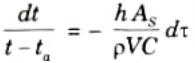
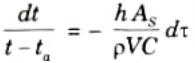
On integrating both sides, we get
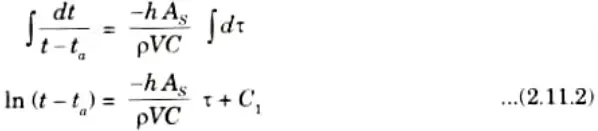
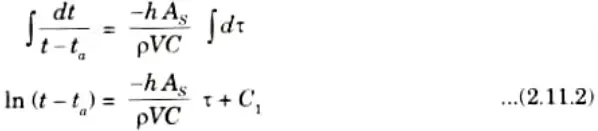
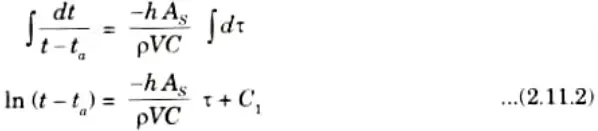
The boundary conditions are :
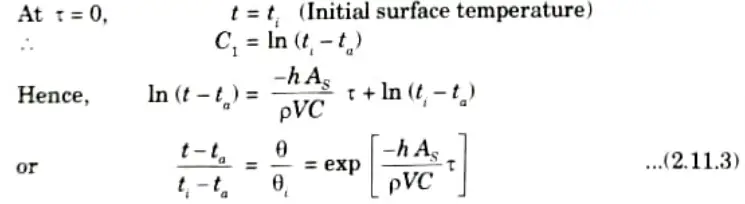
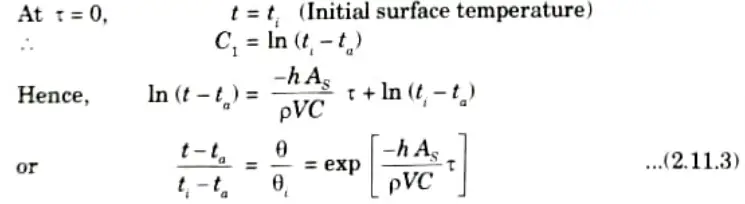
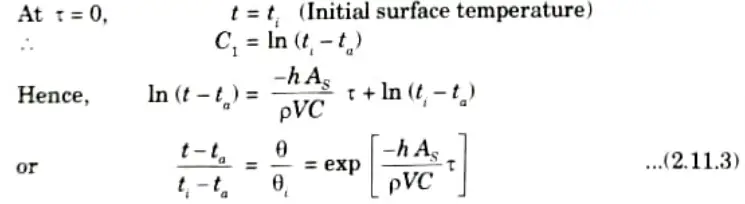



5. In eq. (2.11.4),
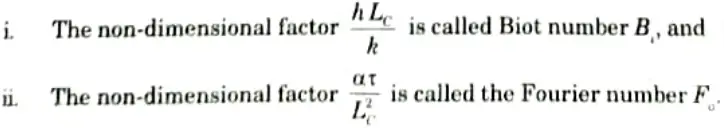
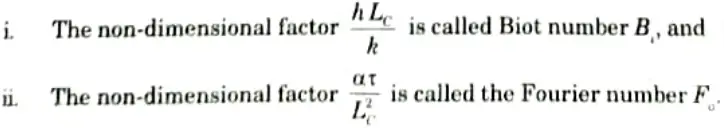
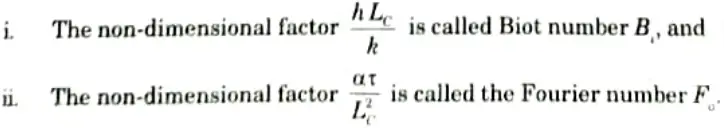
6. Using the non-dimensional term, eq. (2.11.3) becomes
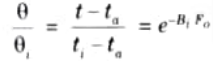
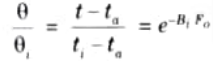
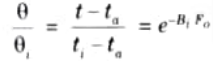
C. Significance of Fourier Number and Biot Number:
1. The Fourier number denotes the degree of heating or cooling action penetration through a substance.
2. The Biot number expresses the ratio of internal resistance (conduction) to surface resistance (convection).
Section 5: Important Solved Numerical
a. A nuclear reactor with its core constructed of parallel vertical plates of 2.2 m high and 1.4 m wide has been designed on free convection heating of liquid bismuth. The maximum temperature of the plate surface is limited to 960 °C while the lowest allowable temperature of the bismuth is 340 °C. Calculate the maximum possible heat dissipation from the both sides of each plate. For the convection coefficient for the plate is
Nu = 0.13 (GrPr)0.333
Where different parameter are evaluated at the mean film temperature.
Ans. Given: h = 2.2 m, b =1.4 m, tmax = 960 °C, tmin = 340 °C
To Find: Heat dissipation.



2. The thermo-physicai properties of bismuth are:
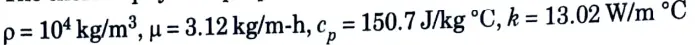
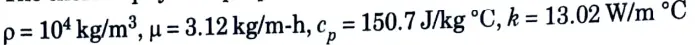
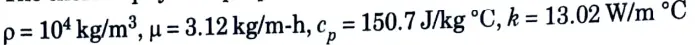



5. On multiplying eq. (1) and eq. (2), we get
GrPr = 9.312 x 1015 x 0.01 93.12 x 1012
6. Using the given correlation,
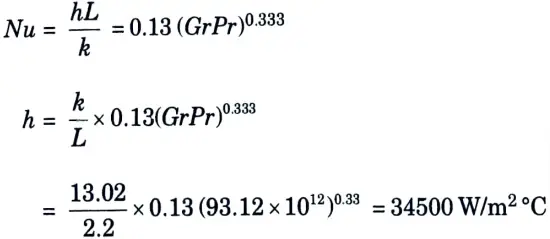
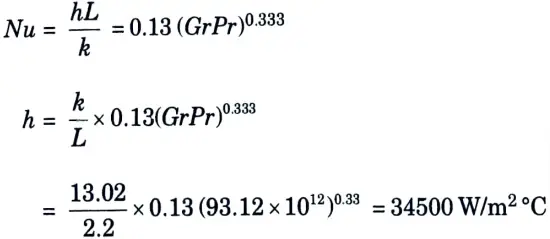
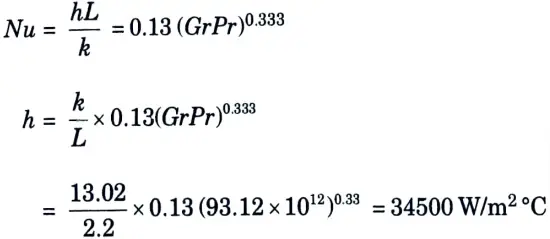
7. Heat dissipation from both sides of each plate,
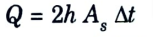
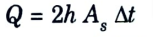
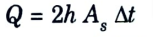
= 2 x 34500 x (2.2 x 1.45) x (960 -340)= 136.47 x 106 W 136.47 MW
b. Air at 20 °C flowing over a flat plate which is 200 mm wide and 500 mm long. The plate is maintained at 100 °C. Find the heat loss per hour from the plate if the air is flowing parallel to 500 mm side with 2 m/s velocity. What will be the effect on heat transfer if the flow is parallel to 200 mm ? The properties of air at (100 20)/2 = 60 °C are v = 18.97 x 10-6 m2/s, k 0.02 Wlm °C and Pr = 0.7.
Ans. Given: b = 200 mm = 0.2 m, L = 500 mm = 0.5 m, ts = 100 °C, t∞ = 20 °C,U =2 m/s, v = 18.97 x 10-6 m2/s, k = 0.025 W/m °C and Pr = 0.7.
To Find: The effect on heat transfer if the flow is parallel to 200 mm side.
Case I: When the flow is parallel to 500 mm side:



Case II: When the flow is parallel to 200 mm side:
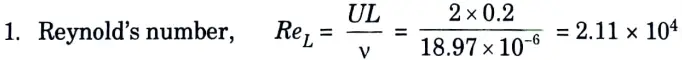
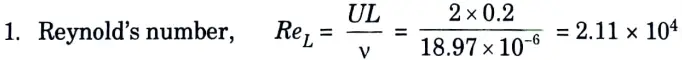
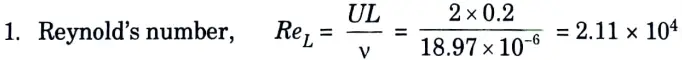
2. Convective heat transfer coefficient,
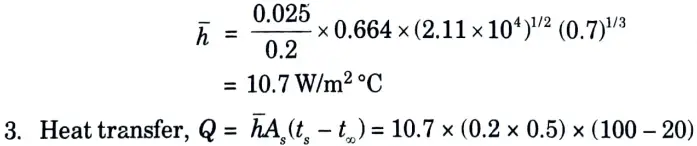
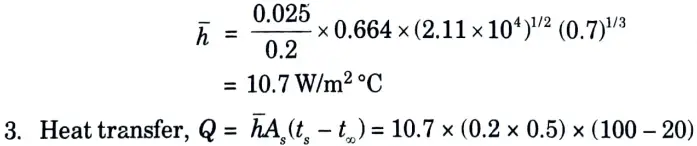
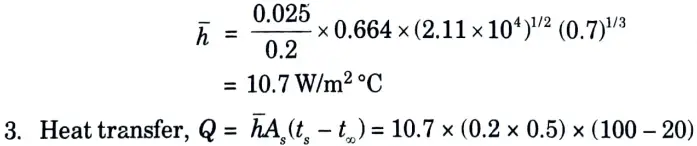
= 85.6 W
Section 6: Heat Exchange Between Black Bodies
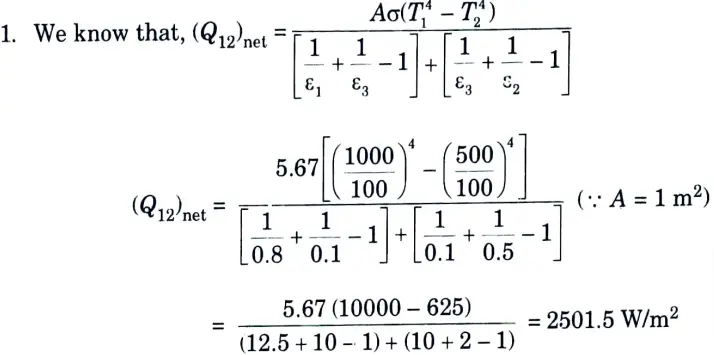
a. Determine the radiant heat exchange in W/m2 between two large parallel steel plates of emissivity’s 0.8 and 0.5 held at temperature of 1000K and 500 K respectively, if a thin copper plate of emissivity 0.1 is introduced as a radiation shield between the two plates. Use σ = 5.67* 10-8 W/ m2K4.
Ans. Given: T1 = 1000 K, ε1 =0.8, T2 = 500 K, ε2 = 0.5, ε3 = 0.1, σ = 5.67 x 10-8 W/m2 K4
To Find: Radiant heat exchange between two large parallel steel plates.


b. Derive the expression for heat exchange between black bodies for infinite parallel planes.
Ans. A. Shape Factor: It is defined as the fraction of radiative energy that is diffused from one surface and directly impacts the other surface with no reflections in between.
B. Salient Features of Shape Factor:
1. When heat transfer takes place between two bodies, the shape factor relation is given by,
A1F1-2 = A2F2-1
This is called reciprocity theorem.
2. The form factor with respect to itself is zero for flat and convex surfaces because the energy leaving the surface never returns on the same surface.
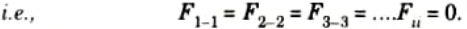
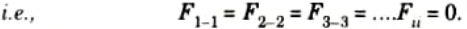
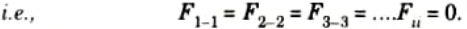
3. The shape factor with respect to itself is never 0 for concave surfaces.
4. The shape factor is solely determined by geometrical characteristics.
C. Proof of Reciprocity Theorem:
1. Considering heat exchange between elementary areas dA1 and dA2 of two black radiating bodies, separated by a non absorbing medium and having areas A1 and A2 and temperatures t1 and t2 respectively.
2. Let d𝜔1 be angle subtended at dA1 by dA2 and d𝜔2 angle subtended at dA2 by dA2. Then
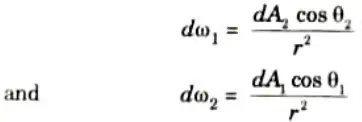
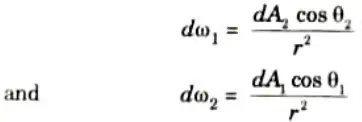
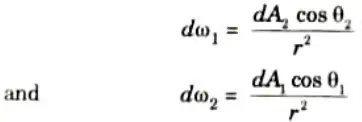
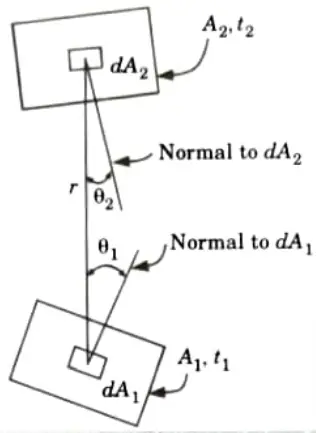


3. The energy leaving dA1 in the direction given by the angle per unit solid angle
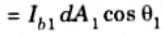
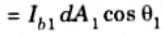
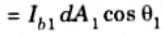
Where, Ib = Black body intensity, and
dA1 cos𝜃1 = Projection of dA1 on the line between the centres.
4. The rate of radiant energy leaving dA1 and striking on dA2 is given by
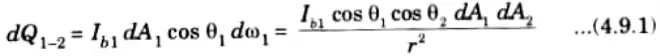
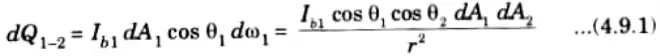
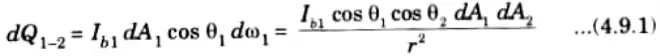
5. Now, the quantity of energy radiated by dA2 and absorbed by dA1 is given by,
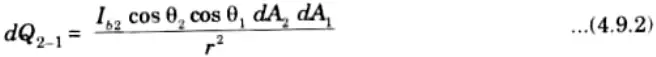
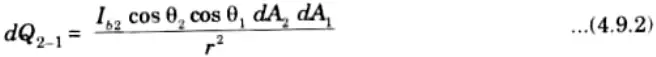
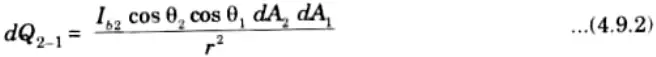
6. The net rate of transfer of energy between dA1 and dA2 is
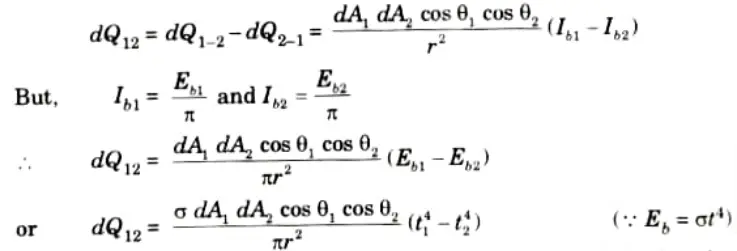
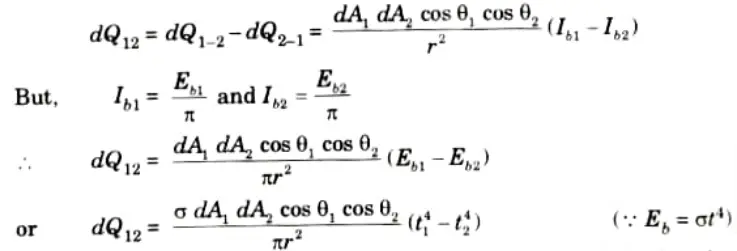
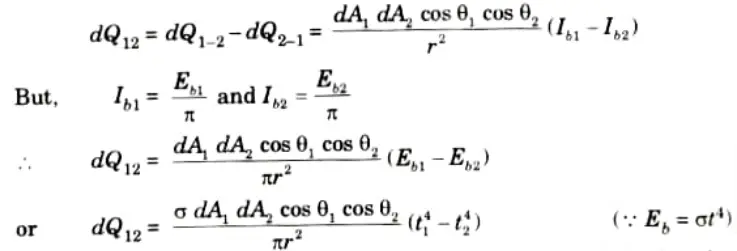
7. The rate of total heat transfer for the total areas A1 and A2 is given by
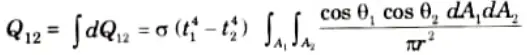
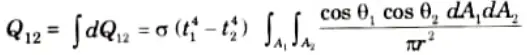
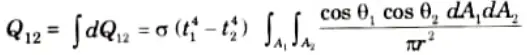
8. Now, from eq. (4.9.1), we get
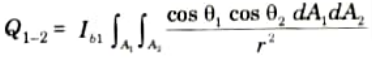
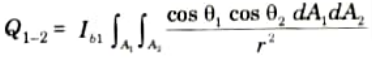
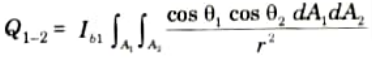
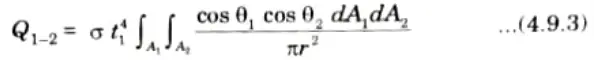
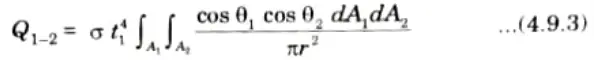
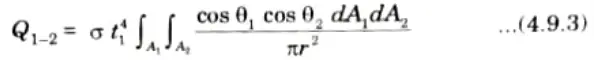
9. The rate of total energy radiated by A1 is given by



10. On dividing eq. (4.9.3) by eq. (4.9.4), we get
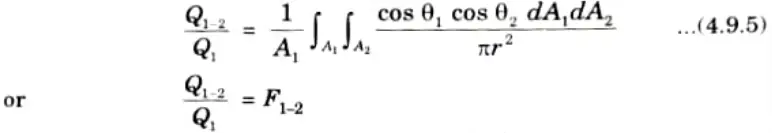
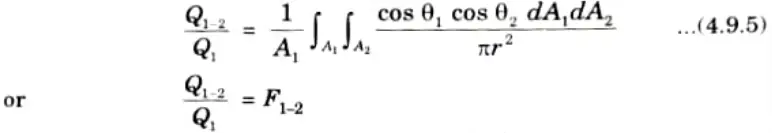
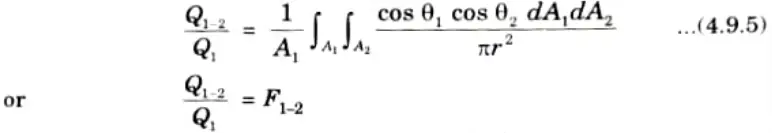
Where F1-2 is surface factor or shape factor between the two radiating surfaces.
11. Thus the amount of radiation leaving A1 and striking A2 is,



12. Similarly, from eq. (4.9.2)
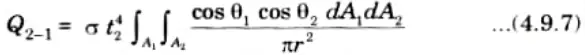
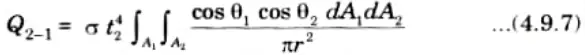
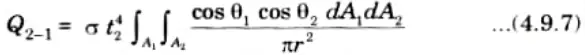
13. The rate of total energy radiated by A2 is given by



14. On dividing eq. (4.9.7) by eq. (4.9.8), we get
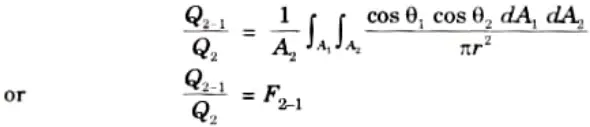
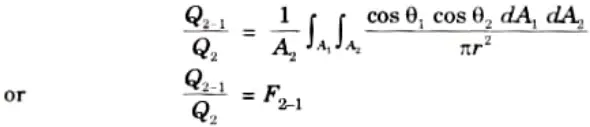
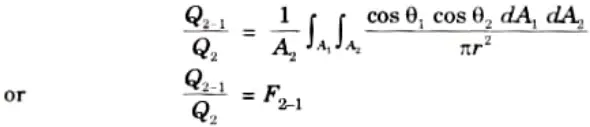
where F2-1 is the shape factor of A2 with respect to A1
15. The amount of radiation leaving A2 and arriving A1 is,



16. Thus, the net rate of heat transfer between two black surfaces A1 and A2 is given by
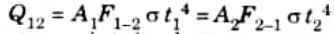
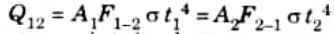
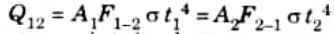
17. When the surface are maintained at same temperature, t1 = t2, there can be no heat exchange
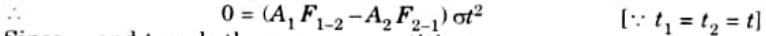
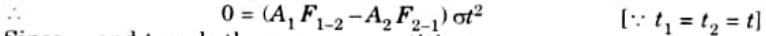
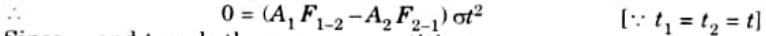
Since, 𝜎 and t are both non zero quantities,
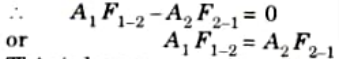
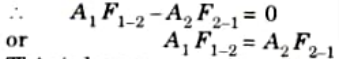
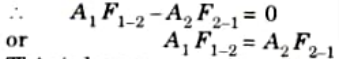
This is known as reciprocity theorem.
Section 7: Mechanisms of Filmwise and Dropwise Condensation
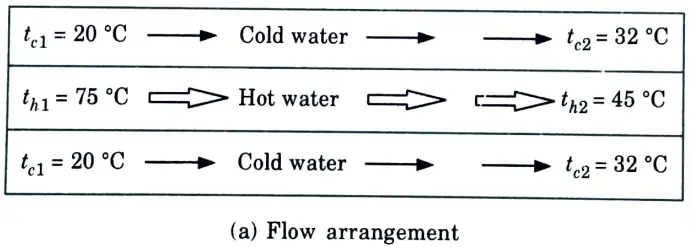
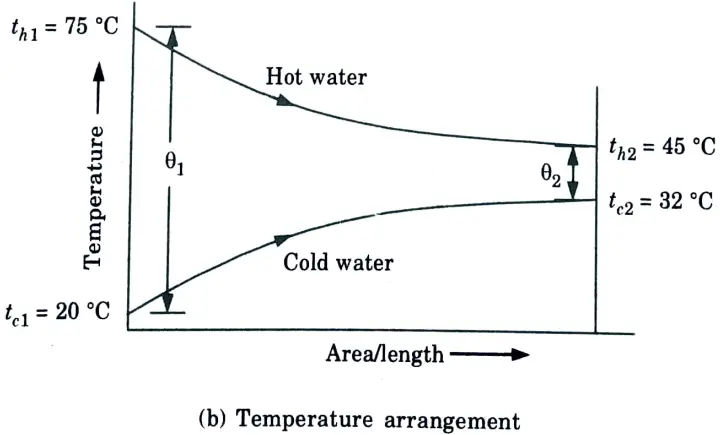
a. The flow rates of hot and cold water streams running through a parallel flow heat exchangers are 0.2 kg/s and 0.5 kg/s respectively the inlet temperatures 75 °C and 20°C respectively. The exit temperature of hot water is 45 °C. If the individual heat transfer coefficient on both sides are 650 W/m2°C. Calculate:
i. The area of heat exchanger.
ii. The rate of heat transfer.
Ans. Given: mh =0.2 kg/s, mc = 0.5 kg/s, th1 =75 °C, th2 = 45 °C, tc1 = 20°C, hi = ho = 650 W/m2°C.
1. The heat exchanger is shown in Fig.(a)
2. The heat transfer rate,



= 0.2 x 4.187 x (75 – 45) = 25.122 kJ/s
3. Heat lost by hot water = Heat gained by cold water
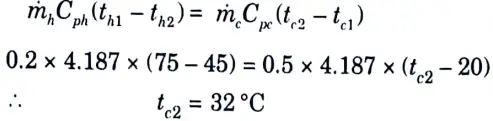
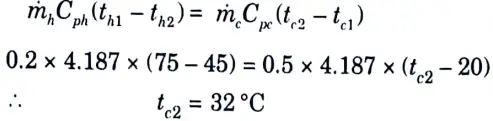
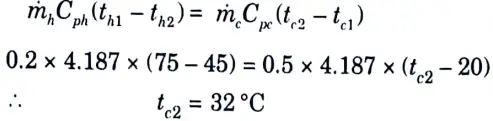
4. Logarithmic mean temperature difference (LMTD) is given by,
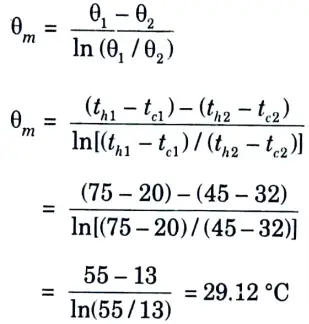
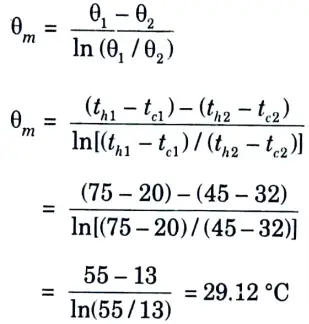
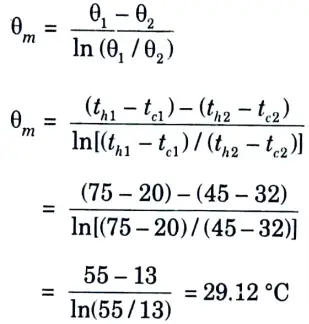




5. Overall heat transfer coefficient U,
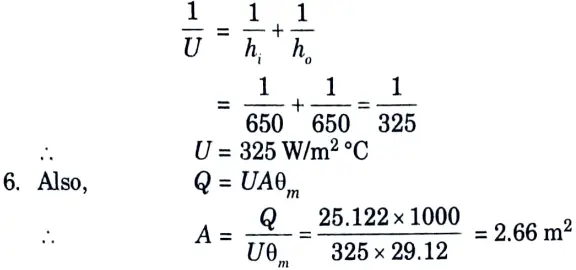
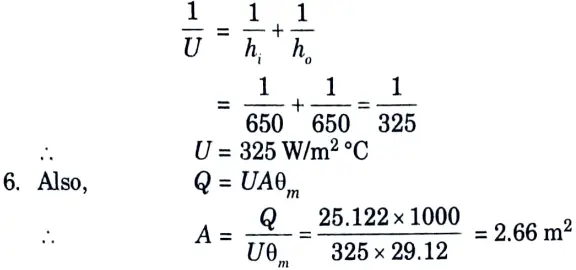
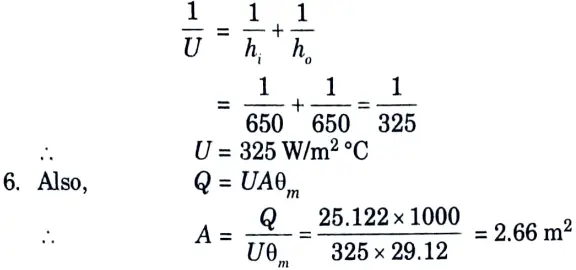
b. Differentiate between the mechanisms of filmwise and dropwise condensation.
Ans.
| S. No. | Filmwise Condensation | Dropwise Condensation |
| 1. | The surface is wetted by liquid condensate. | It does not wet the surface. |
| 2. | Liquid condensate spreads and does not form droplets. | Droplets of liquid condensate form. |
| 3. | It develops continuous sheets all over the surface. | It does not leave a coating on the surface. |
| 4. | Continuous sheet provides resistance and limits heat transmission between vapour and surface. | Because there is no film barrier to heat flow, rapid heat transfer rates occur between vapour and surface. |

6 thoughts on “Heat and Mass Transfer: Aktu Solved Question Paper with Notes”