Utilise the notes from the BCA solved exam to explore the realm of Knowledge Management. Discover how to organise and retrieve information, and obtain insightful knowledge for efficient knowledge use and sharing.
Dudes 🤔.. You want more useful details regarding this subject. Please keep in mind this as well. Important Questions For Knowledge Management: * Important Short Questions * Solved Question Paper * Syllabus
Section A: Knowledge Management Very Short Question Answers
Q1. Explain the term knowledge management.
Ans. Workers in the Knowledge Management System (KMS) develop, organise, and distribute critical knowledge wherever and whenever it is required. Many knowledge management systems, for example, rely on Internet and Intranet websites, knowledge bases, and discussion forums as fundamental technologies for collecting, storing, and sharing company knowledge.
Because the KMS system works with information (though knowledge management as a discipline may transcend beyond the information centric part of any system), it is a type of information system that may build on or use other sources of information.
Q2. Write down three applications showing the use of data mining.
Ans. The applications of data mining are as follows:
- (a) In business/industry, for increasing market share.
- (b) For fraud reduction.
- (c) To improve product or processes.
- (d) For text mining.
- (e) For finding new solutions to difficult problems.
Q3. Compare business expert system and decision support system.
Ans. It is possible to combine ES and DSS. Some components in DSS and ES may resemble one another. However, one must comprehend the distinctions between them. It is clearly evident how integration of ES and DSS can be accomplished.
Differences between DSS and ES are as follows:
- 1. A DSS helps manager to take a decision whereas an ES acts as a decision maker or an advisor to the manager.
- 2. A DSS is meant only for decision making whereas an ES provides expertise to the manager.
- 3. The spectrum of complexity is high in DSS and low in ES since ES addresses issues related to specific area only.
- 4. DSS does not have capability to reason whereas an ES has.
- 5. A DSS cannot provide detailed explanation about the results whereas an ES can.
Hence by integrating the two it is possible to blend their advantages and derive the best out of the two.
Q4. What do you mean by a business intelligence? Explain with example.
Ans. The term Business Intelligence (BI) refers to the tools and processes that play an important role in the corporation’s strategic planning process. These systems enable a corporation to collect, store, access, and analyse corporate data in order to make better decisions. These systems will generally demonstrate business intelligence in areas such as customer profiling, customer assistance, market research, market segmentation, product profitability, statistical analysis, and inventory and distribution analysis, to mention a few.
BI systems gather data from multiple sources and by means of advanced analytics and reporting, if used correctly, support the decision-making process in an outstanding manner.
BI is used from multiple business purpose, including :
- (i) Performance measurement and benchmarking progress towards corporate objectives.
- (ii) Quantitative analysis, including predictive analytics, predictive modelling, business process modelling, and statistical analysis.
- (iii) Reporting on departmental/divisional and enterprise data visualisation, EIS, and OLAP views.
- (iv) Collaborative programmes that enable internal and external corporate entities to collaborate through EDI and data sharing.
- (v) Knowledge management programmes are used to identify and produce insights and experiences for learning management and regulatory compliance.
Q5. ‘Decision-making is a difficult task. Give your views on this statement and justify your answer.
Ans. Making decisions will always be challenging since weighing your options requires time and effort. Second-guessing yourself and feeling indecisive are normal parts of the process. In many ways, they’re a positive thing-a indication that you’re considering your options rather than simply going with the flow.
Section B: Knowledge Management Short Question Answers
Q6. Write a detailed note on the characteristics and capabilities of a decision support system.
Ans. DSS characteristics and capabilities are as follows :
- 1. Support for decision makers in semi-structured and unstructured problems.
- 2. Support managers at all levels.
- 3. Support individuals and groups.
- 4. Support for interdependent or sequential decisions.
- 5. Support intelligence, design, choice and implementation.
- 6. Support variety of decision processes and style.
- 7. DSS should be adaptable and flexible.
- 8. DSS should be interactive case of use.
- 9. Complete control by decision makers.
- 10. Ease of development by end users.
- 11. Support modelling and analysis.
- 12. Data access.
Q7. What is data mining? Discuss any one data mining technique.
Ans. Data mining is the process of discovering information (meaningful new correlations, patterns, and trends) in data by shifting through massive amounts of data (100M-10G) using pattern recognition and statistical and mathematical tools.
A cluster is a collection of data objects.
- 1. Similar to one another in the same cluster.
- 2. Disimilar to the objects in other cluster.
Cluster analysis (or clustering) is the process of identifying characteristics in data and discovering similarities between data objects by grouping similar data objects into clusters.
Cluster analysis is a type of descriptive data mining that is unsupervised. There are no predefined classifications in this study.
Typical Applications : These are as follows :
- 1. As a stand alone tool to get insight into data distribution.
- 2. As a preprocessing step (data cleaning and data reduction) for other data mining algorithm. To simplify analysis, it is easy to analyse a small number of groups of similar items rather than analyse individual items.


Q8. What are the objectives of designing a business expert system? Give the significance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in a business expert system development.
Ans. The primary goal of an expert system is to deliver reasoned advise on a par with that of a human expert. The primary goal of this capacity is to strengthen the skills of top specialists in certain domains while also making a high level of expertise available to less highly educated practitioners.
The first aim takes note of the fact that some areas of human expertise, including the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, are so complicated that even the leading experts can profit from the systematic. Logical approach provided by a computer system will take idea about all the knowledge at its disposal. Idea of each case and will follow known lines of reasoning exhaustively, no matter how complex they are. These capabilities complement the skills of a human gain expert which are generally based on a mixture of knowledge, experience, insight and intuition. The second aim attempts to raise the level of skill of professionals who are not themselves leading experts. A large number of medical practitioners fall into this category, most in developing countries. When expert systems become widely available, the skills of these practitioners should be significantly enhanced. In n some expert systems, the expert knowledge is fixed into system when it is constructed and in others, there is a inbuilt ability to learn from experience, such as from mistakes made by the system.
Simulates human intelligence such as the ability to reason and learn. There are various commercial applications of artificial intelligence which are as follows:
- 1. Expert System: Computerised advisory programs that imitate the reasoning processes of experts in solving difficult problems.
- 2. Neural Network: It is:
- (a) An attempt to emulate the way the human brain works.
- (b) A Fuzzy Logic: a mathematical method of handling imprecise or subjective information.
- 3. Genetic Algorithm: An artificial intelligence system that mimics the evolutionary survival of the fittest process to generate increasingly better solutions to a problem.
- Example: Shopping Bot: Software that will search several retailer websites and provide a comparison of each retailer’s offerings including price and availability.
- 4. Intelligent Agent: Special purpose knowledge-based information system that accomplishes specific tasks on behalf of its users.
- 5. Virtual Reality: A computer-simulated environment that can be a simulation of the real world or an imaginary world.
Section B: Knowledge Management Detailed Question Answers
Q9. (i) How is group decision support system beneficial for an organisation? Explain with example.
Ans. A decision support system or DSS is helpful for an organisation in various ways. It improves the efficiency of the whole organisation. Following five points are enough to show its usefulness for the organisation :
- 1. Improving Personal Efficiency: Many DSS do nothing; a person cannot do anything by themselves. Budgets were created by hand for centuries before spreadsheet software was invented. DSS enables them to complete the task more quickly and with fewer errors.
- 2. Improving Problem Solving: A DSS can help an individual or group solve problems faster or better than they could without it. There is a link between the two, and increasing efficiency in a little work might be beneficial if used correctly. Hopefully adds to the overall solution of the problem. Solving a problem faster is self-explanatory.
- 3. Facilitating Communications: When utilised as a benefit tool, DSS can help to facilitate communication. When a specific action should be taken in the future (offensive use), the system can indicate when a specific action was justified in the past (defensive use).
- 4. Promoting Learning or Training: Using a DSS can also help people learned more about using computers and about software package that are in the DSS. Although this is seldom a specific objective of developing the DSS it can be valuable by project.
- 5. Increasing Organisational Control: Some DSS also have the ability to restrict information regarding an individual’s decision to his or her management. This data may then be used to determine the productivity of the individual questions in terms of how many decisions they make and how good their decisions are.
(ii) Give the benefits and applications of expert systems.
Ans. Expert systems aid in the diagnosis of illnesses, the search for minerals, the analysis of compounds, the recommendation of repairs, and the planning of finances. So, from a strategic business standpoint, expert systems may and are being utilised to optimise every phase of a company’s product cycle, from identifying consumers to shipping items to providing customer support. ES delivers a low-cost solution, consistent recommendations with a low level of mistake, and a solution to handle equipment without human intervention. It has a high level of dependability and a speedier response time. It aids in the resolution of difficult problems within a limited realm.
It can analyse the problem and build a business model that is suited for the application’s characteristics. The model identifies the necessary objectives and restrictions. It identifies the best tools for solving the model. It use tools to address the problem and does what-if analysis to determine the model’s sensitivity.
Q10. (i) Compare Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) and Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) systems.
Ans. Difference between OLTP and OLAP
| S. No. | Basis of differences | OLTP | OLAP |
| 1. | Users | Clerk, IT professional | Knowledge worker |
| 2. | Function | Day to day operations | Decision support |
| 3. | DB design | Applications oriented | Subject oriented |
| 4. | Data | Current, up to date, detailed, flat relational isolated | Historical, summarized, multidimensional integrated, consolidated. |
| 5. | Usage | Repetitive | Ad hoc. |
| 6. | Access | Read/write, index/hash on primary key | Lots of scan |
| 7. | Unit of work | Short, simple transaction | Complex query |
| 8. | Number of records accessed | Tens | Millions |
| 9. | Number of users | Thousands | Hundreds |
| 10. | DB size | 100 MB-GB | 100 GB-TB |
| 11. | Metric | Transaction throughout | Query throughout response. |
(ii) Discuss organisational knowledge hierarchy.
Ans. An Organisational Knowledge Management Process (OKMP) is a “business process” that integrates the many organisational agents, components, and activities of the OKMS into a planned, directed process that produces, maintains, and improves an organization’s knowledge base. It varies from an OKMS in that it is a human-managed process with the goal of controlling that system and its dynamics, whereas the OKMS exists whether or not people deliberately try to manage it.
A business process is a sequence of interrelated activities that transforms inputs into positively or negatively valued outputs. Processes are value streams in that they are oriented toward producing and do produce, value for the enterprise. An OKMP is one of a number of “business processes that may be distinguished in organisations. An OKMP is a process directed by organisational goals and objectives. It is driven by a variety of knowledge management sub-processes, use cases and tasks, whose collective purpose is to perform knowledge management and to control the knowledge management system and its outputs. The OKMP, in other words, is part of the OKMS, a process within it that exerts more or less control, as the case may be, over the more fundamental system and its knowledge base.
An OKMP has four subprocesses: planning, acting, monitoring, and evaluating. Setting goals, objectives, and priorities, forecasting as part of prospective analysis, completing cost/benefit analyses as part of prospective analysis, and updating or reengineering a business process are all examples of planning. Acting entails carrying out the business process or one of its components. Monitoring entails tracking and describing the business process in retrospect. Evaluating involves examining the performance of a business process as a value stream in the past.
Human-based agents (individuals or groups) known as business system actors drive processes and sub-processes in business processes such as the OKMP. A human-based agent performing a certain coherent cluster of actions in respect to a business system or process is referred to as a business system actor. Business Systems Actors are distinguished from other agents, including human-based agents in general, by these structured sets of tasks or roles undertaken by agents. The actor concept is an abstraction from the underlying notion of agent and can refer to either an individual or a group’s position within an organisation.
A business system use case is defined by Jacobson as “A sequence of transactions in a system whose task is to yield a result of measurable value to an individual actor of the business system.” A use case may also be composed of multiple transaction sequences or tasks. A behaviourally-related set of business use cases, in turn, constitutes a business process, and therefore extends over the four sub-processes. Figure shows the relationships of business processes, sub-processes, use cases and tasks to one another :
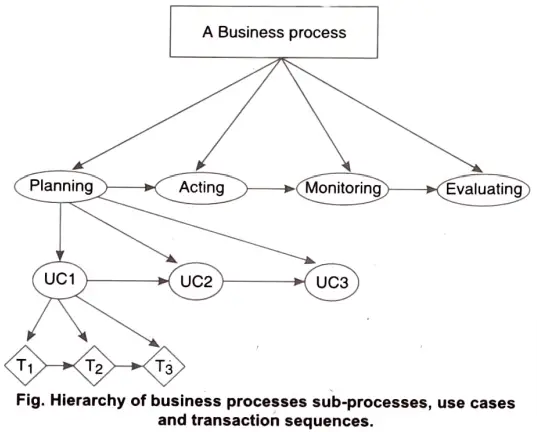


UC1, UC2 and UC3: Use cases participating in the planning sub-processes.
T1, T2, T3 : Transaction participating in UCI.
Horizontal arrow depict use case and transaction sequences.
Q11. What is data warehouse? Give steps for the design of a data warehouse. Give data warehouse architecture.
Ans. Data warehousing can be defined in many different ways:
- 1. A decision support database that is maintained separately from the organisation’s operational database.
- 2. Support information processing by providing a solid platform of consolidated, historical data for analysis.
“A data warehouse is a subject oriented, integrated, time variant and non-volatile collection of data in support of managements decision making process.”
Data Warehousing: Features of data warehousing are as under:
- 1. The process of constructing and using data warehouses.
- 2. Organised around major subjects, such as customer, product, sales.
- 3. Focusing on the modelling and analysis of data for decision makers, not on daily operations or transaction processing,
- 4. Provide a simple and concise view around particular subject issues by excluding data that are not useful in the decision support process.
Steps to Design a Data Warehouse: Following are the seven steps to design a data warehouse:
- (a) Determine business objectives.
- (b) Collect and analyse information.
- (c) Identify core business processes.
- (d) Construct a conceptual data model.
- (e) Locate data sources and plan data transformations.
- (f) Set tracking duration.
- (e) Implement the plan.
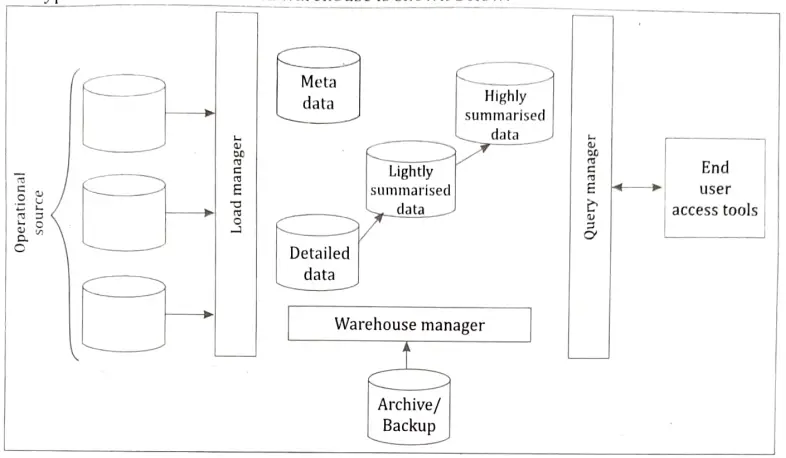
Data Warehouse Architecture: The data in a data warehouse comes from the organization’s operating systems as well as various external sources. These are referred to as source systems collectively. The data retrieved from source systems is kept in a location known as the data staging area, where it is cleaned, converted, merged, and deduplicated in preparation for usage in the data warehouse. The data staging area is often a group of machines that perform simple tasks such as sorting and sequential processing. There are no query or presentation services available in the data staging area. As soon as a system provides query or presentation services, it is categorised as a presentation server: A presentation server is the target machine on which the data is loaded from the data staging area organised and stored for direct querying by end users, report writers and other applications. The three different kinds of systems that are required for a data warehouse are:
- 1. Source systems.
- 2. Data staging area.
- 3. Presentation servers.
The data staging area transports data from source systems to presentation servers. ETL (extract, transform, and load) or ETT (extract, transform, and transfer) refers to the complete process. Oracle Warehouse Builder (0WB) is the ETL tool from Oracle, whereas Data Transformation Services (DTS) is the ETL tool from Microsoft SQL Server.
A typical architecture of a data warehouse is shown below:


Q12. Discuss groupware technologies.
Ans. Groupware Technology: Groupware refers to programmes that enable people to collaborate collectively while being physically separated from one another. Synchronous groupware refers to programmes that allow for real-time collaboration. Calendar sharing, collaborative writing, e-mail management, shared database access, electronic meetings with each member able to see and present information to others, and other activities are examples of groupware services. Groupware, often known as collaborative software, is an essential component of the field of study known as Computer-Supported Cooperative Work, or CSCW. Groupware is frequently classified into two types based on whether or not work group members collaborate in real time (synchronous groupware and asynchronous groupware). Lotus Notes and Microsoft Exchange are two examples of groupware products that allow for calendar sharing, e-mail handling, and file replication across a distributed system so that all users may see the same information. CU-SeeMe and Microsoft Net Meeting facilitate electronic “face-to-face” meetings. There are various forces for adoption of groupware including:
- 1. Increases cost control.
- 2. Increases productivity.
- 3. Improves customer service.
- 4. Supports for total quality management activities.
- 5. Reduces number of meetings.
- 6. Increases automation of routine work flow processes.
- 7. Desire to extend the organisation to include both supplier and customer.
- 8. Need to integrate geophysically dislocated teams.
- 9. Increases competitive advantage through faster time to market.
- 10. Need for better global coordination.
- 11. Creation of services that differentiate the organisation.
- 12. Enlarging of professional expertise and knowledge.
- 13. Availability of widespread network infrastructures.
- 14. Improves price/performance ratios of both hardware and software.
- 15. Increases use of ad hoc teams.
Q13. Write short note on any two of following:
(i) Data mining of large databases.
Ans. Data mining is the process of extracting and detecting patterns in huge data sets using methods from machine learning, statistics, and database systems. It is a computer science and statistics multidisciplinary topic with the overall purpose of extracting information from a data set and transforming the information into an intelligible structure for subsequent use. It is the analysis phase of the ‘knowledge discovery in databases’ (KDD) process. Aside from the raw analysis step, it also includes components of database and data administration, data pre-processing, model and inference considerations, complexity concerns of revealed structures, visualisation, and online updating. It is also the process of sorting through large data sets to identify patterns and relationships that can help solve business problems through data analysis.
(ii) Components of a decision support system.
Ans. Following are the components of the decision support system:
(a) Data Management Sub-system: The data management subsystem consists of a database containing relevant data for the circumstance and is handled by software known as the Database Management System (DBMS). The data management sub-system can be linked to the corporate data warehouse, which is a repository for corporate decision-making data. Typically, data is stored or retrieved by a database web server.
(b) Model Management Sub-system: This is a software package that includes financial, statistical, management science, or other quantitative models that provide analytical skills to the system as well as proper software management. There are various modelling languages offered for creating bespoke models. This programme is commonly referred to as a Model Base Management System (MBMS).
This component can be linked to internal or external model storage. Web development technologies (such as Java) are used to construct model solution methods and management systems that operate on application servers.
(c) User Interface Sub-system: This subsystem is how the user connects with DSS. The user is regarded as a component of the system. Researchers believe that some of the unique contributions of DSS are obtained from the intensive interaction between the computer and the decision-maker: For most DSS, the web browser provides a familiar, consistent graphical user interface framework.
(d) Knowledge-based Management Sub-system: This subsystem can support any of the other subsystems or function alone. It supplies intelligence to supplement that of the decision maker. It can be linked to the organization’s knowledge repository (part of a knowledge management system), also known as the organisational knowledge base. Web servers can supply knowledge. Many artificial intelligence approaches have been incorporated in web development tools such as Java, making them simple to combine with the other DSS components.
(iii) Knowledge acquisition, sharing and utilisation.
Ans. Knowledge acquisition refers to the knowledge that a company can try to get from outside sources such as suppliers, competitors, partners/alliances, customers, and outside experts. These sources can be located in their database, gained through the interchange of data and positive attitudes, or obtained from various internal and external sources of the company. Knowledge sharing is the interchange of knowledge among individuals, communities, organisations, and so on. This bridges the gap between individual and organisational knowledge, increasing absorptive and innovative potential. As a result, both organisations and people will maintain their competitive advantage. Organisations have understood that knowledge is a key intangible asset for establishing and maintaining competitive advantages.
In addition to the typical face-to-face knowledge sharing. Because of its convenience, efficiency, and widespread use, social media is an excellent medium for knowledge sharing.
The application of collected information to solve issues, generate new products, and deal with unfamiliar situations is known as knowledge utilisation. Knowledge is useless unless it is put to use in solving business difficulties.
